Lymph node swelling after surgery
definition
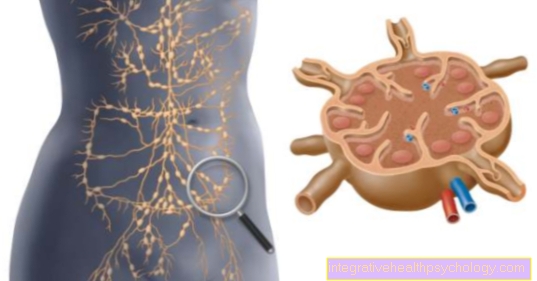
Lymph nodes are found in many different places in the body; large accumulations are found mainly on the neck, armpit and groin. They represent the filter stations of the lymph fluid. There harmful substances are discovered by our immune system and repelled.
They are usually barely palpable, easy to move and painless.

Lymph node swelling occurs when the body has to fight off many foreign substances, for example in the event of an infection or a cold. In this case, the lymph nodes can be painfully enlarged and palpable. However, not every enlarged lymph node is directly evidence of disease, which is why lymph node swelling should always be evaluated together with other findings.
Causes of lymph node swelling after surgery
Lymph node enlargement can occur due to various causes. As mentioned above, lymph nodes swell in the event of an infection, such as an inflammation, as the body has to defend itself against harmful germs. In this case one speaks of one Lymphadenitis. The invaders that our immune system defends against can be bacteria or viruses. For example, in the case of Pfeiffer's glandular fever, which is triggered by the Epstein-Barr virus, heavily swollen lymph nodes can usually be felt on the neck. In the case of tonsillitis, which is mainly caused by bacteria, greatly enlarged lymph nodes can also be found in the neck region.
Read more about the topics:
- Causes of Lymph Node Swelling
- Lymph nodes are swollen - how dangerous is it?
Lymph nodes can also be enlarged due to tumors. They can both because of tumors directly in the lymph node (Lymphoma) as well as swell due to metastases that originate from tumors in another region of the body. Tumor cells can be transported via the lymph and can settle in lymph nodes. Since these represent the filter stations, there is a particular risk of tumor infestation.
Read more on the topic: Lymph node cancer
Pronounced swelling of the lymph nodes can also be a sign of HIV. They occur in the early stages of the disease. Additional symptoms include fatigue, fever, weight loss, and night sweats. If such or similar symptoms are observed, a doctor should be consulted for clarification.
Read more on the topic: Lymph Node Swelling - What Evidence Is There It Is HIV?
Diagnostic procedures
The diagnosis is usually made by palpating the lymph nodes in the areas with large lymph node congestion. By palpating the lymph nodes, the consistency, mobility and painfulness can be found out. When there is inflammation, the lymph nodes are usually soft, easy to move and tend to be tender. If lymphadenitis has healed in the past, they are usually small, hard, painless and movable.
However, if they are small, hard, painless and cannot be moved, but rather have grown together strongly with the surrounding tissue, this indicates a tumor or metastasis. For further diagnosis, some lymph node tissue can be removed using a lymph node biopsy and examined under a microscope.
Concomitant symptoms
Depending on the disease with which the lymph node swelling is associated, the accompanying symptoms differ.
The lymph node swelling is usually not the triggering factor for certain symptoms, but is itself an accompanying symptom of an illness. It arises from the increased defense of the body against possible harmful foreign bodies.
A swelling shows us that the immune system in our body is strongly activated and is defending itself against pests. If there is a swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck due to a cold or flu, you will also find cold symptoms such as runny nose, sore throat or fever.
Symptoms such as weight loss and night sweats can be seen in the lymph node swelling that occurs with cancer.
Among other things, pain can occur at the corresponding points of the enlarged lymph nodes. Long-term swelling of the lymph nodes can lead to overheating, skin rashes and redness. With bacterial infections, purulent abscesses can develop.
Lymph vessels can be damaged as a result of repeated inflammation or during operations and lymphedema can develop. In this case, the lymphatic vessels are so damaged that they can no longer transport the lymph fluid properly and proteins and fluid are deposited in the tissue.
Read more on the topic: Lymph node pain - how dangerous is it? and causes of edema
Treatment of lymph node swelling after surgery
Since lymph node swelling is due to the increased activation of our immune system and it is a sign that our body is defending itself against a disease, no special treatment is usually necessary against lymph node swelling.
Treatment of the underlying disease should be initiated to reduce the swelling. Lymph node swellings are often harmless and swell on their own. In the case of colds, for example, the lymph nodes usually swell again after the disease has ended, without any measures being taken to counteract the swelling. In the case of severe bacterial infections, it can be useful to take antibiotics.
Infections caused by viruses, like Pfeiffer's glandular fever or measles, are usually treated symptomatically. Antivirals are only recommended in isolated cases. If a tumor is the reason for the lymph node swelling, the underlying disease, in this case the tumor, must also be treated, for example with chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
If the lymph node swelling persists for a long time and causes severe pain or, for example, difficulty swallowing or shortness of breath, it is advisable to consult a doctor and investigate the exact cause of the swelling.
Duration of lymph node swelling
The duration of a lymph node swelling can vary greatly depending on the disease and its treatment. Since the lymph nodes serve as filter stations for foreign substances, they are usually swollen until our immune system has fended off and eliminated most of the harmful invaders.
In the case of a cold, the lymph nodes begin to swell after the pathogens penetrate our body and when the pathogens are recognized by our immune system. With the end of the cold, they swell again. In isolated cases, they can remain enlarged a little longer after the illness, but they swell again after a while. In the case of prolonged bacterial infections, the immune system has to fight the bacteria over a longer period of time and thus the lymph nodes remain enlarged for longer. The infection and thus the lymph node swelling can usually be shortened by administering antibiotics.
In tumor diseases, lymph nodes can remain swollen for years because the immune system fights against the tumor cells until they are removed. When the tumor is removed, the nearby lymph nodes are usually removed as well.
Read more on the topic:
Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes
Duration of lymph node swelling
Lymph node swelling depending on the type of operation
After a dental operation
Lymph node swelling after dental surgery is common. Since there are many lymph nodes on the jaw, under the chin, and on the neck, surgery can cause them to swell. Since the immune system is more activated after an operation, enlarged lymph nodes are not uncommon. Most of the time, the lymph nodes near the surgical site are the most swollen. Depending on the extent of the operation, more or less lymph node collections may be affected.
Read more on the topic: Operation on the wisdom tooth
During dental surgery, usually only the lymph nodes on the jaw, under the chin and on the neck are swollen. The swelling should decrease a few days after the operation and will often go away completely on its own. If it does not swell over a longer period after the operation or if it causes other inconveniences such as shortness of breath or swallowing difficulties, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Read more about the topics:
- Lymph node swelling in the lower jaw
- Lymph node swelling in the neck
- Post-op swelling
After an almond operation
The tonsils are located at the transition from the mouth to the throat. During an tonsil operation, the so-called tonsils, which are themselves part of our immune system, are removed.The reason for this can be repeated infections with bacteria or viruses, which can lead to scarring. After removal, as with any surgery, swollen lymph nodes can occur. The closest lymph nodes are in the jaw and neck area and are often the most enlarged. After the operation, the immune system has to process this intervention in our body. This causes the lymph nodes, which act as filter stations for possible foreign matter, to swell. The swelling should subside on its own some time after the operation, as the body no longer has to fight off foreign bodies after a certain time. If the swelling persists for an unusually long time after the operation or causes other symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Read more about the topics:
- Tonsillitis
- Lymph node swelling in the lower jaw
After thyroid surgery
Since the thyroid is located in the front of the neck, the lymph nodes in the neck are typically swollen after thyroid surgery. Due to the swelling of the surgical area itself, the lymph node swellings on the side of the neck are often difficult to feel in the first time after the operation.
In addition, the lymph nodes below the chin and jaw may be swollen as the lymphatic fluid from these areas backs up. In addition, lymph node swelling in the area of the collarbones occurs after thyroid surgery
After shoulder surgery
Depending on the type and extent of the intervention during the operation, the burden on the body and thus on our immune system differs. The lymph node aggregations closest to the shoulder are in the armpit. Accordingly, the lymph nodes there may be enlarged after an operation. In addition, swollen lymph nodes can be felt above and below the collarbone or on the neck. Since the immune system is more active to ward off potentially harmful germs after an operation and lymph nodes play an important role as filter stations, swollen lymph nodes, which cover the area of the operation with their catchment area, are not uncommon.
Read more on the topic:
- Lymph node swelling in the armpit
- Lymph node swelling on the collarbone
- Lymph node swelling in the neck
They remain enlarged until the immune system has fought off all germs. Depending on the extent of the operation, this can take different lengths of time. In rare cases, surgery on the shoulder can damage many lymph vessels. In this case, there is a risk of lymphedema on the arm. This prevents the lymph from being transported out of the arm and deposits of proteins in the tissue can occur. If swollen lymph nodes are observed for a long time after an operation, the causes should be clarified by a doctor.
After breast cancer surgery
Breast cancer often involves swelling of the lymph nodes in the armpit. Often the swollen lymph nodes are strongly fused with the surrounding tissue, but not tender.
e after breast cancer surgery, the surgeon removes the whole breast (mastectomy) or a breast-conserving operation is performed. In both operations, the first axillary lymph node of the breast catchment area, the so-called sentinel lymph node (Sentinel lymph nodes), with removed. This is then examined for existing cancer cells. If it is infected with tumor cells, all other axillary lymph nodes are often also removed during the operation.
Removing the remaining lymph nodes in this area is designed to prevent the tumor from spreading further down the lymphatic pathway. It should also be prevented that spread metastases continue to grow and thus disrupt the lymph drainage in the arm.
In this case, lymphedema of the arm would occur, as the removal of the lymphatic fluid is no longer adequately guaranteed. Growing lymph node metastases may also pinch nerves that run along the area of the lymph node congregation.
If the lymph nodes are tumor-free and left in the body, there may well be swelling after the operation without this indicating any disease value.
Read more about the topics:
- Lymph node swelling in the armpit
- Metastasis in breast cancer
- Breast cancer therapy
After an abdominal surgery
Lymph node swelling in the abdomen after surgery is not uncommon. The tissue injuries during the operation activate the immune system so that the lymph nodes can swell.
During operations in the abdominal cavity, lymph nodes in particular are typically swollen in the abdomen itself; these can usually not be felt. However, lymph nodes in the groin region can also be affected, so that depending on the size of the surgical procedure, there can be a swelling of the lymph nodes on one or both sides.
In addition, lymph nodes can be swollen along the lymphatic drainage path, this can be noticeable below the collarbone on the left side, for example, as this is where all the lymphatic pathways in the abdomen and legs end.
After a groin operation
Groin surgery can be done for a number of reasons.
Depending on the procedure, the surgical incision and thus the wound can vary in size. Since the groin is usually a place that is often moved, wound healing is more difficult there. In addition, depending on your body weight, the groin can be a very warm, sometimes moist area. This favors the growth of germs and increases the risk of impaired wound healing.
There are many lymph nodes in the groin that are swollen after an operation. The immune system is strongly activated and fends off possible harmful substances. Since the collection of lymph nodes is in the immediate vicinity of the surgical site, it can become very enlarged. Depending on the duration of the healing process, the lymph nodes can be swollen for different lengths of time after the operation.
Read more on the topic:
- Lymph node swelling in the groin
- Groin pain these are the most common causes
After prostate surgery
During prostate surgery, lymph node swelling can occur when the lymphatic system begins to remove the fluid that was produced by the body after the operation.
The lymphatic drainage typically starts from the prostate in the direction of the groin. Therefore, after a prostate surgery, lymph node swelling occurs, especially in the groin region. These typically occur on both sides and can persist for a while.
Only when the accumulation of fluid in the operating theater area around the prostate has receded, the conditions in the lymphatic flow area normalize, so that the lymph node swelling decreases.
After knee surgery
After knee surgery, the knee and the lymph nodes located there may swell. Usually you will find enlarged lymph nodes around the knee on the thigh and lower leg. Since a lot of fluid has accumulated in the lymphatic system and the surrounding tissue during the operation and this has to be transported away, the lymphatic system can be overwhelmed at times. This removal can be improved with the help of manual lymphatic drainage by a physiotherapist.
Both superficial and deep lymph nodes can be found on the knee, both of which may be swollen after an operation. The path of lymph drainage from the knee runs towards the thigh and groin. Since there are large collections of lymph nodes in the groin, these can also be enlarged after knee surgery. In the event of complaints due to swollen lymph nodes or poor lymph drainage on the knee, which last longer than usual after the operation, it is advisable to consult a doctor to clarify the cause.
Read more on the topic: Swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin
Recommendations from the editorial team:
These topics could also be of interest to you:
- Lymph node swelling in the armpit
- Metastasis in breast cancer
- Lymph node swelling in the groin
- Causes of Lymph Node Swelling
- Lymph nodes are swollen - how dangerous is it?