Breast-conserving therapy (BET)
introduction
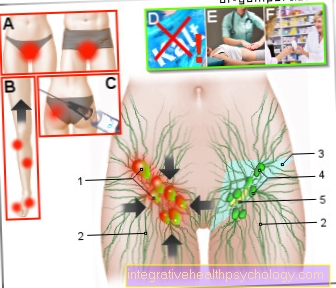
With breast-conserving therapy, only the tumor (cancer) in the breast is removed while the remaining healthy breast tissue is retained.
Nowadays, BET is a common procedure that is usually combined with a subsequent irradiation of the breast. Breast-conserving therapy is used today for around 75% of breast cancers and, provided certain criteria are met, it can offer the same level of safety in the treatment of breast tumors as amputation.
.jpg)
When is BET possible in breast cancer?
Today, BET is the standard procedure in the treatment of breast cancer. Nevertheless, certain criteria must be met for a BET.
These include, among other things, that the tumor is limited, i.e. not scattered across the breast, and that the ratio of the tumor is rather low compared to the rest of the breast tissue. Furthermore, there should be the possibility of irradiation afterwards. As a rule, a BET is always linked to a subsequent radiation treatment - the operation together with the radiation is just as safe a treatment method as a complete breast removal.
You might also be interested in this topic:
- Chemotherapy for breast cancer
When is a BET not possible?
BET cannot be used in inflammatory forms of breast cancer. In this context, the person skilled in the art speaks of an inflammatory breast tumor.
A BET cannot be performed even if the tumor is too large, usually considering the tumor in relation to the healthy breast. In some cases it is possible to “shrink” the tumor through previous chemotherapy - so that after treatment with chemotherapeutic agents, BET can be considered. If the tumor has no clear boundaries, BET is also excluded. Furthermore, a subsequent irradiation is a criterion for a BET - if this cannot be carried out or is rejected by those affected, this also speaks against breast-conserving therapy.
Also read:
- Hormone therapy for breast cancer
Procedure of a BET
A BET is performed by doctors who work in gynecology. They specialize in BET and usually also take care of the pre- and post-treatment. In Germany today there are centers specializing in breast diseases, especially in the big cities.
In BET, the surgeon only removes the part of the breast that is tumorous. The rest of the breast tissue is retained and those affected often notice little or no difference to the non-operated breast afterwards. If a larger amount of tumor tissue is removed, it is possible to build up the operated breast using autologous fat or implants. It is also possible to reduce the size of the healthy breast in order to restore symmetry. Above all, the wishes of those affected are decisive here - some also forego surgical intervention and resort to partial dentures.
In addition to removing the tumor tissue, it is important to look at the lymph nodes in the immediate vicinity of the tumor. You can possibly be attacked by the tumor cells. As a rule, the lymph nodes are examined before the operation - if they appear conspicuous, a small tissue sample is taken. If these tissue samples are free of tumor cells, only the so-called sentinel lymph nodes are removed in the breast-conserving operation. However, if the lymph nodes are already penetrated by tumor cells, it may be necessary to remove additional lymph nodes, especially in the armpits; experts refer to this as an axillary dissection.
- Lymph node involvement in breast cancer
- Surgery for breast cancer
Are the chances of survival better with non-breast-conserving therapy?
With BET, the malignant tissue is completely removed. During the operation, the removed tissue is examined microscopically to see whether the tumor cells are surrounded by healthy cells - this means that the tumor has been removed as a whole. If this is not the case, the surgeons can remove a piece of tissue if necessary.
The BET together with a radiation treatment promises the same safety as a breast removal, also known as amputation. In some cases, those affected decide to have an amputation even if a BET is possible. It is a personal decision that is made in advance by the breast cancer patient.
More information on this topic:
- Life expectancy in breast cancer
- Chances of recovery in breast cancer
advantages
The advantage of BET is that the breast is preserved. Some women find this to be a relief, as only a small change can be seen on the breast. Furthermore, the scars in BET are basically quite small. For women who want to have children, it may well be possible to breastfeed after breast-conserving therapy - it is important that there is still enough glandular tissue in the breast.
disadvantage
An operation on the breast, for example, can cause dents or hardening. Radiation can also contribute to such changes. Furthermore, a scar may be visible through the cuts made during surgery.
With breast-conserving therapy, there is a risk that not all malignant cells have been removed by the operation. To be on the safe side, the removed tissue is examined and checked to see whether there are already benign cells in the edge area, which suggest that the tumor as a whole has been removed. If tumor cells are also found in the outer areas, another intervention is necessary. Together with radiation, BET is just as safe a procedure as amputation, i.e. a complete removal of the breast. However, if irradiation is refused or if it cannot be carried out, the BET is not to be regarded as an equivalent procedure for the treatment of breast cancer.
You may also be interested in this topic:
- Irradiation for breast cancer