Blood test
introduction
It is part of everyday business for the doctor, but it can make the patient sweat: a blood test. It often represents a part of the basic program of medical activity. But why is a blood test carried out so often and on various occasions? What is behind the examined blood values? When is which blood value determined and what conclusions can the doctor draw from it? The following article is intended to provide some answers to these questions.

Occasions
The occasions for one Blood test can die most diverse be. Sometimes blood values are determined to diagnosing a disease deliver.
Common occasions for diagnostic Blood tests are suspected Infections, Thyroid dysfunction, Kidneys-, liver- and Metabolic diseases or the suspicion of Changes in the Blood count, so in the blood cells.
Blood tests will continue to be carried out during the course of these diseases to determine how they develop and how they respond Therapeutic measures to control. Follow-up checks are also important, especially when taking certain Medicationwhose concentration in the blood must be kept within narrow limits so that they work, but do not cause any serious side effects if possible.
Blood test during pregnancy
A pregnancy represents a special situation for the body because Changes in the most diverse body processes surrender.
It is therefore not surprising that there is one Change in blood values can come. For some blood values are Deviations from the normal range known in pregnancy.
The doctor must therefore take this into account when interpreting blood results. As examples are Changes in the number of white blood cells, the calcium concentration, of blood lipids and the coagulation values called.
Certain blood tests may make more sense during pregnancy. This includes, among other things, the examination of the blood count to detect a lack of red blood pigment (hemoglobin) and red blood cells (Erythrocytes) to recognize.
Such as Anemia This situation often occurs during pregnancy through a Iron deficiency on. In order to determine this, the so-called Ferritin, the Transferrin and the Transferrin saturation to be determined.
The determination of the patient's health plays an important role in the preventive examinations during pregnancy Blood group of the pregnant woman, because under certain conditions problems can arise due to the maternal blood group.
In the course of Checkups an examination for a viral hepatitis type B (Hepatitis B) performed by the mother, as this also does Infect child can. It is also advisable to have one at the latest, but preferably before pregnancy HIV test to have carried out. Further tests for pathogens that can cause problems during pregnancy are either carried out routinely or if an infection is suspected. Here will be antibody in the blood the mother examined. The regular preventive examinations include, for example testing for immunity to rubella virus.
If you have special questions also from the umbilical cord Blood can be drawn. Here is under Ultrasound control the umbilical cord through the skin of the pregnant woman dotted. The won blood of the unborn can then for example on changes in the chromosomes (at the Down syndrom and others genetic disorders), if infections are suspected antibody, or even on a suspected Child anemia to be examined. Fortunately, this procedure is rarely necessary.
In the future, the mother's blood test will also gain in importance when it comes to the detection of genetic diseases of the child goes. Currently, this is often still time-consuming and fraught with complications Investigations Necessary: With the mother's blood test alone, the corresponding costly methods can be dispensed with.
Selected blood values: CRP value
To diagnosis and process control of inflammatory reactions CRP value gained great importance. CRP stands for C-reactive protein. This name comes from the property that this body has protein (protein), to the so-called C polysaccharide of a certain Bacterium binds. It then triggers the activation of a number of Immune processes from that to combat intruders bacteria to lead. CRP is made through many things bacteria, Mushrooms and Activated components of cancer cells. Viruses, however, usually do not lead to activation. For this reason, among other things, the CRP is of particular interest to doctors.
The analysis of the CRP level in the blood is suitable for an infection between a bacterial and one viral Distinguish cause. In this way, for example, through the use of Antibiotics to be decided. While bacterial infections, depending on the pathogen and severity, lead to sometimes massive increases in CRP values viral infections usually no, or only small increases in CRP.
A special advantage The CRP value compared to other inflammation values is that it is in a bacterial infection extremely fast and strong increases. Due to this property, the CRP becomes the so-called Acute phase proteins counted.
A long-term and moderately elevated CRP can indicate a Underlying disease, for example, a tumor or an autoimmune disease.
It is important, however, that an increase in CRP does not always have to be a specific indication of inflammation or a malignant disease. For example, it can also go through injuries sustained (also during an operation).
Selected blood values: thyroid diagnostics
The following three values are important in the standard diagnosis of the thyroid gland: the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3 for short) and thyroxine (T4 for short), as well as the control hormone thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). T3 and T4 are more than 99 percent bound to proteins in the blood. If the small proportion of free, i.e. unbound, T3 and T4 is determined, the values are referred to as fT3 and fT4. The determination of these unbound hormones provides better information about the function of the thyroid gland than the corresponding total values.
While T3 and T4 are made in the thyroid, TSH is made in a special area of the brain called the pituitary gland. Its job in the body is to control the release of thyroid hormones. The following control loop exists in healthy people: When T3 and T4 are lowered, more TSH is released. TSH increases the release of T3 and T4 from the thyroid: T3 and T4 increase. This in turn reduces the TSH release. This mechanism means that the body always has exactly the amount of hormones available that it needs.
For various reasons, however, the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood can be too high (overactive thyroid, hyperthyroidism) or too low (underactive thyroid, hypothyroidism). By determining (f) T3, (f) T4 and TSH, the doctor can then identify the extent of the disorder and also frequently possible causes for it. In practice, sometimes only the TSH value is determined, since in the majority of cases it can already give a good indication of a disturbed thyroid function.
Common causes of hyper- and hypothreosis are two autoimmune diseases: autoimmune hypothyroidism (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) for underactive and autoimmune hyperthyroidism (Graves’s disease) for overactive. These diseases often involve antibodies against the body's own structures that can be detected in the blood. In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, these are antibodies against the enzyme thyroid peroxidase (TPO-AK) and the protein thyroglobulin. In Graves' disease, TPO-AK and so-called TSH receptor antibodies (TRAK) are also determined. Other special thyroid values are used to diagnose and control malignant thyroid tumors and are therefore referred to as tumor markers. For the thyroid, depending on the type of tumor, these are caltitonin and thyroglobulin.
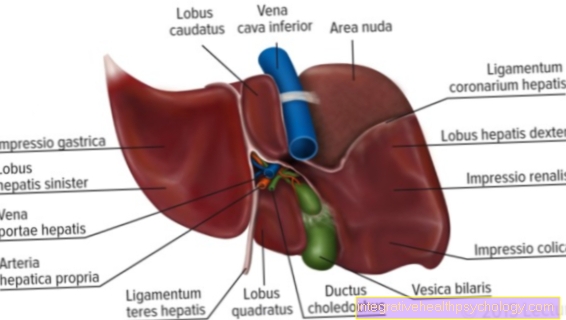
Selected blood values: liver values
Among the so-called Liver values can various blood tests be summarized. In a narrower sense, the liver values are two enzymes with long names: the Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, ASAT or referred to as GOT for glutamate oxalacetate transaminase) and the Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, ALAT, or referred to as GPT for glutamate pyruvate transaminase). The AST and OLD will also be short together summarized as transaminases and usually at the same time certainly. Both enzymes are found in all cells in the body, but they are most concentrated in the liver. In this fact lies the diagnostic importance of the Transamniases justified. At a damage The corresponding enzymes enter the liver cells blood over and can be determined from this. A increase the transamniases can be an indication of a Liver damage give. The advantage here is that the values often increase even with minor damage to the liver and thus have a high diagnostic weight.
Common causes for increased liver values are heavy alcohol consumption or taking medication. Other important causes are inflammation of the liver (hepatitis), for example by Viruses can be caused, but also hereditary diseases, like the so-called Hemochromatosis or the Wilson diseasethat become a Damage to liver tissue to lead. Even with one Cirrhosis of the liver and at Liver cancer can increased transaminases Find. However, it should be noted that in liver cirrhosis, the transaminases are often almost in the normal range, or can even fall below this, if a large part of the liver tissue has already been destroyed and through connective tissue was replaced.
It is also important to mention that increases in AST and ALT are very often due to problems in the liver are caused, but this does not always have to be the case. Disruptive factors can for example vigorous physical activity, muscle- or also Heart disease which can also lead to an increase in the values.
Vitamin D (calcitriol)
Vitamin D can in its preliminary stages from food recorded and then in liver and kidney through chemical changes in the active vitamin D (calcitriol) being transformed. A large part also arises from a forerunner of cholesterol in human skin under Exposure to UV light.
The active vitamin D has the function of a in the body Messenger substance (hormone), which is crucial to the Regulation of the body's own calcium balance is involved. The concentration increases of vitamin D in the blood, increases also the calcium concentration. This can be explained by the fact that calcitriol increases the absorption (absorption) of Calcium from food in the intestine. It promotes that Structure of the bone substance.
The determination of calcitriol belongs to the less common blood tests performed. Use is limited to a few sensible occasions. This is always about diseases that affect the Calcium balance affect. It is a matter of bone- or Kidney disease and Parathyroid disorders. Both Bone disease is the question of a possibly causal Vitamin D deficiency in the foreground.
Calcitriol plays a role in kidney disease because of its education even from the Function of the kidneys is dependent. At a impaired kidney function (Renal insufficiency) are thus reduced Calcitriol levels. The importance of vitamin D when a disease of the parathyroid glands is suspected is due to the fact that the so-called Parathyroid hormone is formed. Since parathyroid hormone also has a Influence on the calcitriol concentration in the blood Determination of calcitriol can be used diagnostically in certain diseases of the parathyroid glands makes sense be.