Spine training
Back pain
General medical information on the cause, diagnosis and treatment of back pain can be found at Back pain.
Effectiveness of local muscle training for back pain
2 patient groups were examined 1 year and 3 years after the first appearance of Back pain in the Lumbar region.
The first group was treated exclusively with medication, the second group with a training program for the deep muscles.
The recurrence rate in the first group was 84% after 1 year and 78% after 3 years.
The recurrence rate in the second group was 30% after one year and 32% after 3 years.
Pain intensity, functional impairment, range of motion and the muscle cross-section of the deep muscles were also examined Back muscles. Here too, significant improvements in favor of the exercise group were found.
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Exercise program to train the local muscles
- the exercises cannot be learned without professional guidance from a physiotherapist, as intensive training in perception is necessary and the exercise assignments can only be conveyed through "pictures"
- Exercise period: daily for 10-12 weeks
- Number of repetitions / exercise: 30 daily, 3 units of 10 repetitions are useful, and exercises can be incorporated into everyday life
- Starting positions: after learning the exercise seat, stand, gait, as the deep muscles work better against gravity
- Voltage duration: approx. 10sec. / Exercise
- Tension sequence like a wave, slow start, hold, slow relaxation, if the muscles "twitch" when tensing, the global muscles are tensed instead
- Tense only 30% of the maximum force
- After the 3 months, daily "reminder exercises"
- Integration into general training
- Integration into everyday life
- Take the exercises seriously, even if they have little to do with strength training or exercise
- If the acute pain occurs again, repeat intensive daily practice for 4-6 weeks
1. Rehabilitation of the internal abdominal muscle (Musculus transversus abdominis)
Transversus abdominis muscle lies in a ring under the large abdominal muscles, helps with coughing, laughing, pressing, supports breathing, protects the abdominal organs and stabilizes the lumbar spine via a connective tissue connection.
Starting positions: to learn lateral position, four-footed position, later sitting, standing, initially hand on the lower abdomen
- Let the abdominal wall lie loosely in your hand (no tension in the large abdominal muscles)
- Tension begins in the lower part of the abdomen
- Voltage order:
- Abdominal wall consists of 2 layers, pull the inner part inwards away from the outer part (e.g. wool coat with lining)
- Tighten the inner corset, the outer corset remains loose
- Let the abdominal wall rest in your hand, very carefully pull your navel towards your spine
- Possibly. Combination of tension and exhalation
More information about the anatomy can also be obtained from:
- internal oblique abdominal muscles
- external oblique abdominal muscles
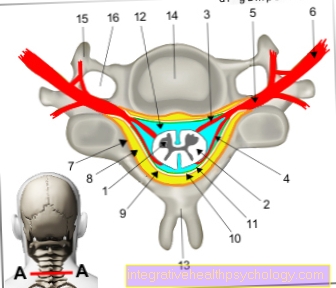
2. Rehabilitation of deep back muscles (M. multifidi)
The deep back muscles are built up like a fir tree and stabilize them Lumbar spine about the tension in the individual lumbar vertebrae. They also offer good protection for the intervertebral discs. A weakness of the deep back muscles can in combination with an imbalance (imbalance) of the abdomen - and Pelvic floor muscles Lead to pain in the lumbar spine and can cause a Herniated disc in the lumbar spine area favor.
Starting position: to learn prone position or side position (pain side up), later sitting, standing, at the beginning fingers directly next to the lower lumbar vertebrae or tennis balls next to the lumbar spine
- Voltage order:
- Pull vertebrae away from fingers (or balls)
- "Hollow back at the level of a vertebra"
- Very carefully pull the vertebra towards the navel
- The vertebra is a drawer and is drawn in by the muscles
3. Pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation
The pelvic floor muscles secure the small pelvis downwards, stabilize the sacrum and iliac joint and the lumbar spine in combination with the back, abdominal and hip muscles and ensure continence.
A weakness of the pelvic floor muscles in combination with an imbalance of the abdominal and back muscles can lead to complaints in the lumbar and pelvic area and promote the development of incontinence.
Starting position: to learn to lie on your back or side, later sitting and standing
Voltage order:
Women:
- Cherry with the stem pointing upwards in the vagina, carefully pull the cherry up without crushing it
- Carefully pull up the sponge, do not crush it
- urethra shorten
- Pull up the pelvic floor as you exhale (do not pinch it) and loosen it as you inhale
Men:
- Shorten or pull up the urethra
- Jump mentally into the deep end
Combination of deep abdominal muscles, deep back muscles, pelvic floor (exercise 1,2,3)
After learning and training the three muscle groups, the individual tensions can be combined into one exercise.
Voltage order:
- Introduction of tension with the pelvic floor
- Belly button and vertebrae approach
- A silk thread is stretched between the navel and the lumbar spine to relieve this thread
- There is a balloon in the abdomen, squeeze gently from all sides
- Lace inner corset
4. Rehabilitation of the deep neck flexors
The short neck flexors are located on the front of the neck and are responsible for the stability of the cervical spine (has great mobility) and the protection of the intervertebral discs.
The shoulder and neck area is very prone to stress, constant sitting and work at the screen can lead to an imbalance in the shoulderNeck muscles and lead to cervical spine dysfunction. This often results in neck pain and headaches.
Starting position: Supine position, cervical spine in the middle position between flexion and extension, later sitting (pay attention to the upright position) and standing
Voltage application:
- Small nodding movement with the head, the back of the head pushes slightly towards the ceiling, gentle, slow tension of the deep cervical flexors
- Chin is carefully pulled towards the neck, keeping tension
- Combine tension with exhalation, paying attention to relaxation of the mouth muscles and the large throat muscles (control with your hands)
5. Rehabilitation of the short deep neck extensors (M.Multifidi)
The short neck extenders are located in a fan shape at the back along the cervical spine and stabilize the cervical spine from the back. A weakness of the deep neck extensor, triggered e.g. Increased sitting or whiplash trauma in combination with dysfunction of the neck flexors can lead to head or neck pain, dizziness or damage to the intervertebral discs.
Starting position: prone position, later sitting (pay attention to the upright position) or standing
Voltage order:
- Place fingers right / left next to the cervical spine, pull the vertebrae away from the fingers towards the chin
- Vertebra is a drawer that is pulled in towards the chin
- The muscles are a spring, the body is attached to it
6. Rehabilitation scapula stabilizers
The shoulder blade stabilizers sit between the shoulder blade and ribs and between the lower shoulder blade angle and the spine. A good function of these muscles relieves the shoulder area, since it comes to a relaxation of the often cramped shoulder muscles on top of the shoulders. Important is
the training of this muscle group, especially in the case of "desk criminals", when the shoulders are pulled up due to stress or in the case of so-called "wing shoulders".
Starting position: prone position, upright sitting and standing
Voltage order:
- Roll your shoulders over a small hill (in the direction of your trouser pockets) behind the hill next to your thoracic spine, hold there
- Glue the lower angle of the shoulder blade to the ribs after the shoulder roll, taking care not to stretch the thoracic spine too much
Combination of short neck flexors, short neck extensors, shoulder blade stabilizers (Exercise 4,5,6)
After learning and training the three muscle groups, the individual tensions can be combined into one exercise.
Starting position: upright sitting, standing
- Initiate the tension build-up with the shoulder blade control
- The chin and cervical vertebrae approach in the middle of the neck
- A silk thread is stretched between the chin and neck vertebra, try to relieve it
- In the middle of the neck there is a balloon, carefully squeeze it from all sides
The most common mistakes in learning
- too much effort, only 30% is necessary
- resorting to the global muscle system
- insufficient endurance and concentration when practicing
When perception and control of the individual muscle groups have been trained, all 6 exercises can be combined into a basic tension, further practice can then be easily integrated into everyday life (at the desk, in the kitchen, in front of the television).
After completing this tutorial, the general Strength endurance while tensing the local muscles (Synergy local / global muscle system) trained. The skills learned to tense the deep muscles in combination should be automated so that the patient can call them up during every exercise (e.g. on the strength machine).
Training in everyday situations is the final stage in the treatment of spinal instability. In particular, activities are practiced that cause difficulties for the patient or that previously triggered the known pain. The patient must feel that his spine is muscular at all times.
Summary
For optimal treatment of a patient with instability-related movement disorders of the spine and back or neck pain, the training program for the local muscular system should be included in addition to the standard therapy. This is supported by the effectiveness, which has also been proven in studies, in terms of pain reduction and a decrease in recurrence rates.













.jpg)