Endocrine system
introduction

The messenger substances of the endocrine system are the body's own signal substances called hormones. They control and regulate the metabolism, growth and function of many organs and are, for example, essential for reproduction. Hormones are mainly produced by glands and nerve cells, but many organs have individual cells that are also capable of producing hormones.
After production, the hormones can be released and distributed in the body via the bloodstream or along nerve fibers and act on their respective target structures.
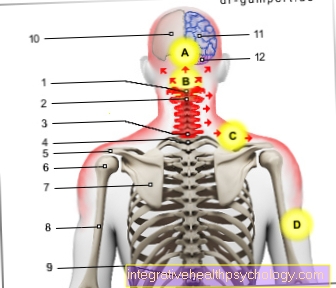
To the hormone-producing organs counting:
- Parts of the Brain and the Pituitary gland
- the thyroid
- the Parathyroid glands
- the Adrenal gland
- of the stomach
- the pancreas
- the Ovaries or Testicles.
Classification and control
In the simplest case, the Formation and release of a hormone and is controlled directly via the influencing metabolic parameters independent of the brain. The increase or decrease in this parameter causes increased or decreased hormone production. So for example introduces Increase in blood sugar level, after ingested food, to one increased release of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that is found in the pancreas is formed and for that Lowering blood sugar levels responsible for. In addition to this, insulin has the hormone Glucagon as an opponentwhich ensures that the blood sugar level does not drop too much. With such a control loop it is possible for the body to Blood sugar level relatively constant even though the body has to absorb and process a lot of sugar in a short period of time through a meal or drink and must not be hypoglycemic even in phases of eating without.
A far more complicated control loop consists three hierarchically arranged levels:
The top level of control in the control circuit of the endocrine system form the Hypothalamic hormones, part of the brain. You get over Blood vessels to their target organ, the Pituitary gland (Pituitary gland) and promote or prevent the here Release of other hormones. This pituitary gland is the Central of the endocrine system, through which, on the one hand, another series of hormones are released, which are ultimately released into the Downstream endocrine glands produce effector hormones trigger. These are named because they are the last resort Effect on the target organ to have.
On the other hand, hormones are released here that act on their target organ without an intermediate stage can. These include hormones that are responsible for the Control of the thyroid, of the Reproductive organs and the Adrenal cortex are responsible. These effector hormones get there via the blood route to your successful organs, but they can also get to the brain and pituitary gland via a Feedback here will stop the production of further hormones. This effect is called negative feedback. He is very important to one Avoid overproduction of hormones and to keep the hormone concentration constant. On the other hand, this negative feedback can also be absent and thus lead to an increased production of the hormone.
In the human body, many control loops intervene and overlap, so that one Disorder numerous effects Has.
Additionally, hormones can be adjusted according to their chemical properties to be grouped. Be here water- and fat-soluble hormones that can affect your target structure in different ways. In addition, these hormones are differentiated by theirs Effective time. The fat-soluble hormones work much longer because their structure protects them from rapid degradation.
In addition to breaking them down, hormones can also be released from the body inactivated become. This happens mainly in the liver. After this inactivation, they can be recycled or by the Urine or bile excreted become.
Disorders of the endocrine system
The causes for Disorders in the endocrine system can be diverse. Here can every stage, be affected by the production via the effect on the successful organ, the signal transmission in the target cell and the degradation.
The hormonal effects can either increased or reduced be.One is responsible for an increased hormonal effect Overproduction this hormone through Multiplication of hormone-producing cells. The cause for this can be either a tumor, as well as a more harmless variant of cell reproduction.
Additionally can Autoimmune diseases about the Antibody production ensure that the target organs are increasingly stimulated by hormones. Likewise, autoimmune diseases can also work for a decreased hormonal effects worry by destroying glandular tissue. This is for example a very well-known thyroid disease, the Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the case.
It can also Hormone resistance exist, which are mostly genetic. A well-known example of this is the disease Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
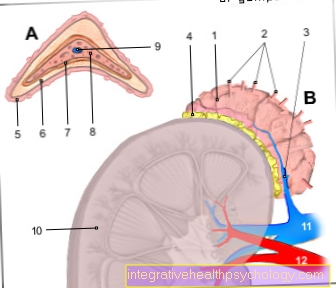
Thyroid hormones

The thyroid forms the Hormones thyroxine and thriiodothyronineif enough iodine is present in the body. She gives the hormones via the bloodstream so that they can act on different body cells. Thyroid controls metabolism, heat balance and protein production, it also has an influence on Emotions and Mood.
At a Lack of hormones it can lead to symptoms like Weight gain, fatigue, depression, Cold intolerance, Hair loss and Constipation come.
A Overactive thyroid rather cares for increased sweating, Restlessness, sleep disorders, nervousness, Weight loss, Disorders of female menstruation and high blood pressure.
Parathyroid hormones
In the Parathyroid glands, which lie as four pea-sized balls on the back of the thyroid gland, this will Parathyroid hormone made which the Regulation of the calcium balance controls and the Vitamin D formation of the body reinforced. It is important for, among other things Bone density and the teeth. If the calcium level is too low, the food intake, which takes place in the intestines, increases and calcium released from the bone.
Endocrine system of the adrenal gland
in the Mark the Adrenal gland will the Hormones adrenaline and Norepinephrine produced mainly in Stressful situations be distributed and among other things for a Increase in heart rate and alertness to care.
The Cortex of the adrenal gland is, in contrast, for the production of Steroid hormones responsible. Have this diverse tasks and are also used in Stressful situations and at increased energy demand released like that Cortisol, or can go to Regualtion of blood pressure and the Salt excretion contribute.
They also have an impact on the gender-specific sex characteristics and the Sexual function: For example through a long-term therapy with cortisol (e.g. at Joint disease) it can become a Hyperfunction coming from the adrenal cortex. This disease will Cushing's Syndrome called and has effects on the whole body due to the increased hormone production.
Symptoms such as:
- the Full moon face
- one Trunk obesity
- Muscle weakness
- depression
- high blood pressure
- and one diabetic metabolic status with too high a Blood sugar level.
By a degeneration or other causes can also lead to a Loss of function of the adrenal cortex come, here one speaks of the disease Addison's disease, which is characterized by the lack of important hormones and, above all, one Hyperacidity and Redistribution of Ions in the body as well weakness, nausea, Weight loss, Hypoglycaemia and a Overpigmentation of the skin triggers.
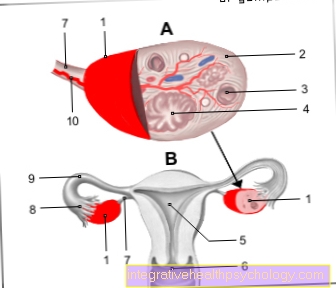
Hormonal system of the sex glands
To the Sex glands count ovaries and Testicles. This support the function of the adrenal cortex and produce the hormones estrogen, progesterone, Androgen and testosterone.
Since they at man and at the woman in different amounts are produced, others develop primary and secondary sexual characteristics. They also serve the Reproduction and have other, non-sex-specific effects.
For the female body are mainly the sex hormones of the group of Estrogens and the progestin relevant.
she control the female cycle and can take the body to an upcoming one pregnancy to prepare.
The cycle consists of the Maturation of an egg cell and the Changes in the lining of the uterus as preparation for the implantation of an embryo.
Estrogen is in the Follicles of the Ovaries produced. As these ripen at the beginning of the cycle, the levels of estrogen in the body continue to increase until the day of the Ovulation. After that, concentration falls off and on Corpus luteum are reinforced Progestins produced.
The corpus luteum is the remaining covering of the egg cell, which recedes if fertilization has not occurred. Have progestin pregnancy-sustaining effects and increase sharply in the event of fertilization.
Progestins are also used as oral contraceptives in the form of the Birth control pills utilized.
If the egg has not been fertilized, the regressed corpus luteum stops producing gestagens and the adult one stops The lining of the uterus is shed and within the period spilled out. Then the mucous membrane regenerates and the cycle starts all over again.
At the man mainly the hormone dominates testosteronewhich is in the Testicles is produced and for growth, differentiation, libido and Sperm maturation and thus for the power responsible for.
In both men and women, the production of hormones in the sex glands is dependent on hormones in the Pituitary gland be released. This control loop is also based on the principle of negative feedback.
Growth hormone

The Growth hormone Somatotropin differs from the previous hormones in that it is directly in that anterior lobe of the pituitary gland is formed. It controls many different ones Metabolic processes and controls the growth and differentiation of body cells. By activating another hormone called IGF it controls this in the liver Body growth and also influences the protein-, fat- and Carbohydrate metabolismto create optimal growing conditions. At a Growth hormone deficiency it can be supplied to the body from the outside, usually a syringe with the appropriate dose is given.
Pituitary hormones
In the back lobe of the pituitary gland the hormones are Vasopressin and Oxytocin stored and released into the blood. Vasopressin contributes Regulation of the fluid balance and can reduce urine excretion to a minimum if there is a lack of fluids. Oxytocin does this in women Tension of the uterine muscles and helps with the Development of contractionsthat are important for expelling a child. It also takes care of the Milk delivery from the mother's breast to the infant.
Tissue hormones
Also tissues like that heart or the Gastrointestinal trackt have cells that can produce hormones. They act partly as Tissue hormones, that means that the production location and target structure are close to one another. They mostly will paracrine Transferred, i.e. directly via the cell gap to the neighboring cell, without entering the bloodstream to get.
The hormone that is produced by the heart muscle cells is called BNP and provides for an increased expansion of the heart chamber Vasodilation in the body's circulation. It is used in diagnosing the Heart failure used.
The Incretins are the Gastric hormones and have one very complex effect. You will be at Ingestion poured out and cause a Insulin secretion in the pancreas to process the ingested carbohydrates, and they also trigger a Feeling of satiety in the brain and one slowed gastric emptying.
There is a variety of other tissue hormonesthat are indispensable for the body. This also includes the Inflammation mediators, which among other things at the Pain mediation are important and also Cause a fever can. you will be Prostaglandins called. Also important are hormones that constricting or expanding on the vascular system Act. They come especially at Injuries to wear and protect the body from being too strong Blood loss.
Also in brain there are other hormones present in addition to the previously mentioned control circuit consisting of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. in the Brain stem becomes the hormone Serotonin produced, which affects the State of mind, the Joke transmission, the Sex drive, the Sleep rhythm and the Body temperature Has. Additionally, it contributes to the local Narrowing of blood vessels at. However, most of the body's own serotonin is found in cells of the Intestines produced.
Summary
The Hormones are for the human body indispensable and significantly regulate the metabolism and the Adaptation of the body to extreme situations.
The field that deals with the endocrine system and its disorders is known in medicine as endocrinology designated and the responsible doctor is a endocrinologist.