Treatment by radiation therapy
Synonyms
- Radiation oncology
- Irradiation
- Tumor irradiation
treatment
One qualitatively high quality cancer therapy takes place today in consultation between the responsible medical departments (surgical subjects, internal oncology, radiation therapy) and the patient.
At the beginning a consensus has to be found for the achievable therapy goal. Important questions here are whether the tumor can be cured, whether there are symptoms that need to be treated, what is the willingness and resilience of the patient, etc.
After defining the therapy goal, a treatment plan should be drawn up that takes into account the currently applicable therapy recommendations of the medical professional associations and ongoing study results.
Possible therapy options are:
- Tumor surgery
- radiotherapy
- Classic chemotherapy
- Hormone therapies
- Antibody therapies
- Immunotherapies
- Etc.
A combination of the individual therapy options is usually carried out.
According to the place of action, three higher-level forms of therapy can be distinguished.
- The operation as a purely local therapy method
- Radiation therapy as a regional therapy method
- The drug therapy as a systemic therapy method (works in the whole body).
Depending on the requirements, radiation therapy can be carried out as a single therapy or in combination, or before or after the other therapies.
If there is an indication for irradiation, medical information regarding the goal, implementation and possible side effects of the therapy must take place in advance.
Read more on the subject at: Side effects of radiation
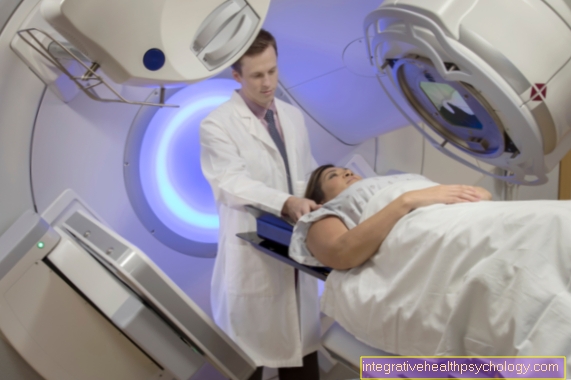
In order to ensure that the effective radiation dose also reaches the tumor area, the radiation treatment is planned before the actual start of therapy.
For this purpose, a computed tomography of the affected body region is usually made today. A three-dimensional model of the patient is calculated from this image data, in which the treatment region and the adjacent organs can be seen.
In this model, it is now determined which area should be effectively treated with radiation therapy. It also defines which organs must be spared from radiation. Based on these specifications, a treatment plan is calculated that allows the therapeutic radiation dose to be placed with millimeter precision.
Except for skin tumors, the treatment area is a few centimeters below the body surface.
In the case of electrons, the area of greatest energy transfer is very close to the surface and drops steeply in the depth.
Photon beams have their transmission maximum one to two centimeters below the skin. In order to treat deeper regions effectively without damaging the neighboring tissue, the desired therapy dose is divided over several radiation fields that meet in the therapy region. This adds the dose of each field to that of the remaining fields. This means that the maximum radiation dose is available in the tumor region and the radiation exposure drops significantly in the vicinity.
In order to ensure that the same region is treated with each session, aids are used with which the patient can be positioned safely and stably.
Would you like to know what long-term effects can occur after irradiation?
- Find out about the Long-term effects after radiation treatment.