Muscle aches
introduction
Almost everyone has probably had muscle pain at some point. This is due to the fact that you have over 650 muscles in your body, which of course can hurt anybody.
In addition, “muscle pain” (medically: myalgia) does not only arise from pathological processes that actually take place in the muscle itself, but also from diseases of the joints, nerves, bones and various underlying diseases.
Most muscle pain is relatively harmless, not a big cause for concern, except for the individual suffering, and easy to treat. These common forms include, for example, sore muscles, muscle cramps, tension or pain following injuries to the muscles, as often occurs in sports.

Appointment with a sports orthopedic specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
As a passionate athlete, I have specialized in the treatment of sports diseases for professionals and hobby athletes.
The focus is therefore on diseases of the muscles, tendons and joints.
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Causes of muscle pain
Muscle pain, in medical terminology too Myalgia called, can have many different causes and appear in different forms. Muscle pain is mostly temporary and comparatively harmless, but some can indicate serious illnesses. Muscle pain, especially permanent, should therefore be clarified medically. Possible causes of muscle pain include, for example, tension in the muscles due to poor posture or lack of exercise or what is known as "sore muscles" after overexertion. Muscle injuries such as strains, torn muscle fibers or bruises as a result of sports accidents can also trigger muscle pain. Painful cramps, on the other hand, can indicate a nutritional deficiency.
In addition, infections such as a simple flu-like infection can be the cause of whole-body muscle pain. Serious causes of muscle pain include degenerative muscle diseases such as the Muscular dystrophy or Myotonia. Some rheumatic diseases can be accompanied by muscle pain, as can diseases of the nervous system. Hormonal disorders can also lead to muscle pain. In addition, some drugs can also cause muscle pain, especially the so-called statins (e.g. simvastatin), which are used for high blood lipid levels. Also Penicillins (certain antibiotics), the anti-Parkinson drug levodopa, cardiovascular drugs, and other drugs can cause muscle pain as a side effect. Substances such as alcohol, amphetamines, cocaine, heroin or methadone also sometimes lead to so-called toxic myopathies. In addition, diseases of the central nervous system can trigger muscle pain. These include multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson's disease.
Muscle pain can therefore be the symptom of various diseases and should therefore be clarified.
aching
Muscle soreness occurs a day or two after unusual or massive physical exertion, especially if there has been no physical activity for a long period of time. If the muscle is overused, the smallest muscle fiber tears occur, which are not that bad, but can sometimes be very painful. After a further one to two days, the sore muscles will usually subside without any treatment.
Here you can find information on the topic: Pain like sore muscles - what can it be?
Muscle spasms
Muscle spasms can basically occur in any muscle, but by far the most common ones are the calf muscles or the ankle muscles (at the front of the shin).
The cramps are caused by an unbalanced metabolism in the muscles concerned, usually due to a lack of magnesium.
The pain here usually occurs very suddenly and is accompanied by hardening and contraction of the corresponding muscle. Sometimes cramps are triggered by physical exertion, but traditionally they tend to develop at night.
In the case of a muscle cramp, it is usually enough to tense the affected muscle to get rid of it, so in the case of a calf cramp, for example, you should get up and take a few steps. A sufficient supply of magnesium can be ensured as a preventive measure.
At this point you should also deal with the topic of muscle hardening, read about it: What is muscle hardening?
Does hyperacidity play a role?
Chronic acidification of the body can cause various complaints. Muscle pain and cramps are possible symptoms of acidosis. Due to the changed pH value, the absorption of nutrients from the blood into the muscles is reduced. As a result, muscles lack essential minerals such as calcium and magnesium for their function.
Deacidifying the body can be useful in order to eliminate the muscle pain caused by acidification.
This article might also interest you: Acid-base diet.
Muscle tension
Muscle tension (myogelosis) is also known as muscle tension. This is because when the muscles are tense, the affected muscle or muscle group has increased muscle tension and thus becomes shortened and very hard. This phenomenon can usually be felt as a knot and cannot be completely loosened even when massaging.
There are various reasons for muscle tension. Above all, there is a lack of movement and poor posture. This mainly causes pain in the back muscles, which can sometimes spread to the head or arm. Other triggers for muscle tension are injuries, stress, incorrect movements, insufficient warm-up before sporting activities or an imbalance between muscle groups that work antagonistically.
Read more about this under: This is the best way to solve a muscle hardening
Muscle injuries
Muscle injuries include bruises, strains and tears or tears in the muscles.
- To a bruise (Contusion) it comes from a short, violent external force, for example a blow, impact or fall. The pain is acute and sometimes severe. Most of the time, there is also a bruise in the corresponding area.Fortunately, bruises almost always heal within a short time without any complications.
- Muscle strains are practically the preliminary stage of a ruptured muscle fiber. A strain is caused by overstretching the muscles, which occurs, for example, when a muscle is overstrained by a sudden jerky movement. This is typically the case with start and stop movements, such as those that occur particularly in sports such as soccer, badminton or tennis. The pain is usually short and cramping. If it persists longer, one must
- Muscle fiber rupture can be thought of in which the muscles were not only overstretched and thereby irritated, but rather stretched to such an extent that it actually tore off some muscle fibers.
Please also read the following article: Torn muscle fiber of the forearm
- When a muscle tears, the entire muscle tears apart. These are worse conditions and should be treated by a doctor.
Muscle inflammation
Muscle inflammation can be caused by different causes. Some viruses, such as Coxsackie viruses or echoviruses, bacteria (e.g. Borrelia) and parasites can trigger muscle inflammation. Sometimes, however, no germs can be isolated from an existing inflammation. Then either an autoimmune disease (i.e. a disease in which the own immune system turns against the muscles, for example dermatomyositis) or a disease from the rheumatic group (e.g. polymyalgia rheumatica) comes into question. Sometimes muscle inflammation is also detected in diseases of the blood vessels (vasculitis).
Read more on the topic: Muscle inflammation
Other causes
Other, more rare diseases that are also associated with muscular pain include: fibromyalgia (this disease is characterized by pain in the muscles of the entire body), Parkinson's, muscular dystrophies (of the Duchenne or Becker type, both are hereditary diseases that are characterized by a more or less pronounced loss of muscle tissue), some metabolic diseases, disorders of the hormonal balance (for example diseases of the thyroid gland), multiple sclerosis (MS) or diseases of the peripheral nervous system such as Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Many people also complain of muscle pain in the context of flu-like infections. In addition, some medications can cause muscle pain as side effects. These include the blood lipid lowering drugs statins. In addition, excessive consumption of alcohol and other drugs such as heroin can cause muscle pain in some. Other toxins like strychnine can also cause muscle pain.
Medication and muscle pain
There are a number of medications that can cause muscle pain when taken. In the event that the patient experiences muscle pain, he should consult his treating physician in order to try to adjust the therapy. Together with the patient, the doctor will weigh up whether another preparation can be used or whether it is even necessary to discontinue the therapy in the event of severe limitations. Discontinuing medication should always be discussed with your doctor. Statins are among the most important drugs that can trigger muscle pain. These are drugs that lower blood lipid levels, which is beneficial in patients with cardiovascular problems, metabolic syndrome or diabetes, as well as other risk factors, play a central role in the prevention of strokes or heart attacks.
Statins must not be combined with fibrates, another group used to treat high blood lipid levels. This increases the risk for Myopathies. Furthermore can also Penicillin derivatives lead to muscle inflammation and muscle pain. The antihistamine cimetidine, which is sometimes used for reflux, can also cause severe muscle pain. Muscle cramps, on the other hand, are typical for ACTH, levodopa or quinidine. Because they cause potassium deficiency, diuretics and laxatives can also lead to muscle pain. Finally, alcohol, amphetamines, cocaine, heroin, ecstasy or methadone can also lead to muscle pain, in the worst case even acute Rhabdomyolysis with kidney failure.
Find out all about the topic here: Rhabdomyolysis.
Muscle pain from statins
Statins are commonly used cholesterol-lowering drugs that have a positive effect on blood lipid levels. A characteristic side effect of these drugs is muscle pain. In addition to harmless muscle pain and cramps, however, a serious myopathy can also be triggered, the so-called "statin myopathy". This muscle disease can lead to dangerous decomposition of the muscle tissue, known as rhabdomyolysis.
Rhabdomyolysis often causes acute kidney failure and can cause the muscles of the heart and diaphragm to break down, making it life-threatening
If muscle pain develops as part of statin therapy, the family doctor must be informed immediately.
You may also be interested in this article: Simvastatin.
Can cortisone trigger muscle pain?
Long-term therapy with cortisone can cause numerous side effects. Cortisone promotes numerous degrading metabolic processes in the body, including the breakdown of muscle tissue. As a result, myopathy and muscle atrophy, muscle wasting, can develop. During physical activity, muscle wasting can lead to muscle soreness and cramps more quickly than in healthy people.
Muscle pain can therefore be a result of long-term therapy with cortisone.
Find out more about the topic here: Side effects of cortisone.
Why do you have muscle pain when you have the flu?
Our body fights against pathogens during a flu and releases various messenger substances, including the so-called prostaglandins.
Prostaglandins have a positive effect on the defense against pathogens. But at the same time they dock on nerve cells and reduce our body's sensitivity to pain. The result is that practically everything hurts those affected.
Read more about the topic here: Symptoms of the flu.
Muscle pain after an insect bite
After an insect bite, there may be signs of inflammation in the area of the bite, such as redness, swelling, and warming. Since insects sting superficially, muscle pain is not a classic symptom after an insect bite. If the areas are exceptionally large, you can get the feeling that the muscles below are painful, for example from exotic mosquitoes that have only recently arrived in Germany.
A tick can be overlooked quickly and leave a reddening after a bite that resembles a typical insect bite. A tick can transmit Lyme disease, a disease that causes muscle pain in the early stages, among other things. If you suffer from muscle pain after an apparent insect bite, Lyme disease should be ruled out as a precaution in order to avoid long-term consequences.
Find out more about the clinical picture of the Lyme disease.
Muscle pain in pregnancy
Pregnancy affects the entire body. As the uterus continues to grow and the body gains weight, the back has to carry more load than before. As a result, the back muscles also grow.
In the course of time, the pregnant women often suffer from back pain, i.e. muscle pain in the area of the back muscles. Sore muscles and muscle tension are common causes of muscle pain during pregnancy.
Menopausal muscle pain
Muscle pain, along with joint pain, is a common symptom of menopause. These symptoms affect up to seventy percent of all menopausal women.
The cause of menopausal muscle pain is not fully understood; some scientists describe the condition as a common sign of wear and tear, while other scientists believe it is related to declining levels of estrogen.
Muscle pain in fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a common, chronic pain syndrome. Those affected suffer from chronic pain, which is particularly severe in the area of the muscle and tendon attachments. In addition to the painful pressure points, the sick often suffer from depressive moods, sleep disorders, dry mouth and tremor.
There is no therapy that can eliminate the muscle pain associated with fibromyalgia. Regular sports units, relaxation exercises and physiotherapy should have a positive effect on the painful pressure points.
Find out more about the topic here: Fibromyalgia.
Can stress play a role?
Stress can negatively affect all body functions. Chronic back pain, a widespread disease in Germany, so to speak, is often associated with stress. In addition, stress often leads to muscle tension as a result of poor posture.
This means that stress can cause muscle pain in a number of different ways.
Read more about the topic here: Consequences of stress.
What deficiency can muscle pain indicate?
Calcium and magnesium are important electrolytes in the muscles. If there is a deficiency, pain and muscle cramps develop. Vitamin B12 is an important vitamin that the body cannot produce itself and must therefore take in with food. A strong vitamin B12 deficiency can cause muscle pain in addition to various other complaints.
In addition, a vitamin D deficiency or insufficient sunlight can also trigger muscle pain. Furthermore, muscle pain can be the result of a pronounced iron deficiency.
More information on the topic Vitamin B12 deficiency you'll find here.
Iron deficiency as a possible cause
Iron is an important trace element that our body needs to get in with food. Iron deficiency leads to anemia and symptoms such as chronic exhaustion and listlessness. A chronic iron deficiency can cause a chronic fatigue syndrome called myalgic encephalomyelitis. In addition to memory, sleep and concentration disorders, this syndrome includes pronounced muscle pain.
Find out more about the topic here: Iron deficiency.
Accompanying symptoms of muscle pain
Depending on the cause, accompanying symptoms can also be manifold. You should definitely be mentioned during the medical interview in order to identify and treat the underlying disease. Initially, muscle pain can occur in specific areas or generalized, i.e. throughout the body. Infections, for example, are associated with whole-body muscle pain, as well as physical malaise, temperature increases or fever, cough, runny nose, headache and other complaints. In the case of local tension or hardening, the muscle pain can also radiate to other areas (for example from the neck to the jaw or shoulder and arm) and painfully restrict movements.
Torn muscle fibers can cause bruising and swelling, as well as strains and bruises. Muscle diseases such as muscular dystrophy can lead to increasing muscle wasting and loss of strength, rheumatoid diseases lead to joint problems in addition to muscle pain and diseases of the nervous system are accompanied by a wide variety of accompanying complaints, such as rigidity in the face and tremors in Parkinson's disease. In addition to muscle pain, statins can even trigger liver dysfunction, as can the so-called Rhabdomyolysis, a breakdown of muscle fibers.
Localization of the muscle pain
Muscle pain in the thigh
Muscle pain in the thigh can affect different sections and appear differently. They can have various causes and affect the person affected to different degrees, and they can also be temporary or chronic. The pain character ranges from dull to stabbing pain, locally limited or radiating to other areas. Muscle pain is usually the result of sports injuries or accidents. A past traumatic event and the course of the accident can therefore be useful in diagnosing muscle pain. The most common causes of muscle pain in the thigh include pulled muscles, torn muscles, or bruises. Muscle soreness after overexertion can also lead to temporary muscle pain.
The front thigh is from Quadrips femoris muscle educated. It is the extensor of the knee joint and of great importance in straightening the body. Typical movements that lead to an injury to the muscle and thus pain in the front thigh are jerky extension of the knee, especially during exercise. Older patients in particular can be affected by a so-called quadriceps tendon rupture, which can be palpated and is also associated with severe pain in the front thigh. Injuries to the rear thigh are less common, usually also in connection with exercise. The muscle groups in the back of the thigh are responsible for flexion and rotation in the knee. If injuries occur, these movements are painfully restricted.
Outer thigh pain occurs when there is an injury to the tendon plate. It is a typical injury for runners who expose themselves to excessive stress and long runs. In the event of an injury, physical activity should be stopped immediately and paused for a few weeks. Tears and fiber tears in particular can result in lengthy healing processes. Muscle pain in the thigh can also have other causes besides sports injuries. This includes, for example, the herniated disc. The pain can move from the back to the thigh and affect the whole leg. Bad posture and incorrect loading can also lead to chronic pain in the hips and legs. Chronic pain in the thigh that cannot be explained by a sports injury should be evaluated and treated by a doctor.
More information can be found here: Thigh Pain
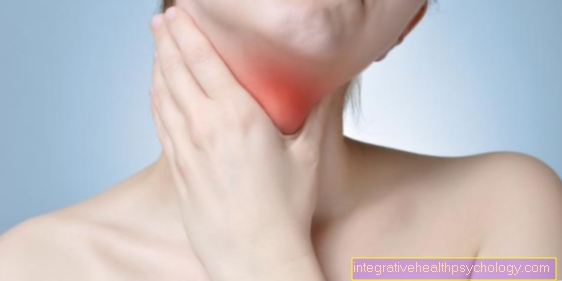
Muscle pain in the back
Muscle pain in the back is usually caused by tension in the neck, shoulder and back caused by a sedentary lifestyle and poor posture. Back pain is often chronic and can be a major burden for those affected. Tension can be prevented through sufficient exercise in everyday life, active strength training and stretching exercises. Massages and local heat can also be used as therapy. Relaxation exercises, meditation and stress reduction in everyday life can also alleviate the symptoms, as chronic back pain is often also caused by stress. Muscle pain in the back also occurs with herniated discs. Depending on the affected nerve root, the pain can radiate into the legs and, less often, the arms and trigger other accompanying complaints such as paresthesia. Back pain can also occur temporarily with muscle injuries such as strains. Especially chronic pain or back pain with accompanying symptoms should be clarified and treated by a doctor.
You can find more information here: Back pain
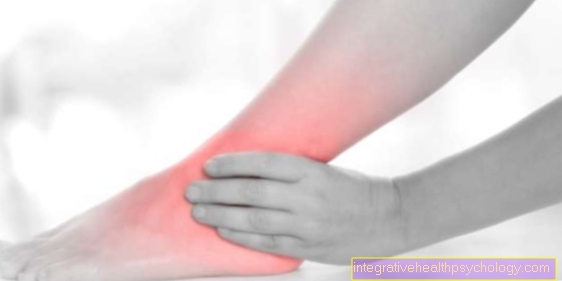
Muscle pain in the calf
Calf pain can have a variety of causes, muscular causes are among the most common. The affected muscles are the two-headed ones Gastrocnemius muscle and the clod muscle. Typical injuries include bruises, strains and torn muscle fibers as a result of sports accidents or sore muscles after overexertion. Tension can also lead to muscle pain. Depending on the severity of the injury, the severity of the pain can vary; in any case, a strict break in sports should be observed for several days to weeks. Painful feelings of tension in the calf, which are accompanied by overheating, thickening and discoloration of the affected extremity, must be taken seriously. These are important warning symptoms for a so-called phlebothrombosis, a vein blockage in the lower leg region. This must be treated early in order to avoid life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
You can find more information here: Calf pain
Muscle pain in the arm
Muscle pain in the arm can also have a variety of causes. Muscle injuries and sore muscles after overexertion should be listed again. In the event of a muscle injury, you should definitely take a break from exercising. Tension in the neck area can also pull into the arm and trigger muscle pain.Herniated discs in the cervical spine can cause pain that radiates into the arm. In addition, numbness or tingling occurs. A doctor should be consulted with these accompanying symptoms. In the event of sudden, severe pain, especially in the left arm, a heart attack should always be considered. In addition to arm and chest pain, other symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea, dizziness and a feeling of weakness can occur. In the event of the slightest indication of a possible heart attack, the emergency doctor must be informed immediately, as it is a life-threatening emergency.
You may also be interested in this article: Upper arm pain
Which doctor treats muscle pain?If you have muscle pain, the first thing we recommend is a visit to your doctor. As a contact and forwarding point, this is necessary anyway in order to issue a possible prescription for a specialist. In the event of muscle pain, the family doctor should have a detailed discussion with the person concerned about the symptoms and conduct a thorough physical examination.
Depending on what the family doctor suspects to be the cause or what kind of illnesses he rules out, further visits to the appropriate specialists are indicated. A referral to a neurologist, orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist is made by the family doctor.
Diagnosis
The diagnosisThe underlying cause of the muscle pain in a particular case is mostly about the detailed description of symptoms and medical history possible, which is why a detailed anamnesis by the doctor is of great importance. However, if this is not enough, there are various examinations that can be carried out in addition: physical examinations, analyzes of Blood work, imaging procedures (Ultrasonic, MRI or CT) or rarely one Muscle biopsy, in which a tissue sample can be taken from a muscle and examined more closely.
Therapy of muscle pain
The therapy of muscle pain depends on the cause. In the case of acute complaints, no treatment at all is usually necessary. If the pain is very severe, you can only resort to painkillers, preferably from the group of anti-inflammatory drugs (for example ibuprofen). Or another option is to apply some horse ointment to the affected area of the body to relieve the pain. In addition, the muscle should be spared and possibly cooled. For long-term chronic pain, muscle relaxants can also be administered as medication.
In addition, electro therapy and neural therapy are available for treatment. Furthermore, in such cases, a long-term strengthening of the muscles through physiotherapy or relaxation techniques should be sought. The addition of heat (in the form of compresses, compresses, saunas or baths) often provides relief here. In addition, regular physical activity (cycling or swimming are particularly suitable) has a positive effect on the pain and can also prevent new pain.
Of course, if the muscle pain was caused by another disease, it is necessary to adequately treat that disease to get rid of the pain in the muscles as well.
Read more on the subject at:
- proff® pain cream
Which cream can help?
There are various creams, gels, and ointments that help relieve muscle pain. Diclofenac and ibuprofen are popular agents that relieve pain and have anti-inflammatory effects.
The ThermaCare® pain gel contains the active ingredient Felbinac, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and cooling effect. There are also herbal creams for muscle pain, for example products with arnica. The Horse Medical Ointment, which cools the painful tissue, promotes blood circulation and thus reaches deeper muscle layers, is also tried and tested.
More information on the topic ThermaCare® pain gel you'll find here.
Duration of muscle pain
Muscle pain can be acute or chronic depending on the underlying disease, and also depending on the medical treatment. In the case of a simple infection, the whole-body pain can precede the accompanying symptoms, but the muscle pain is usually temporary. In the case of injuries, the extent of the damage determines the healing process: muscle soreness rarely lasts for several days, strains are painful for a few days to weeks, while fiber tears can cause discomfort for a long time. Tension can be caused by poor posture, which is anatomical or caused by a sedentary lifestyle, and can therefore often only be treated symptomatically. Chronic diseases such as muscle degeneration, rheumatic diseases and neurological diseases can be associated with persistent muscle pain that can even worsen over time.



.jpg)













-mit-ten-(titanic-elastic-nail)-oder-sten.jpg)