The broken rib
introduction
A rib fracture (so-called rib fracture) is a fracture of the rib in the bony or cartilaginous part. A rib series break occurs when at least three or more adjacent ribs are broken.
One speaks of a broken rib when a rib is broken twice, when a piece of rib has broken out, so to speak. As a rule, rib fractures only occur after considerable external violence, as can occur in traffic accidents or bicycle falls at high speed.

The cause
As a rule, a broken rib is caused by a direct accident mechanism such as the fall on the chest. Known osteoporosis can lead to a broken rib even without an accident, as the bone density is greatly reduced and consequently the stability decreases.
In the event of strong violence, such as traffic accidents or riding accidents, several ribs can break at the same time. In the case of less severe violence, the ribs can only be bruised, but this initially shows up with similar symptoms.
Find out all about the topic here: Bruised ribs.
Broken ribs from coughing
Under normal circumstances, coughing will not break your ribs. However, certain chronic lung diseases such as Bronchitis, allergic asthma, COPD and existing osteoporosis lead to the disease. In osteoporosis, bone density and stability are reduced, which leads to what is known as a fatigue fracture of the ribs due to coughing.
A fracture can also occur in pregnant women, as the constantly growing child and the ever-expanding uterus reduce the space inside the abdominal cavity. This increases the pressure and tension on the ribs, which is why they can break due to coughing.
Therefore it is important to control an existing cough in the above-mentioned risk patients and to ensure normal breathing.
Read more about the topic here: Osteoporosis.
The symptoms
Typical symptoms of a broken rib are the local pain that increases with breathing. In particular, deep breathing and coughing cause pain just above the fracture area. Due to the pain, superficial breathing or inhibition of breathing can occur, which can have a problematic effect on the oxygen supply, especially in older patients. Breathing inhibition can occur, particularly in a series of rib fractures.
As a rule, breaks in the anterior chest wall have a stronger effect on breathing than breaks in the back, as the ribs are additionally stabilized by the back muscles.
If several ribs lying next to each other, possibly broken several times (broken ribs), so-called paradoxical or inverse breathing can occur. The chest pulls in - contrary to natural movement - when you inhale and bulges accordingly when you exhale.
The greatest risk with a broken rib is injury to the lungs, heart or the main artery (aorta) from the broken rib. This can lead to massive bleeding into the lungs (hemothorax) or collapse of the lungs (pneumothorax).
For more information, read on: Symptoms of a broken rib.
The pain as a symptom
Severe pain is the central symptom after a broken rib. They worsen when you inhale, exhale and cough. Therefore, the significant reduction in pain is an important goal of the treatment, so that the patient can breathe and cough without problems. If this is not possible, so-called non-breathing occurs, in which the lungs are no longer adequately supplied with air or are no longer adequately “ventilated”. As a result, pneumonia and sticking of lung tissue can occur, which significantly restrict breathing.
In addition to pain therapy, breathing exercises, breathing exercises and expectorant drugs should be used. The pain usually improves within 2 weeks.
Find out more about the topic here: Pain in a broken rib.
The back pain as a symptom
Back pain can have many different causes. In rare cases, back pain is an indication of a broken rib. Nevertheless, injuries to the rear part of the ribs facing the spine, bruises or damage to nerves and vertebral bodies can lead to problems.
Because breathing is difficult, most patients develop an unnatural relieving posture, which causes muscle tension in the back after a broken rib.
The risks to the lungs
A broken rib can produce sharp-edged fragments that injure the lungs and cause acute shortness of breath. These clinical pictures include the pneumothorax and the hemothorax. In the case of a pneumothorax, air enters the so-called pleural space. This is a gap between the outer and inner lungs where, under normal circumstances, there is negative pressure. When this gap is broken, air flows in and out of this gap, causing the lungs to collapse.
With a hemothorax, blood enters the pleural space due to an injury to blood vessels. Both clinical pictures belong to the acute, life-threatening emergencies that require immediate, emergency treatment (by laying special drains).
Furthermore, if the chest is unstable, unnatural breathing movements develop in the form of paradoxical, inverse breathing. In healthy people, the chest rises and falls when inhaling and exhaling. In the case of paradoxical, inverse breathing, it pulls inward when inhaling and arches outward when exhaling. As a result, the lungs are constricted, no longer properly filled with air and breathing is no longer sufficient. Injuries to blood vessels and nerves in the ribs and lungs are possible after a broken rib, fortunately, they are relatively rare. The ability to cough up enough mucus is also an important factor in preventing pneumonia. This is the most common concomitant disease following a broken rib.
You can read more about the subject here Hemothorax read.
Which doctor should I see?
Fractured ribs as well as serial rib fractures are serious injuries and must be examined by a doctor because of their consequences for the lungs and the surrounding organs. You should either go straight to a hospital or see a specialist in orthopedics and trauma surgery. These two have all the necessary devices for diagnosis (X-ray, CT or MRT).
At the same time, if life-threatening side effects occur, such as Shortness of breath or acute bleeding, react quickly and efficiently and initiate the necessary measures.
The diagnosis
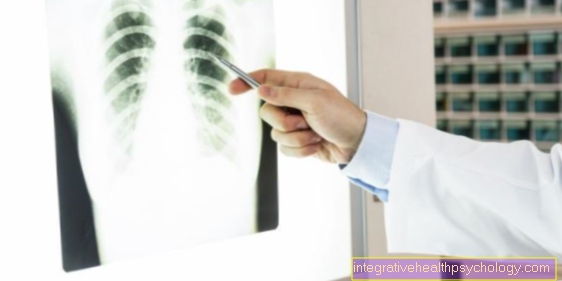
The diagnosis of a broken rib is made through the X-ray. For this purpose, the chest must be x-rayed in two planes. Individual unshifted rib fractures can sometimes only be recognized after days. If the symptoms remain the same, it is advisable to take an X-ray control image (so-called comparison image).
If the rib breaks, the bone can injure one of the lungs. As a result, the affected lung can collapse. This clinical picture is called pneumothorax and should be ruled out by means of a targeted x-ray examination in exhalation.
Sonography (ultrasound examination) can be performed to rule out further injuries to internal organs. This can be used to determine whether there is liquid in the lungs, e.g. as a result of bleeding from the lungs (pleural effusion) or when the spleen, liver and / or kidney have been injured. If a heart injury is suspected or if there is a series of rib fractures, an ECG should be written. In the case of a serial rib fracture, computed tomography (CT) may be useful for the overall assessment.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
The palpation and auscultation
Before the mentioned diagnostic tools such as the chest X-ray are used, a clinical diagnosis can be made in advance. For this purpose, the doctor palpates (= technique of clinical examination in which body structures can be felt with one or more fingers) the place where one suspects the break.
Palpation can cause severe pain, but it is possible to feel the fracture. However, this does not always have to be the case, as there are also broken ribs in which there was no palpable displacement of the bony structures. However, the finding can be confirmed by the presence of pain and crepitations. The term crepitations describes the audible crackling noise that occurs when the bone fragments are rubbed together.
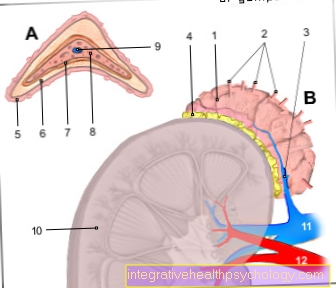
In addition to palpation, the clinical examination also includes listening (Ausculation). A broken rib is a traumatic cause of a pneumothorax. The broken rib injures the lung membrane (Pleura), which consists of two lung leaves. Air can then enter the so-called pleural space between the two lungs. The result is a collapse of the affected lung, as the adhesion of the two pleural leaves has been lost.
If the fracture of the rib has actually caused a pneumothorax, the examiner would hear a weakened or even canceled breathing sound.
The x-ray
The chest X-ray is a standardized examination method and is part of the basic diagnosis of a broken rib. X-ray images are created from the chest area. These are recorded in 2 levels, i.e. once the body is irradiated from the back to the front and a second time from the side. This is an X-ray diagnostic overview image. If a more precise localization is already known in advance or if this can be determined after an overview image, an X-ray target image is useful. In addition, the chest X-ray also allows an assessment of the lungs and heart.
If a pneumothorax is suspected due to a rib fracture, a functional X-ray can be helpful, in which the X-ray is taken while exhaling.
In addition to the existing X-ray image, it may happen that a second image is indicated. The reason for this can be the persistence of pain or other complaints. That X-ray is then also referred to as control recordings. Sometimes the rib fracture is not recognized in an initial X-ray immediately after the event. However, if there is a suspicion, a kind of comparison recording can be made a short time later.
It is worth mentioning that the chest x-ray alone often does not allow a clear distinction from a bruised rib, so that ultrasound images are made for better differentiation.
You can find more information on this topic at: X-ray of the chest.
The sonography
Sonography is another diagnostic tool. Here, organic tissue can be visualized and assessed using ultrasound. Sonography is indicated if, in the case of a broken rib, there is a suspicion that surrounding structures in the chest and abdomen have been affected so that, among other things, internal bleeding can be detected.
In the worst case, a broken rib can also damage the heart. In order to rule out an injury, an EKG (= electrocardiogram) can also be written in addition to the sonography.
The CT
In the case of rib series breaks, a CT (= Computed Tomography) carried out. This is also an X-ray, but a CT is more complex because it creates many individual cross-sectional images. In addition to showing the structure of the bony, this cross-sectional method also enables the assessment of soft tissue and is therefore used when the degree of severity or the extent has to be found out more precisely.
Find out more about the topic here: Computed Tomography.
The therapy

The undisplaced rib fracture can be conservatively treated with pain medication such as Ibuprofen or Tramadol (Tramundin®) or Novalgin are treated well. If there is a dry cough, this should also be dampened with medication. For this, e.g. Paracodeine - drops in question. When breathing gently, care must be taken to ensure that no infections develop from the reduced ventilation.
In the case of a serial rib fracture, the oxygen level in the blood should be measured to check that the oxygen supply is ensured.
If a lung (pneumothorax) collapses, it has to be unfolded again for a short time. For this purpose, a small tube (drainage) is inserted from the outside into the lungs, more precisely into the pleura. A negative pressure (25 - 30 cm H20) that is attached to the suction pipes (hose) can now reject the incorrectly introduced air into the pleura and unfold the lungs. This is a minor surgical procedure.
Read more on this topic at: Therapy of a broken rib
Medication for pain
Which pain reliever medication is used depends on how severe the injury is or whether one or more ribs (series of ribs fractures) are broken. So-called NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as diclofenac or ibuprofen are usually sufficient for pain relief. In the case of serial rib fractures, drugs from the group of opiates are used because of the usually greater pain.
In addition, a blockage of nerves can be helpful, with which complete freedom from pain is achieved for a few hours. In this procedure, a local anesthetic is injected into the area of the nerves supplying the ribs using a syringe. This can be done once or several times.
Also read the article: Nerve block.
Kinesio tape
It may be useful to put on a kinesio tape or a therapeutic adhesive bandage. Mostly, however, the surrounding muscles and the bony membranes ensure adequate stabilization of the chest after a broken rib. Nevertheless, many patients have had good experiences with the kinesiotape. These special tapes follow every movement without any problems and ensure improved blood circulation and increased lymphatic drainage in the area used.
Plaster of paris and other support bandages are no longer applied nowadays because they limit the mobility of the chest and lungs.
For more information, see: Kinesio tape.
The duration of a broken rib
As there are different forms of rib fracture, the time it takes to fully heal varies from case to case. In this context, the exact location of the rib fracture plays a crucial role. In most cases, an immense force exerted on the chest leads to a rib fracture in the area of the anterior or posterior third of the bone. In addition, the simple rib fracture, in which a single rib breaks, must be differentiated from the so-called series rib fracture.
In general, it can be assumed that the healing time for a broken rib is approximately 12 weeks. During this time, the body's own phagocytes begin to break down the destroyed bone tissue. Then the ends of the rib fracture can grow together again.
As a rule, the connection between the ends of the fracture, even in the case of a broken rib, does not occur directly through the build-up of new bone tissue. After the destroyed bone fragments have been broken down, the organism initially begins to produce bone substitute material (so-called callus). In most cases, this phase of fracture healing takes about 3-4 weeks. The callus connecting the fracture ends consists of a substance similar to the actual bone. In direct comparison to normal bone, however, the substitute material is much more flexible and therefore less resilient. Nevertheless, the affected patients report a noticeable decrease or complete disappearance of the pain after this healing phase. Over time, the bone substitute material is replaced by resilient bone.
Complicated forms of the rib fracture can even require surgical treatment. The stabilization of the fracture ends of the rib fracture is usually ensured by inserting screws and plates. In most cases, forms of the rib fracture treated in this way show a significantly shorter time until complete healing. The reason for this is the fact that the formation of new bone material can be accelerated by the reduced mobility of the rib fracture.
Read more on this topic at: Duration of a broken rib.
Exercise for a broken rib
The healing of broken ribs takes about 4 - 6 weeks. In exceptional cases this period can be extended if bone healing is impaired or delayed. Basically, the risk of a new fracture (refracture) after a rib fracture is increased, which is why one should engage in vigorous contact sports such as martial arts, ice hockey or the like. should do without.
In the first 6 weeks after the injury, no sport may be done in order not to endanger the complete healing. Heavy, physical work should also be avoided during this time. After consulting the attending physician, gentle sports such as cycling, walks or gymnastic exercises to stretch the muscles can be started again. As a rule of thumb, the fewer complaints there are, the more intense the physical strain can be.
Since prevention is always better than aftercare, one should protect oneself from a new break when performing high-risk sports. So-called protectors, in this case breastplates, are also available for recreational athletes at affordable prices in specialist shops and protect the chest from bumps and falls. Ideally, they do not hinder the athlete's freedom of movement.
Read more on the topic: Exercise for a broken rib
The aftercare
An x-ray check-up is usually not necessary.
Breathing training should be carried out, especially in older patients, as pain-related breathing can lead to insufficient ventilation of parts of the lungs or a collapse of small parts of the lungs (atelectasis).
Prognosis
In most cases, fractures of the ribs heal back together without any problems, even with fractures or serial fractures.
A vessel - nerve bundle - runs below each rib. If the nerve is injured, pain in the rib area, known as intercostal neuralgia, which is also known as intercostal neuralgia, can result.
Find out more about the topic here: Intercostal neuralgia.
Related topics

How long does it take to heal a broken rib

What are the symptoms of a broken rib

How can you treat a broken rib?