The peanut allergy
What is a peanut allergy?
The peanut allergy is a particularly strong form of allergy. Since peanuts contain many allergens (allergy-causing substances), their allergenic potential is particularly high, which is why many people are allergic to peanuts and the allergic reaction is particularly impressive.
The allergic reaction is an immediate-type reaction in which the allergy occurs immediately after contact with the allergen. The peanuts are usually ingested through the mouth, which is why the allergy is particularly pronounced in the mouth and throat. A strong reaction to even minimal amounts is particularly common with peanuts.

causes
The cause of an allergy is basically an excessive reaction of the immune system to foreign substances. When the body first comes into contact with the allergen, antibodies are formed; this is called sensitization. The second time it comes into contact with the substance, the body recognizes it immediately and starts an excessive immune response.
In peanut allergy, the body reacts to various allergens that are on the surface and in the peanut. Why such pronounced allergies develop in some people has not yet been finally clarified. However, it is certain that there is a genetic component in the development of allergies.
Read more on the subject under: Allergic reaction
Cross allergy
The cross allergy is an intensified immune reaction of the body to a certain type of exogenous substances. The immune system reacts to several allergens that are particularly similar.
The immune cells that are directed against a certain allergen also recognize other substances because they are very similar in their chemical form. Cross-allergies with peanuts are often found with birch, which includes other foods such as apple / pear / cherry but also almond / hazelnut. Banana / mango / orange as well as avocado / tomato and parsley / basil are rarer.
Read more on the subject at: Cross allergy and Hazelnut allergy
diagnosis
Diagnosing a peanut allergy can be carried out in two different ways. The allergy can be diagnosed purely symptomatically through a provocation attempt.
The person concerned eats peanuts and waits to see whether an allergic reaction occurs.
Since this provocation test can be dangerous due to the strong reaction to peanuts, a so-called prick test is often carried out. A minimal dose of the allergens (allergy-causing substances) is injected into the skin on the forearm. Then you wait to see whether the body reacts to this substance. The reaction will show up as redness, swelling, and itching at the site of the injection.
Read more on the subject at: Diagnosing an allergy
Symptoms
The peanut is one of the particularly allergenic substances, which means that only small amounts often cause a very strong allergic reaction.
Typically, symptoms appear immediately after consuming peanuts or peanut-containing products. The symptoms can range from a furry tongue to burning, itching and rashes to life-threatening allergic shock with complete swelling of the airways and an unstable circulatory situation.
Read more about this under Symptoms of an allergy.
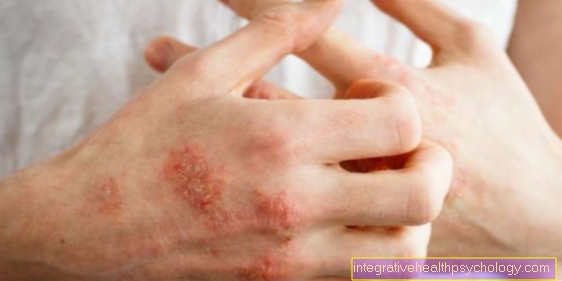
skin rash
Strong peanut allergies usually not only affect the oral mucosa and the throat, where there is direct contact with the peanuts. In addition, there is also a systemic whole body response to the peanuts. The contact puts the body's immune system on absolute alert. The blood vessels are widened by the body so that produced antibodies can quickly reach everywhere. Among other things, immune cells are washed into the skin, where the triggered immune response manifests itself in the form of a rash. This is usually strongest near the point of contact with the peanuts, i.e. on the face.
For more information, see Rash from an allergy.
itching
The itching, which is a symptom of peanut allergy, can manifest itself in different ways. If you only react slightly to peanuts, you may feel a slight itchiness in the mouth and throat, where there was direct contact with the peanuts. Strong allergic reactions are characterized by a defensive reaction throughout the body. Immune cells (which can cause itching) are washed to several parts of the body. The itching is usually particularly severe near the point of contact with the peanuts.
therapy
Therapy for a peanut allergy consists of various components. The most important of these is the withdrawal of the allergy-causing substance. You should therefore absolutely refrain from consuming peanuts or products containing peanuts. This can prevent an allergic reaction. In the event that contact with the allergen has nevertheless taken place, the therapy depends on how strong the reaction of the immune system is. Mild reactions consisting of itching, burning sensation and rash can usually be awaited.
Possible drugs that are used in such situations are so-called antihistamines. They counteract the histamine, which the body uses as a messenger substance for the allergic reaction.
Read more on this topic at: Food allergy therapy
In the case of more severe reactions, the emergency use of the so-called Epi-Pen is often necessary. This contains the active ingredient epinephrine, also called adrenaline, and can be injected directly into the thigh muscle in the event of a severe allergic reaction.
The pen is easy to use and can be used by affected persons within a few seconds, even in an emergency. In addition, severe shortness of breath often occurs due to swelling of the airways and throat. On the other hand there are bronchodilator drugs, i.e. substances that widen the airways. Augmentation measures such as a temporary dose of oxygen are also helpful. Such an allergic shock is a life-threatening emergency, so an ambulance must be called immediately to administer the necessary medication.
For more information, see: Allergy emergency kit
Who needs an allergy emergency kit?
A peanut allergy can trigger an allergic (including anaphylactic) shock in some affected people. This extremely strong reaction rarely occurs, but is then life-threatening. An allergic shock can be seen as the reaction of various body functions to the consumption of peanuts.
This includes a strong contraction of the smallest airways, which leads to pronounced shortness of breath, and the cardiovascular system is also strongly influenced. The combination of symptoms can be fatal within minutes.
Read also: The allergic shock
Does desensitization make sense?
Desensitization is used in many allergies to reduce the allergic reaction to certain substances. In most cases, minimal amounts of the allergen are administered at approximately one-month intervals over months to years. The amount is large enough for the body to respond. At the same time, the amount of the allergen is too small to trigger a strong allergic reaction.
Over time, the dose is increased so that the body gets used to increasing amounts of the allergen. Such desensitization is often particularly difficult in the case of food allergies. Desensitization is therefore not part of the usual therapeutic measures for peanut allergy.
Stages of a peanut allergy
Peanut allergies can be classified on the one hand based on the strength of the reaction and on the other hand based on the amount to which a person reacts. The mildest allergic reactions occur in people who do not have a “real” peanut allergy.
Instead, they are allergic to any of the substances that could cause cross-allergies with peanuts. The allergens (allergy-causing substances) are similar, so that affected people can easily react to peanuts with their antibodies. The symptoms of peanut allergy can take on all forms, from a slight burning sensation in the mouth to an irritated throat to severe shortness of breath with allergic shock.
In addition, there are people who react to even the smallest amounts of peanuts, while others react to raw peanuts, but are not allergic to processed nuts (e.g. roasted peanuts), as the heat can change some allergens. The degree of severity is divided into four levels, but is more geared towards allergic reactions such as hay fever. As it is based on the duration, frequency and severity of the reaction during long-term (pollen) exposure.
Can a peanut allergy be cured?
Anyone who is affected by a peanut allergy retains this allergy their entire life. However, avoiding contact with peanuts can completely prevent an allergic reaction. Symptoms of an allergic reaction to peanuts appear within seconds to minutes after consuming the peanuts and persist for a few hours depending on the severity of the allergy.
In the event of an allergic shock, emergency medication must be administered as soon as possible, otherwise the symptoms last within a few minutes to hours and can lead to death
Can a peanut allergy be fatal?
A peanut allergy can trigger an allergic (including anaphylactic) shock in some affected people. This extremely strong reaction rarely occurs, but is then life-threatening.
An allergic shock can be seen as the reaction of various body functions to the consumption of peanuts. This includes a strong contraction of the smallest airways, which leads to pronounced shortness of breath, and the cardiovascular system is also strongly influenced. The combination of symptoms can be fatal within minutes.















.jpg)