Marfan's Syndrome
Synonyms in a broader sense
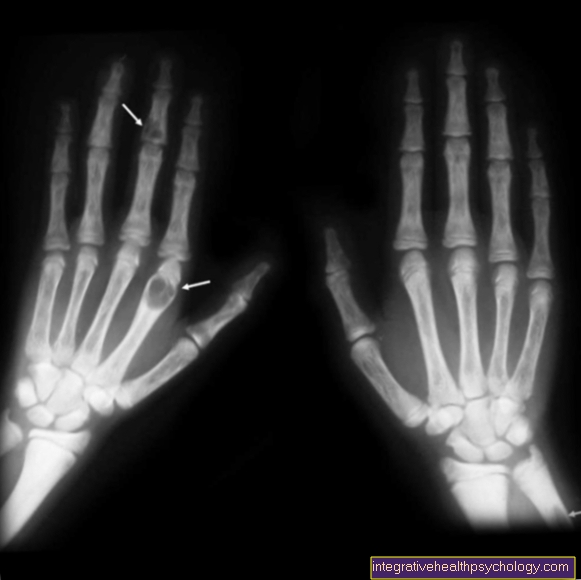
Type 1 fibrillopathy; Arachnodactyly syndrome; Spider finger; Achard-Marfan Syndrome; MFS
definition
Marfan's syndrome is a rare, genetic disease of the Connective tissue with abnormal changes heart, Vessels, eye and skeleton with the main symptom of long, narrow or spider limbs. Marfan's syndrome is based on a genetic change (mutation) of the fibrillin-1 gene, which can either be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner from the parents or occasionally occur as a new mutation.
Epidemiology
With a prevalence (Disease incidence) from 1:10.000 and approx. 8000 affected people in Germany can Marfan's Syndrome be counted among the rare diseases. Men and women are equally affected because the disease does not affect the sex chromosomes. The Marfan syndrome got its name from one of its first descriptions, Antoine Marfanwho observed abnormally long and narrow fingers in a little girl in 1896.
The connective tissue
The connective tissue of the human body is located outside the cells, one also speaks of the extracellular matrix that occurs everywhere in the body. You can find it mainly in the bone, cartilage, Tendons and Blood vessels, but also in all other organ systems, the connective tissue has the task of binding, enveloping and serving as a guide structure. The connective tissue is composed of proteins (amino acids) and sugar chains (Saccharides). These proteins can assemble with the sugar chains to form large aggregates and then form e.g. the collagen fibrils (building blocks of collagen fibers) of the bone or the hair. The microfibrils of the connective tissue are also aggregates made up of fibrillin components, other proteins and sugars. These microfibrils are found in most connective tissues and are always found on the surface of elastic fibers, which e.g. the tissues of the skin give their elasticity. But they also have their tasks in the fibers of cartilage and tendons. For each of the different fibrillins that make up the backbone of the microfibrils, there is the genetic information needed to produce them Proteins is needed on different chromosomes.
The tasks of fibrillin-1 include the formation of microfibrils, but this must be done during its production (synthesis) in the cell (Fibroblast) have been folded correctly, i.e. have adopted the correct structure. When the microfibrils are formed, the fibrillin needs various helper molecules that are necessary for stabilization when the fibrils are cross-linked. That includes that too calcium.
So it is understandable that the lack of functional microfibrils leads to an expansion of the main artery (Aortic dilatation), as their stabilizing function is no longer available due to the defect in the fibrillin.
The excessive growth of the limbs is due to the lack of a regulating function of the microfibrils in the longitudinal growth of the long bones. The same applies to the zonular fibers of the eye (the suspension apparatus of the Eye lens) which lose immensely in stability and thus become "Lentil shrapnel" to lead.
In order to carry out this necessary correct folding of the fibrils and their aggregate formation, they must be calcium be bound, which also protects them from premature degradation. Often, however, it is precisely the region in the fibrillin that is affected by the mutation that is responsible for calcium binding. As a result, the folding can then fail and the microfibrils are subjected to accelerated degradation.
In summary, the various symptoms of Marfan syndrome are caused by weakened or even missing microfibrils that could not be properly built up due to a defective fibrillin gene.
therapy

First step in the therapy of the Marfan's Syndrome is usually an immediate lifestyle adjustment after diagnosis. Serious injuries like a Whiplash (Acceleration trauma) or clashes with others, as they did when basketball, volleyball or Soccer occur, should be avoided if possible with existing Marfan syndrome, as this creates the risk of splitting the aorta (Dissection) can be increased. This is problematic precisely because many patients with Marfan syndrome have chosen sports such as basketball because of their height. The same danger is found in sports in which maximally elevated blood pressure values (Blood pressure spikes) occur, as e.g. at the Bodybuilding the case is. Regular monitoring of the condition of the affected vessels is essential in every case Marfan's Syndrome displayed. If the aortic diameter is less than 40 millimeters, an annual check is sufficient. If there is a risk of the aorta rupturing, surgery is unavoidable.
If there is an urgent desire to have children, a family history with splitting of the aorta or at the same time inadequate closure of the heart valves (Aortic or mitral regurgitation) an operation can already be performed with an expansion of the aorta (Aneurysm) of 50 millimeters. The lethality of the procedure increases from 1% for planned operations to 27% for emergency operations.
Usually the technique is to extract the enlarged part of the aorta (Surgery after Bentall). Here the ascending aorta and the Aortic valve through a flap-carrying "Composite“Prosthesis replaced. A disadvantage of this procedure is the lifelong intake of anticoagulants (Anticoagulants). To avoid this, the valve-preserving technology is increasingly being used David or Yacoub used, replacing only the aorta with a prosthesis. However, the valve that has been preserved often degenerates over the years, which makes a second operation necessary. If, on the other hand, there is a weakness of the left heart valve (Mitral valve regurgitation) this should be replaced by a valve prosthesis to avoid further expansion of the ascending aorta. Here, too, a lifelong inhibition of blood coagulation becomes inevitable. If the mitral valve is reconstructed, these medications can be dispensed with, which is particularly advantageous for young patients.
The treatment of lens dislocation usually consists of the surgical removal of the lens and the provision of a correspondingly highly refractive glasses construction or the removal of the excessively long lens fibers while preserving the lens and the eyesight. Often, however, the myopia can also be corrected by adjusting a glasses or contact lenses sufficient.
In the area of the skeletal system, scoliosis of the spine, which occurs in half of patients, can be helpful, especially in children, when wearing a corset. The aim is to prevent the bent spine from deteriorating as it grows. However, it does not cause permanent straightening. If scoliosis is over 40 degrees, an orthopedic surgeon should consider surgical straightening of the spine to prevent lung problems and back pain.
In most cases, treatment of the funnel or keel chest is only carried out for cosmetic reasons; only in the rarest cases is there compression of the lungs, heart or aorta, which must be surgically corrected.
The discomfort in the case of flat feet can go through insoles and appropriate footwear relieve pain and improve walking comfort. Surgical restoration of the arch of the foot is only rarely necessary in Marfan's syndrome.
The bulging of the acetabulum is only due to about 5% of affected adults Hip pain and restricted mobility requires treatment and comes with a artificial hip joint treated.
prophylaxis
The prophylactic use of blood pressure lowering drugs den Beta blockers, to delay the expansion of the aorta, is particularly evident in younger, non-operated patients with Marfan's Syndrome as effective. No efficacy could be established in elderly or already treated patients.
Endocarditis prophylaxis, i.e. antibiotic therapy to avoid inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, must be carried out in Marfan patients for all interventions or major injuries, as they are particularly susceptible to this due to the damaged vessels and heart valves.
forecast
The Marfan Syndrome Life Expectancy is significantly reduced in untreated patients. With optimal therapy, however, up to 60 years of life can be reached, provided that the disease and its life-threatening complications are diagnosed at an early stage. However, the prognostic assessment in patients who do not meet all criteria for a disease is problematic. Since that Marfan's Syndrome is a phenotypic continuum that can range from neonatal Marfan syndrome with a life expectancy of less than a year to mild forms with no external manifestations and almost no complications in the cardiovascular area, it is often difficult to estimate the course over time.