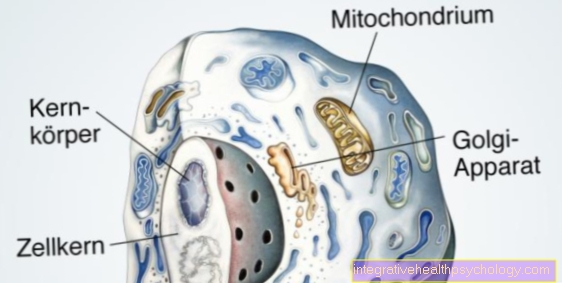
sebaceous gland
definition
The sebum glands are glands that, according to the holocrine mechanism, produce a fatty secretion tallow or Sebum secrete. They belong to the skin appendages, i.e. they are closely connected to the skin, but function independently.

Types of the sebum gland
In humans, the sebum gland is found almost everywhere on the body in the dermis. There are two types of sebum glands:
- free sebum glands (free in the skin) and
- Hair follicle glands (always in relation to a hair follicle)
In the free glands, the tubular, unbranched ducts are oriented on the hair shaft and the openings open next to the hair, together with those of the eccrine sweat glands, always in the area of the hair on the skin surface.
Occurrence of the sebum gland
The free sebum can only be found in the area of
- Lips
- Eyelids
- Anus and
- Genital organs
On the other hand, there are the Hair follicle glands, but of course only in the skin of the field, so the hairy skin (soles and Palms therefore contain no sebum glands). Here are the glands, however irregularly distributed.
While there is the sebum on the Scalp, in the face, in the Genital area and along the Sweat trough of the upper body in very close density there are, other regions of the body are only sparsely occupied with them. On average, however, you can say that on one Square centimeters of skin have about 40 sebum glands are located.
Function of the sebum gland
The job of the sebum is to produce sebum. This is a substance that is largely made up of various fats (triglycerides, fatty acids, waxes and cholesterol) and also contains proteins.
The exact composition of the various substances varies from person to person, which contributes to the individual oiliness of the skin. The amount of sebum produced by the sebum gland depends on various factors. In addition to various influences of the person himself like
- Age
- gender
- Disposition
- Hormones
- nutrition
Environmental influences also play an important role here. On average, a person produces about 1 to 2 grams of sebum per day, although this secretion naturally decreases with age, which is why the skin of older people becomes drier and therefore more vulnerable. The sebum is primarily used to lubricate and protect the skin from drying out.
Sebum glands on the head
Next to the eyelid are also located in the head area on the Lips and the Oral mucosa sebum glands. A sebum is usually associated with one hair connected, since this is not the case in the mouth and on the lips, these sebum glands are called "free sebum glands"Or"Fordyce glands" designated. You can recognize them as small, white-yellowish spots that stand out from the otherwise reddish lips. you are without disease value, and can removed if necessary become. The means of choice for this is either one CO² laser, or acid. However, this is a purely cosmetic procedure.
In the so-called T-zone in the head area (Between right eye, left eye and lips) clogged glands and pus-filled pimples should not be squeezed out, as there is a risk of the pus entering via the venous drainage brain got.
Much more is one cooling and disinfecting therapy indicated, if there is no improvement, it can also open Antibiotics can be used.
Sebum glands on the face
in the face kick two different types of sebum glands. The Hair follicle glands are sebum glands that are always associated with one Hair associated are. They occur on the entire body on the hairy skin, including the face.
Reduced sebum production in the glands leads to dry facial skin (sebostasis). On the other hand, there is one especially during puberty due to hormonal imbalances excessive sebum production instead of. This mainly happens in areas where the sebum glands are densely grouped, the so-called T-zone (forehead, nose, chin). The consequences are Blackheads (Comedones) and acne.
Free sebum glands however, are found in hairless regions, on the face on the eyelids, lips and the oral mucosa.
Sebum glands on the eye
Sebum glands are found on the head in the area of the eyes and lips.
There are a total of five glands on the eyelid, two of which are responsible for producing sebum: the so-called Zeis glands (named after the German surgeon Eduard Zeis) open at the eyelashes and together with the meibomian glands form the so-called "Eye butter". This is a high-fat substance that prevents tear fluid from spilling out of the eye. The meibomian glands (after the German doctor Heinrich Meibom) lie on the inside of the eyelid. There are about 30 meibomian glands on the upper eyelid and about 20 on the lower eyelid.
Typical diseases of the sebum gland in the eye area are stye (Hordeolum) and in its chronic form the hailstone. The cause is almost always a blockage of the excretory ducts of the sebum gland, as a result of which the subsequently produced sebum accumulates and swells into a plug.
Infections from bacteria such as staphylococci can also cause inflammation. Patients usually suffer from an impairment of the field of vision and an unpleasant throbbing sensation of heat on the eyelid. Here antibiotic and disinfecting therapy can quickly provide relief.
For more information on this topic, read our article below: Sebum on the eye - anatomy, function and diseases
Sebum glands on the lip
Also at the Lip may have sebum glands occur, these are not associated with a hair follicle, but free. They are also known as Fordyce's glands and have no disease value. They can occur both individually and in groups and are often found at the transition from the red lips to the skin of the face.
It's tiny small, mostly grouped yellowish pointsthat aren't painful or itchy. Their occurrence is described above all at the onset of puberty. In the case of sebum glands on the lip, it is not a disease, but a normal variant, which is estimated to be 30-60% of the population occurs. Removal is therefore not necessary, but can be carried out for cosmetic reasons if the findings are pronounced. Tried and tested methods of removal are CO2 laser therapy or acid treatment.
Sebum glands on the labia
Also on the inner labia (Labium minus) there are sebum glands. They open at the roots of the pubic hair and secrete a fatty secretion.
A blockage leads to a nodular, movable thickening that is white-yellowish. According to the principle ubi pus ibi evacua (Where there is pus, empty it there) an attempt can be made in the first instance to express it. If this does not work, zinc ointment helps against the inflammation; the pimple can be gently removed using laser treatment.
It is not a dangerous clinical picture in the medical sense, but many patients find it uncomfortable and annoying. A pus vesicle is not necessarily a sign of poor hygiene and may be associated with tampons that are inserted during periods and put pressure on the sebum gland. As a result, it may not be able to empty itself - this creates a build-up.
Read more on this topic at: The sebum on the labia.
Sebum glands on the chest
Also about them nipple can get around enlarged sebum glands are located. These glands, known as areolar glands or Montgomery's glands, are arranged in a circle around the nipple and become especially if the nipple erects visible. Above all, they are supposed to protect the skin of the breastfeeding woman and secrete a fragrance that brings the baby to the nipple.
Sebum glands on the glans penis or foreskin
Free sebum glands, i.e. sebum glands that are not associated with a hair follicle, can also at the Glans of the penis and on the foreskin occur. They are called Tyson's glands here and occur especially next to the foreskin often at a depression in the limb, which is located behind the glans, the so-called sulcus coronarius. Here they are called Papillae coronae glandis or Hirsuties papillares coronae glandis.
The sebum glands occurring here are also a standard variant, which is approx. Affects 20% of men.
Removal is not necessary, the sebum glands are neither painful nor itchy or even contagious. If there are pronounced findings that are cosmetically disturbing for the patient, removal with the CO2 laser can be carried out.
Not to be confused are these harmless sebum glands With so-called Genital wartscaused by the HPV virus. However, these are irregular, larger and grow like cauliflowers. Treatment should be given here because the virus can cause cervical cancer in women and is considered a sexually transmitted disease.
Sebum glands on the testicle
Sebum glands also appear on the scrotum and can be enlarged here, especially during puberty. However, inflammation is very rare.
Often the sebum glands on the testicles are mistakenly mistaken for pimples or even warts. These are small, bright spots that are usually evenly spaced on the testicle. They are neither itchy nor painful nor contagious and completely harmless. It is just a standard variant that is completely harmless.
Read more on this topic at: The sebum glands on the testicle.
Sebaceous nevaevus
A Sebaceous nevus (Naevus sebaceus) is a local reproduction of sebum glands and occurs especially on the face or on the hairy scalp on.
Usually a sebum nevus occurs individually on and is innate. The sebum nevus is yellow or reddish discolored and can have a smooth to nodular surface. Hair usually does not grow in the area of the nevus. Since a sebum nevus can turn into a benign or, more rarely, a malignant tumor in up to 30%, removal is usually sought in childhood.
Diseases of the sebaceous gland
Diseases of the sebum are particularly noticeable in the quantity and / or quality of the secreted substance. If there is an increased secretion of sebum, one speaks of Seborrhea, a decreased production is known as Sebostasis.
In addition, the sebaceous gland is a popular starting point for infections (this is favored when the secretion builds up in the glands, which can also lead to the formation of blackheads), which leads to the clinical picture of acne. The sebum gland can rarely become malignant, which leads to sebum carcinoma.
Read more on the topic: Clogged sebum - what to do?
Inflammation of the sebum
With acne there is an excessive production of sebum, whereby the sebum cannot drain away. Certain bacteria feel particularly at home in this environment, which in retrospect leads to bacterial colonization and inflammation.
This manifests itself in blackheads, nodules, and pus pimples. A cyst filled with secretion, a so-called atheroma, can develop, especially on the hairy scalp, due to a blocked sebum duct. If it becomes infected with bacteria, surgical removal may be necessary.
Read more about these topics: Inflammation of the sebum - this must be observed! Remove sebum and bags of groats
Sebum carcinoma
The sebum gland carcinoma is a rare, malignant tumor that originates from altered sebum glands.
Carcinoma of the sebaceous gland occurs mainly in older adults, very rarely in children. The tumor usually occurs around the eye, often on the lids. In addition, the cancer of the neck is more common. Occurrence on the trunk is rare; occasionally an involvement of the vulva (external female genitals) or parotid (parotid gland) has been described.
The sebum carcinomas are divided into ocular (around the eye, on the lid) and non-ocular tumors according to their location. It is usually a knot about 0.5-2 cm in diameter. From a purely external point of view, differentiation from other benign or malignant tumors is difficult because there is no serious distinguishing feature. The lump may be red or yellow in color and covered with crusts or appear scratched.
In some cases, sebum gland cancer is associated with Muir-Torre syndrome, a genetic defect that prevents defective genetic material from being repaired. These patients also very often suffer from colon cancer, uterine cancer or bladder cancer.
Ocular sebum cancer is treated by an ophthalmologist. A complete removal of the tumor should be carried out with a safe distance, which can be problematic in the eye region. In addition, it should be checked whether there is any lymph node involvement and the corresponding lymph nodes removed.
Read more on the subject at: Sebum carcinoma