Pregnancy Hypertension - Is It Dangerous?
Synonyms in a broader sense
- Hypertension of pregnancy
- Gestational hypertension
- Gestational hypertension
- Eclampsia
- pre-eclampsia
- HELLP syndrome
- Poisoning during pregnancy
English: Hypertension in gravidity
definition
High blood pressure in pregnancy is defined as follows:
Blood pressure measured several times by the doctor with values above 140/90 mmHg is considered to be elevated and means that the pregnant woman has high blood pressure.
One speaks of a slight increase in blood pressure when the blood pressure values are between 140 / 90mmHg and 159 / 109mmHg. There is a severe increase in blood pressure during pregnancy if the measured values are above 160/110 mmHg.

Occurrence in the population
An increase in blood pressure occurs in about 10% of all pregnancies. Pregnancy high blood pressure with severe symptoms, eclampsia, occurs in 1 in 2,000 to 3,500 pregnancies.
root cause
The exact cause of an increase in blood pressure during pregnancy is still unknown, but risk factors can be named which lead to the fact that pregnant women develop high blood pressure (see section "Risk factors").
Meaning - Can high blood pressure be dangerous?
High blood pressure can be extremely dangerous for both mother and child, especially when the complications typically associated with it occur, which is why it is important to monitor your blood pressure regularly during pregnancy.
If the mother's high blood pressure remains undetected and persists for a long period of time, this can, for example, damage the blood vessels of the placenta (placenta) to lead. The baby, which is supplied with nutrients via these vessels, suffers from an undersupply and in addition to insufficient nutrients also receives insufficient oxygen, which can result in a delay in its growth, in the worst case in a miscarriage.
It is important to distinguish between the sub-forms of pregnancy high blood pressure, which can manifest itself in a merely observable phenomenon up to acute complications such as an epileptic seizure.
In the mildest form, uncomplicated pregnancy hypertension, there is a temporary increase in blood pressure, which should be observed and possibly treated with medication. No adverse effects on the fetus are to be expected here.
If, however, the pregnant woman also excretes proteins in the urine, this indicates damage to the kidney and corresponds to the clinical picture of preeclampsia. As a result of protein loss and kidney damage, the pregnant woman also tends to lose fluids, which can lead to a deterioration in the blood supply to the unborn child. It also poses a risk for the manifestation of acute eclampsia, which is characterized by the sudden occurrence of an epileptic seizure.
In summary, the occurrence of high blood pressure is not dangerous in principle, but should be checked and treated by a doctor in any case, as the possible complications can pose a danger to mother and child. Expectant mothers who are still working might consider taking maternity leave, especially for physical work or very stressful jobs.
You might also be interested in: Maternity leave - you should know that!
Info: Avoiding the consequences of high blood pressure
The early detection of high blood pressure values and the urine test in the context of prenatal care enable the immediate detection, treatment and avoidance of unfavorable courses for mother and child.
Risk factors for developing high blood pressure during pregnancy
If the pregnant woman had high blood pressure in a previous pregnancy, or if her family has a history of high blood pressure during pregnancy, the risk of developing high blood pressure in the current pregnancy increases. Subject to the uterus high elongation, e.g. If there are twin pregnancies or large babies, they are more likely to have high blood pressure. Does the mother have one before she becomes pregnant? Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) or high blood pressure, the risk of pregnancy high blood pressure is also increased.
There are different forms of hypertension in pregnancy
The division of high blood pressure associated with pregnancy into different forms takes into account the following aspects:
- Did you have high blood pressure before pregnancy?
- In addition to the high blood pressure values, can a high amount of proteins be found in the urine?
If both of these questions can be answered in the negative by the pregnant woman and with the help of a urine test, then there is uncomplicated pregnancy high blood pressure, also known as gestational hypertension. It often affects young women who are expecting their first child. This form of pregnancy high blood pressure is characterized by the fact that neither the blood pressure values were high before the 20th week of pregnancy, nor that the increased values last longer than six weeks after the birth. The high blood pressure is therefore limited to the period of pregnancy or a six-week phase after the birth of the child. Apart from the high blood pressure values, the pregnant woman has no other symptoms.
In the so-called preeclampsia, the question of protein excretion can be answered with “yes”. In addition to high blood pressure values, pregnant women with preeclampsia also have abnormal urine findings:
It excretes more proteins with the urine. This form of pregnancy high blood pressure can also lead to water retention (edema) in the body. If a persistent rise in blood pressure is found and an unusually strong weight gain of approx. 1 kg per week is noticed or if the pregnant woman notices thick legs (edema), the doctor should be consulted immediately, as these are signs of preeclampsia. For values above 160/100 mmHg, even without edema or severe weight gain, an examination by a doctor should be carried out in order to get to the bottom of the cause of the increased values! Vision or sensitivity to light.
These complaints should be clarified by the doctor, as serious complications can arise.
It can lead to an undersupply of the child, which one absolutely wants to avoid. Regular visits to the doctor can identify increases in blood pressure or the occurrence of protein in the urine during pregnancy and appropriate therapy can be carried out.
Eclampsia and HELLP syndrome are special forms of preeclampsia (see below).
Chronic hypertension is defined as high blood pressure that occurs before pregnancy or before the 20th week of pregnancy and continues for at least six weeks after the birth. This form of high blood pressure is not directly related to pregnancy like gestational hypertension and preeclampsia with their special forms.
The so-called Propfgestose is when the woman already had high blood pressure before pregnancy and this worsens during pregnancy, i.e. even higher blood pressure values can be achieved.
The following table clearly summarizes the information.
Forms and characteristics of high blood pressure in pregnancy
- Gestational hypertension:
- high blood pressure caused by pregnancy
- in the last trimester of pregnancy
- no increased excretion of proteins with the urine
- Subsides after birth
- Pre-eclampsia:
- high blood pressure is caused by pregnancy
- In addition, increased protein excretion in the urine (proteinuria) and fluid accumulation in the tissue (edema formation)
- to be treated urgently, because without therapy it can lead to seizures and seizures (eclampsia) and the HELLP syndrome
- chronic hypertension:
- high blood pressure not caused by pregnancy
- no increased protein excretion in the urine was found
- Propfgestosis:
- Kidney or high blood pressure problems that existed before pregnancy
- pregnancy worsens these pre-existing diseases
There are special forms of high blood pressure during pregnancy:
If preeclampsia turns into eclampsia, the following symptoms may occur in addition to the increased blood pressure and protein excretion in the urine:
- strong headache
- Flicker before the eyes
- general malaise
- excessive muscle reflexes
- Seizures
- and impaired consciousness.
Eclampsia can occur even after the birth. In only 0.1% of the cases, preclampsia turns into eclampsia.
There are different treatment strategies for the presence of eclampsia:
In the case of an acute seizure, muscle-relaxing medication such as diazepam (e.g. Valium®) is given and prophylactic therapy with magnesium sulfate is carried out after the attack to prevent further seizures. The patient is also receiving antihypertensive therapy.
The baby can be delivered by caesarean section when the seizure has subsided and the pregnant woman is in a stable condition. Before and after the delivery she receives antihypertensive and seizure preventive therapy. If the pregnant woman is still in an early phase of pregnancy, after an ecstatic seizure, wait and see behavior may be possible in individual cases, so that the child can be born in a more mature state. Eclampsia can also occur during the puerperium, i.e. within 6-8 weeks after the birth of the child.
If a pregnant woman who is over the 17th week of pregnancy experiences pain in the right upper abdomen, a HELLP syndrome should be clarified as the cause.
HELLP is derived from the original English name of the disease and describes the symptoms that occur in the course of the disease. The HELLP syndrome is characterized by the combination of an increased breakdown of red blood cells, increased liver values and a low level of blood platelets. HE stands for the breakdown of red blood cells (hemolysis), L for the elevated liver enzymes and LP for the low platelets.
The symptoms can lead to a bleeding disorder and it is possible that the child is not optimally supplied by the placenta due to the maternal illness.
There is an increased risk of developing HELLP syndrome if ...
- the pregnant woman about pain in the upper abdomen, especially on the right complains.
- high blood pressure values over 140 / 90mmHg are measured several times.
- Increased protein is excreted in the urine.
- the number of platelets in the blood test is low.
- There are signs of red blood cell breakdown.
- you notice increased inflammation values in the blood test.
- the baby shows growth retardation on the ultrasound scan.
If these symptoms are present, the patient must be monitored immediately in the hospital.
You can find a lot more information under our topic: HELLP syndrome
Special forms of preeclampsia
- Eclampsia:
- high blood pressure
- Increased protein excretion in the urine (proteinuria) and the formation of fluid accumulations in the tissue
- neurological symptoms: seizures and loss of consciousness
- HELLP syndrome:
- high blood pressure
- right side pain in the upper abdomen
- low level of blood platelets increased liver values and increased breakdown of red blood cells
diagnosis
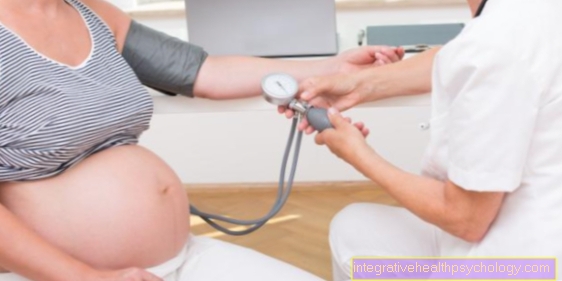
Measurements of the Blood pressure in the doctor's office during the examinations as part of the Prenatal care be given. In the Mother pass the blood pressure values are entered so that a comparison with values determined during the course of pregnancy is possible.
However, since 20% of pregnant women tend to have higher blood pressure values in the doctor's office than at home in the familiar environment, if the blood pressure values are high, a 24-hour blood pressure measurement be carried out, the course of the Blood pressure readings shows in the everyday life of pregnant women.
Another possibility of making a diagnosis is the measurement of the blood pressure by the pregnant woman herself:
With the help of an electronic Blood pressure monitor the patient determines her blood pressure values every day and records them. If the values are also increased in these measurements, the suspicion of hypertension in pregnancy is confirmed and appropriate therapy is started.
With the help of urine test strips, the urine of the pregnant woman is also examined for proteins as part of the preventive examinations.
Is there any suspicion of a pre-eclampsia, a blood test is usually carried out to check the function of the organ systems.
therapy
Info: Blood pressure medication during pregnancy
Some of the common antihypertensive drugs can damage the fetus and are therefore not suitable for high blood pressure therapy during pregnancy. The therapy is carried out with drugs that have no teratogenic effects.
Long-term treatment of high blood pressure during pregnancy should only be carried out with repeated high blood pressure values above 160-170 / 100 mmHg.
These drugs include alpha-methyldopa (e.g. Presinol®), certain Beta blockers such as atenolol (e.g. Atebeta ®) and the calcium antagonist nifedipine (e.g. Adalat®). The first choice is to treat hypertension in pregnancy Alpha methyldopabecause it is very effective, has few side effects and is therefore well tolerated.
For patients with pregnancy high blood pressure (gestational hypertension), drug treatment with antihypertensive agents is the therapy of choice.
If there is preeclampsia, the therapy is extended:
In addition to the antihypertensive treatment with the appropriate medication, a muscle-relaxing therapy with Magnesium sulfate carried out to prevent seizures. Often, additional infusions have to be administered in order to keep the patient's fluid balance stable and thus to ensure good care for the child.
The benefit of prophylactic administration of vitamins C and E has been proven in recent studies:
The taking of Vitamin C and E. during pregnancy can lower the risk of preeclampsia.
For the HELLP syndrome Basically the following therapy procedure applies:
First of all, consistent antihypertensive and muscle-relaxing treatment with medication is necessary. The only causal therapy for HELLP syndrome, however, is the delivery of the child so as not to endanger the lives of mother and child and to protect both from consequential damage. The delivery of the child can be delayed under the following conditions:
If the mother is in the course of pregnancy before the 34th week of pregnancy and both mother and child are in a stable situation, it is possible to wait until delivery. The child's lung maturation can be influenced by the administration of the drug Dexamethasone be encouraged so that the child is best prepared for the delivery.
However, if the HELLP syndrome progresses and / or leads to an unstable condition in the mother or child, immediate delivery, usually by Caesarean section (Caesarean section). After the 34th week of pregnancy, if the HELLP syndrome has been proven, delivery should always be sought.
Read more about the topic here: Lowering blood pressure during pregnancy
Possible consequences
Consequences for the mother
Pure high blood pressure during pregnancy usually has no other consequences for the mother than high blood pressure that occurs independently of pregnancy. Symptoms such as headache, ringing in the ears and dizziness can occur. In contrast to long-term high blood pressure in non-pregnant women, the risks of consequential damage, which often only appear after years of illness, are low.
However, pregnancy high blood pressure can also be more severe and develop into what is known as preeclampsia. This can lead to circulatory disorders in various organs. The maximum form of the disease is eclampsia, where the expectant mother has seizures. This clinical picture is extremely dangerous for mother and child and requires close medical supervision. Therefore the occurrence of headaches / ringing in the ears / dizziness during pregnancy is a symptom that should be considered and clarified by a doctor.
Consequences for the child
The pure pregnancy high blood pressure usually has no relevant effects on the unborn child. However, it is not uncommon for the pure high blood pressure to develop into a more severe form, the so-called preeclampsia (also popularly known as pregnancy poisoning). This can be recognized diagnostically by an increased protein excretion in the urine. If preeclampsia is present, circulatory disorders in various organs of the mother can occur. If the placenta is affected, this can lead to an insufficient supply of the unborn child. This can lead to the growth lagging behind and in the worst case to the death of the child.
Read more on the topic: Placental insufficiency
Consequences after childbirth
By definition, pregnancy high blood pressure occurs in a period of time which extends from the completed 20th week of pregnancy to the 12th week after birth. High blood pressure that persists after the birth is accordingly no longer referred to as pregnancy high blood pressure, but is considered pregnancy-independent high blood pressure. In most women who suffer from high blood pressure during pregnancy, blood pressure returns to normal after giving birth, but often not until a few weeks after giving birth.