Diagnosing a herniated disc
Definition of a herniated disc
At a disc prolapse is it a wear-related disease The spine. For years Incorrect or overloading the gelatinous ring of the intervertebral disc loses its elasticity and can shift as a result.

introduction
Although most people who suffer from persistent back pain assume a herniated disc, everyday clinical practice shows that the disc prolapse is more likely rare cause represents for severe back pain. In many cases, a herniated disc even calls no pain emerged.
People who develop a herniated disc as a result of long-term improper or excessive strain may notice it Sensory disturbances such as numbness or tingling and an increasing Muscle weakness. In addition, it can also lead to the emergence of Pain come in the affected spinal segment.
People who observe such symptoms should urgently consult a specialist immediately. If there is a herniated disc, the symptoms can only be alleviated after a detailed diagnosis and the initiation of suitable treatment measures.
You can find more information about the Symptoms of a herniated disc
diagnosis
Diagnosing a suspected herniated disc usually involves several steps. Above all, the detailed doctor-patient discussion (in short: anamnesis) can help to sort out the complaints of the person concerned and to make an initial suspected diagnosis. During this interview, the patient concerned should describe the symptoms as precisely as possible.
When diagnosing a herniated disc, pain in one or more spinal column segments plays a decisive role. Depending on the severity of the herniated disc, this pain can also radiate into the arms, buttocks or legs. In addition, in the course of the herniated disc, nerve root compression can lead to sensory disturbances (for example, numbness or tingling) come. In the advanced stage, many of the affected patients also have limitations in muscle strength (Muscle weakness) on. Depending on the exact location of the herniated disc, the symptoms of coughing or sneezing can worsen.
The doctor-patient conversation in the course of the diagnosis of a herniated disc also includes questions about urinary and stool behavior. The reason for this is the fact that a deep herniated disc may lead to urination disorders (so-called urinary incontinence) or bowel movements (so-called fecal incontinence) can come. These complaints are often associated with pronounced sensory disturbances in the anus and / or genitals. In addition, there may be restrictions in sensitivity on the inside of the thighs.
Appointment with a specialist for a herniated disc?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
A herniated disc is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
Therefore, treating a herniated disc requires a lot of experience.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Following the doctor-patient conversation, there is an orientation physical examination instead of. In this investigation, the Muscle strength, sensitivity and Reflexes checked. In addition, if a deep disc herniation is suspected, the diagnosis includes various exercises that check the functionality of the key muscles of the most important spinal column segments. In patients who have no problems walk on your toes and heels paralysis of the relevant muscles can be specifically excluded with the help of this simple diagnostic method.
If the suspicion of a herniated disc is confirmed during the physical exam, the diagnosis must continue. Especially imaging procedures, which are suitable for mapping the spine including the intervertebral discs, play a crucial role in the diagnosis of a herniated disc.
Making more ordinary X-rays is of little help in diagnosing a herniated disc. For this reason, a Computed Tomography (CT) or one Magnetic resonance imaging of the herniated disc (MRI). Due to the better representation of the intervertebral discs, magnetic resonance tomography is the imaging method of first choice in the diagnosis of a herniated disc.
Since an advanced herniated disc can often lead to impairment of sensitivity and / or muscle strength, the diagnostic measures should be expanded in patients with the corresponding symptoms. Especially the so-called Electromyography (EMG) and the Electroneurography (CLOSELY) can help to determine whether sensory disorders and symptoms of paralysis are associated with a herniated disc.
With the help of electromyography, the attending physician can measure whether individual Muscles are electrically excited via the associated nerve fibers. Electronurography can, if necessary, determine which Nerve root is affected by the herniated disc.
In the course of diagnosing a herniated disc, this information is particularly useful in choosing the most suitable one Treatment strategy crucial. In addition, different Infectious diseasesthat can cause symptoms similar to a herniated disc can be excluded.
You can find more information on our page "How can you recognize a herniated disc?'
Diagnosis with MRI
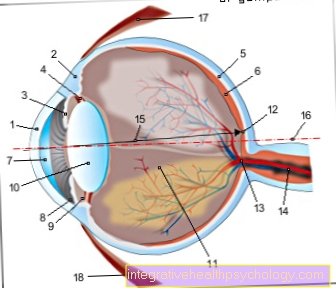
The MRI is used when a herniated disc is suspected Diagnostic assurance, it's the drug of choice for imaging in herniated discs. The MRI is particularly suitable for Tissue structures, annoy and the Band washers to represent yourself.
Images of the various segments of the spine are taken to assess which portion is affected.
It is advantageous that the patient has an MRI none Radiation exposure is exposed. A disadvantage, however, is that the production of an MRI takes a long time and is complete in this time lie still got to. However, the herniated disc cannot be diagnosed with certainty without an MRI, which is why an MRI should always be performed if it is suspected.
Further information can be found on our website MRI for a herniated disc
Diagnosis without an MRI
In general, it should be assumed that computed or magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose a herniated disc is only useful if the results of the preliminary physical examination match the initial one Suspected diagnosis hardening. In patients with pronounced loss of sensitivity and / or limitations in muscle strength, the diagnosis not without an MRI be asked. The reason for this is the fact that without an MRI neither the exact location, nor the Expression of the herniated disc can be determined. In addition, a Operation indication cannot be made properly when diagnosed without an MRI.
Diagnosis by X-ray
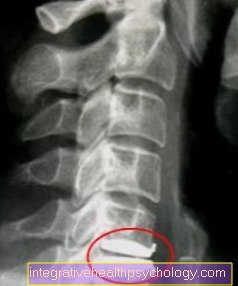
Conventional X-rays are considered to be in the diagnosis of a herniated disc unsuitable imaging procedure. The X-ray in several planes allows the bony structures the spine can be adequately represented, but an assessment of tissue structures or nerve fibers is not possible.
Because of this, the diagnosis of a herniated disc must be made abnormal physical examination performing a Computed Tomography (short: CT) or one Magnetic resonance imaging (in short: MRI) include. In general, magnetic resonance imaging is the first choice in diagnosing a herniated disc. Only at questionable findings, which are determined in the course of the doctor-patient conversation and / or the physical examination, the X-ray can be useful.
For people who, for example immediately after trauma complain of severe back pain Fractions the bony spinal structures can be excluded by the X-ray.
Diagnostic tests
Various tests can be done to diagnose a herniated disc. The classic test to confirm the diagnosis "disc prolapse“Should enable statements to be made regarding sensitivity, reflexes and muscle strength. Already during a detailed doctor-patient discussion, the symptoms described should be used to define which vertebral segment a possible herniated disc could affect.
Based on this information, an appropriate test should then be performed during the physical exam. To rule out possible sensory disorders, the attending physician must coat both sides of the body at the same time. If the affected patient perceives different sensations on both halves of the body, the test is considered positive. Then the muscle strength of the extremities must be checked in side-by-side comparison. During this test, the doctor applies pressure to the extremities and asks the patient, for example, to raise their legs against the pressure. When diagnosing "advanced herniated disc“There would be a page difference in this test.
In addition, the classic characteristic muscles of certain spinal column segments can be tested with the help of the so-called toe and heel gait. Muscle paralysis can be ruled out in a patient who can easily walk on toes and heels. If one of these tests confirms the suspicion of a herniated disc, the diagnosis may need to be supplemented by imaging tests.
The Lasègue test is also pioneering: the patient lies stretched out on his back and the doctor begins to slowly bend the extended leg in the hip joint. If the test can no longer be continued from about 70-80 ° flexion due to severe shooting pain in the leg, it is considered positive.
Further information can be found on our website Functional test for a herniated disc
Diagnosis of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine
People who suspect one Herniated disc of the lumbar spine (Lumbar spine) should consult a specialist as soon as possible. Complications can only be avoided through a detailed diagnosis and the introduction of suitable treatment measures. In the case of a deep herniated disc in the lumbar spine, damage to the nerve roots can lead to the development of a Urinary and / or fecal incontinence come.
Even if there is a suspicion of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine, the actual diagnosis begins with a detailed anamnesis. People who suffer from a herniated disc of the lumbar spine typically describe Sensory disturbances (Numbness and / or tingling sensation) in the area of the Buttocks and the Thigh and lower leg. The exact extent of these sensory disorders can provide an initial indication of the segment of the spine in which the herniated disc is present.
In addition, the Muscle strength in the legs be significantly restricted in the case of an advanced herniated disc of the lumbar spine. The ability to walk on your heels and tiptoe is also an important criterion in the diagnosis of a herniated disc of the lumbar spine. Affected people may no longer be able to do this without any problems due to their limited muscle strength.
If the suspicion of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine is confirmed, the diagnosis should include imaging procedures (for example a magnetic resonance tomography) are backed up.
Further information can be found on our page about the Herniated disc of the lumbar spine
Diagnosis of a herniated disc in the cervical spine
Diagnosing one Herniated disc of the cervical spine (Cervical spine) consists of several steps. Even during the extensive doctor-patient conversation (anamnese) the complaints described by the person concerned can justify an initial suspected diagnosis.
People who have a herniated disc in the area of the cervical spine often suffer from Sensory disorders in the arms. In the case of an advanced herniated disc of the cervical spine, which is accompanied by significant compression of the nerve root, muscle strength can also be limited.
To diagnose "Herniated disc of the cervical spine“To be able to secure, the doctor-patient conversation has to be orientated physical examination connected. The specialist checks the sensitivity by brushing both arms side by side. At a Side difference the sensation perception can be assumed to be a herniated disc. In addition, the diagnosis includes the examination of the vertebral segment-specific Reflexes and the Muscle strength. Imaging should be initiated if the suspected diagnosis is confirmed during the physical exam.
Which doctor can diagnose a herniated disc?
A herniated disc is usually a case for an orthopedic surgeon. This specializes in all diseases of the musculoskeletal system and looks at the herniated disc primarily from the clinical side. During the physical examination, he can do special tests that provide clues about the herniated disc. The orthopedic surgeon can therefore diagnose a suspected herniated disc. However, the final proof is usually an MRI, which shows the herniated disc visually.