Inflammation of the cervical vertebrae
Synonyms
Spondylodiscitis, infectious spondylodiscitis, spondylitis, osteomyelitis, spondylitis
introduction
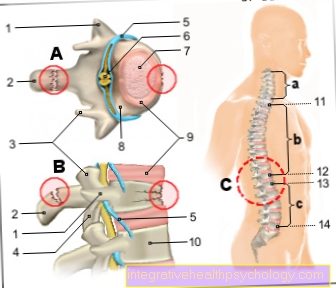
Spondylodiscitis or spondylitis is generally understood to mean the inflammation of the intervertebral disc and the surrounding soft tissues such as the base and cover plates of the spinal segment.
The osteomyelitis of a vertebral body caused by unspecific pathogens is differentiated from inflammation caused by specific pathogens. Specific pathogens include syphilis, tuberculosis, and Bang's disease. The latter is an infection caused by Brucella, which can be ingested by ingesting unpasteurized milk.
causes
An inflammation of the cervical vertebrae can be caused by various bacteria, viruses, fungi but also parasites.
Most infections are caused by Staphylococcus aureus, a gram-positive bacterium found in clusters that is resistant to some antibiotics. Other non-specific germs that can trigger such an infection are Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus viridans, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pneumococci, Clostridium perfringens, Proteus mirabilis.
The specific pathogens are Mycobacterium tuberculosae (Pathogen of Tuberculosis), Mycobacterium leprae (Leprosy pathogen), Brucella bacteria (Causative agent of Brucellosis, Malta fever), Salmonella typhosa (disease of the digestive tract) were counted.
The main representatives of the fungi are Candida albicans and Aspergillus. The pathogens can be carried through the bloodstream from other inflammatory areas in the body. In this case one speaks of a hematogenous spread. Another possibility is infection as a result of minor surgery, which is then referred to as iatrogenic. These can also be further away from the spine, but direct bacterial contamination can also be the cause. Some patients may be more prone to bacterial inflammation in the cervical spine due to an underlying disease. These underlying diseases include alcoholism, diabetes mellitus and long-term use of the immunosuppressive cortisone.
Read more on the topic:
- Brucellosis
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Inflammation of the nerves in the cervical vertebra
Neuritis of the cervical spine is a painful inflammation of a nerve that bundles together from many nerve fibers and then emerges at the level of the cervical spine.
Irritation and pressure from other physical structures, metabolic toxins, multiple sclerosis, insufficient supply and many other reasons can lead to nerve inflammation. Often the cause can be explained by long-term tension and poor posture in the neck area.
The severity of neuritis on the cervical vertebra is different for each patient and ranges from slight paresthesia to functional failures. Most of this discomfort would then show up in the arms or shoulder area. This can be explained by the fact that the nerves that emerge at the cervical vertebrae mainly supply the shoulder and arm region. If a nerve is irritated in its course, the symptoms can show up along its entire extension and lead to problems and pain.
In most cases, the symptoms only last for a few days and go away on their own. If, for example, a chronic malposition is found in the cervical spine and this is not corrected, the inflammation can drag on for a long time.
- Cervical spine syndrome
Inflammation of the joint on the cervical vertebra
In the case of complaints in the cervical spine area, inflammation of the joint from a cervical vertebra can also be the cause.
A typical occurrence of this symptom is attributed to rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation, especially in the area of small joints, such as the cervical joints. Then it is a rare special form of rheumatoid arthritis, which is known as cervical arthritis. Often one of the first symptoms is the sensation of pain in the neck area, which is intensified when turning the head. An early morning pain in the neck, which is considered to be characteristic of this disease, is also particularly noticeable.
A diagnosis of cervical arthritis should be made as early as possible, as the inflammatory processes can also destroy the ligaments of the cervical spine. The ligaments are very important for stabilizing the cervical spine, which is ultimately responsible for protecting the spinal cord. If there is a reduction in stability, this can in the worst case lead to injuries to the spinal cord.
multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system and can manifest itself as pain in the neck area, among other things. In contrast to the inflammation of the cervical vertebrae, however, the nerve tissue is inflamed here.
The differences between the two diseases can easily be determined using diagnostic imaging techniques. However, if the immune system is shut down by drugs during the therapy of multiple sclerosis, this can promote the development of a cervical vertebrae.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease and is characterized by an increase in symptoms as it progresses. One of the goals is to use drugs to stop the triggering processes in the patient's immune system that drive multiple sclerosis. However, this can mean that in other parts of the body where the immune system is necessary, pathogens can no longer be warded off so well and diseases spread that have no chance in the normal population. A typical symptom of multiple sclerosis is Lehrmitt’s sign, which makes the patient feel electrifying sensations from the neck down as they bend their head forward.
Read more on this topic:
- Therapy of multiple sclerosis
- Course of multiple sclerosis
Symptoms
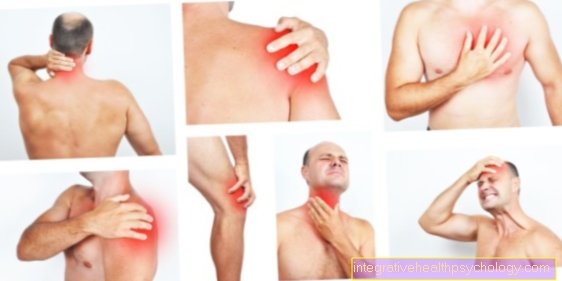
Patients express themselves especially in the acute phase of the inflammation severe back pain to have. They describe this pain as knocking and pulsing, as well as a sense of Jam and pressure in the area of the affected vertebral body segment. Often the pain increases with movement, especially turning and tilting the head leads to load-dependent back pain. You can too radiate into the arms or also to a headache contribute. The surrounding muscles can feel hardened.
If the Inflammation continues and finally that Spinal cord including gelatinous core (Nucleus pulposus) and fiber ring (Annulus fibrosus) attacks, it can also in these more serious cases neurological failures to lead. Destroyed parts of the gelatinous core and the fiber ring can ultimately affect the Spinal nerves to press. The symptoms like Sensory disturbances can occur in the arms but also in the legs, depending on the severity of the damage. The movement of the individual extremities can be restricted to different degrees. Laboratory chemistry shows an increase in the classical Inflammation parameters in blood. These include C-reactive protein, Sedimentation rate (BSG) and the Leukocytes. Come in addition fever, which, depending on the severity of the inflammation, can increase sharply and become recurrent.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the cervical vertebra
After a detailed survey the patient's acute complaints and subsequent clinical examination should be a X-ray can be made to either rule out a suspected diagnosis of spinal inflammation or to confirm the diagnosis. If the inflammation is confirmed, extensive defects in the base and cover plates can be seen in the X-ray image.
Spondylodiscitis can occur much earlier in the Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine or that Skeletal scintigraphy be recognized. These two procedures are significantly more sensitive and the full extent of any deformities and degenerative processes that may be present can be better assessed.
In the case of a bacterial infection, the pathogens can pass through the Creating a blood culture to be determined. The Puncture of inflammationwhich should be performed during a computed or magnetic resonance imaging due to the sensitivity and course of numerous nerves and vessels. The determination of the germs is relevant in order to then initiate therapy with the correct antibiotic.
If an infection caused by tuberculosis pathogens is suspected, the examination of sputum (sputum) of the lung and gastric juice useful.
Conservative therapy
In order to guarantee successful therapy in the case of inflammation in the vertebral area, it is important to immobilize the affected region. The bed rest can be prescribed by the doctor for up to several weeks. A intravenous treatment with antibiotics is especially seizing when it is upfront Resistance of bacteria has been tested.
When infected with tuberculosis pathogens, a combination of 4 different tuberculostatic drugs administered. In addition, any existing secondary diseases such as Hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar levels) or alcoholism be treated. Treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis with antibiotics is usually protracted, as the course of the disease can take several weeks.
Operative therapy
If the adequate therapy with antibiotics is not sufficient to contain the inflammation foci and the defects are also widespread, an operation is indicated.
During an operation, the entire region of the inflammation is cleared out (Dedridement). The spine is thereby relieved and damage to the annoy can be prevented. The spine is then rebuilt and stabilized with replacement materials. Accompanying the operation is a Antibiotic treatment for 6 to 12 weeks necessary for the surgical wound to heal without infection.












.jpg)