Fever after an operation
What is a fever after an operation?
Fever after an operation, also called postoperative fever, is an increase in body temperature above 38 ° C between the day of the operation and the tenth postoperative day.
A slight increase in temperature of 38 - 38.5 ° C in the first three days after the operation is harmless and is based on the so-called post-aggressive metabolism. Post-aggression metabolism occurs in the body as a result of tissue damage.Surgery is often associated with tissue damage and fluid loss.
It releases hormones that cause clinical symptoms such as fever, increased breathing and heartbeat or tiredness. After a major trauma, such as extensive surgery, a fever can occur for one to two days.
If, on the other hand, the body temperature increases significantly in the days after the operation, clarification is required. A fever can indicate an infection.
The cause can be, for example, a wound infection or a urinary tract infection.

Possible causes of the fever
- IV cannula infection
- Urinary tract infection
- Wound infection
- Respiratory infection
- pneumonia
- Blood poisoning (sepsis)
- Thrombosis / pulmonary embolism
- Cholecystitis
- Colitis
- Intra-abdominal abscess
- Anastomotic leakage
Wound infection
Postoperative fever can be a sign of wound infection. By an infected wound, I mean the entry of microorganisms such as bacteria into the wound. Most often it is bacteria that can colonize the wound.
Viruses, fungi or parasites rarely cause wound infection. The germs cause inflammation in the wound. An infected wound needs to be opened and cleaned.
Thrombosis / pulmonary embolism
A thrombosis forms a blood clot (thrombus) in a blood vessel or in the heart. Thromboses often develop in the deep veins of the legs. Thrombosis is dangerous because the blood clot can break loose and be transported to other organs.
Mild fever is a common symptom of deep vein thrombosis.
An embolism occurs when a blood clot is washed away with the blood and reaches distant vessel sections. A pulmonary embolism occurs when a vessel in the lungs becomes blocked. Extensive operations, broken bones and interventions such as a total hip replacement (hip joint endoprosthesis) have an increased risk of developing a pulmonary embolism.
Please also read the article: How can you recognize a thrombosis?
How long does a fever last after an operation?
The duration of a fever after an operation depends on the cause of the fever and the fever therapy.
- Post-operative fever for a day or two often occurs after trauma.
- So-called "drug fever" caused by allergic reactions to medication such as cytostatics or antibiotics can last for up to eight days.
- In the case of thromboembolism, fever usually only occurs about four days after the operation and lasts until the tenth postoperative day.
In addition to the non-infectious causes mentioned for postoperative fever, there are also infectious reasons.
- In the context of aspiration pneumonia, for example, those affected often suffer from fever for the first two postoperative days.
- In infections such as a urinary tract infection, pneumonia or abscess, the fever usually lasts from the third to eighth day after the operation.
- In the case of a wound infection, those affected suffer from postoperative fever on average from the fifth to tenth day.
In general, the duration of the fever can provide clues as to the underlying cause. Read more about the duration of a fever on the following page: How long does a fever last?
Also read more on the topic: When should I see a doctor with a fever?
Can a fever be normal after an operation?
One to two days after an operation, a mild fever of up to 38.5 ° C is usually harmless.
The body increases its temperature in order to adapt to changes inside. Fever arises due to an increase in the set point of body temperature in the hypothalamus in the brain. Surgery can be traumatic and stressful for the body.
If the body temperature rises above 38 ° C, this is not normal and requires medical clarification.
Fever after a wisdom tooth operation
If a wisdom tooth to be removed lies completely in the bone and possibly also transversely, an osteotomy is surgically necessary. If soft tissue complications such as bruising or tearing of the skin and gums occur during the operation, the injuries are more pronounced.
Even if a wisdom tooth operation is a small operation area, the operation and possibly complications of the procedure can manipulate the tissue.
Deep-seated wisdom teeth can leave a wound that is disinfected during surgery.
Nevertheless, the wound can become infected and cause symptoms such as chills and fever. Elevated temperatures above 38.5 ° C after a wisdom tooth operation indicate an infection.
Anti-inflammatory treatment is necessary in the event of a fever to prevent the infection from spreading.
Please also read the article: Inflammation after a wisdom tooth op
Fever after an almond operation
The tonsil operation is one of the most common operations in the ear, nose and throat area, after which a fever often develops.
If the fever lasts longer than a day, a medical examination is necessary and, if necessary, antibiotic therapy.
Fever after an appendix operation
Appendectomy operations are carried out routinely throughout Germany. Even if it is a frequently performed operation, it is still an operation in the abdominal cavity.
A slightly elevated temperature is most likely harmless one to two days after the operation.
If temperatures are above 38.5 ° C, the fever needs to be clarified.
An infection in the surgical area can be responsible for the fever and needs treatment.
If a urinary catheter is also in place, there may also be a urinary tract infection and the fever.
Fever after joint surgery (hip replacement, knee replacement)
Knee or hip TEP operations (TEP = total endoprosthesis) are particularly common among joint ops.
As part of a joint TEP operation, a joint, for example the knee or hip joint, is replaced by an artificial joint.
Depending on the surgical technique, complications and general health of the patient, the extent of such an operation can vary. Joint operations are major interventions and are often associated with gross mechanical violence.
An increase in temperature is usually harmless on the first and second day after such a trauma.
If the fever lasts longer, there may be another cause, such as a wound infection, a urinary tract infection due to a urinary catheter infection, pneumonia or the like. If you have a high fever over a longer period of time, you must be checked by a doctor.
Please also read the article: Complication of hip replacement surgery
Fever after biliary surgery
An infection rarely occurs as part of an operation on the gallbladder.
In this case, a fever can indicate an infection from the biliary surgery.
Fever after prostate surgery
Prostate surgery is a common procedure for prostate cancer. A radical prostate operation is often performed, in which structures adjacent to the prostate such as the seminal vesicles and pelvic lymph nodes are removed.
This can damage neighboring organs and vessels. Like any operation, there is also a risk of wound infection with prostate surgery. Postoperative fever can be a sign of a wound infection in the surgical site.
One to two days of increased temperature is usually harmless after an operation on the prostate.
Severe fever that lasts for several days requires a thorough investigation of the cause and, if necessary, therapy.
treatment
Treatment of fever after an operation involves eliminating the cause first.
This can be, for example, the removal of an indwelling venous catheter or a surgical revision.
If possible, an antibiogram should be performed and a corresponding antibiogram performed.
In addition, there is the treatment of symptomatic measures. Antipyretic drugs like acetaminophen are often used to reduce the fever.
Please also read the article: How can you lower a fever?
Home remedies
There are some home remedies for a fever. However, drug treatment is necessary for bacterial infections.
- Apple cider vinegar is a tried and tested means for internal and external use. The acid contained in apple cider vinegar is said to promote the release of heat through the skin.
Apple cider vinegar can be put in bath water or mixed with water in cooling compresses on the skin of the forehead, stomach and feet.
To cool down internally, add two tablespoons of apple cider vinegar and, if necessary, honey to a glass of water. - Basil is also said to have an antipyretic effect. To do this, you put a few leaves of the plant in boiling water, let it boil down and drink the brew throughout the day.
- Honey, garlic, ginger, raspberries and cranberries are also said to be anti-inflammatory and antipyretic.
- Rest is also important. Bed rest is one of the best home remedies for a fever and is mostly necessary.
- You should also drink a lot. When the body temperature rises, teas such as chamomile, rose hips, linden blossom, thyme, lemongrass and many more are suitable.
- A simple home remedy are leg wraps. To do this, you moisten cloths with water that is about 5 ° colder than you and wrap the cloths around your feet and calves. This is why you wrap dry towels and take them off when the wrap has warmed up to body temperature. The process can be repeated for about 30 minutes.
Please also read the article: Home remedies for a fever
homeopathy
There are several homeopathic remedies that are believed to help lower the fever from within.
These include, for example, globules with Ferrum phosphoricum, Atropa belladonna, Aconitum napellus, Gelsemium and Eupatorium perfoliatum.
The globules are effective in different forms of fever and differ in their homeopathic potency and dosage. In order to filter out the individually most effective product, you should discuss the selection with an alternative practitioner or general practitioner with homeopathic training.
If the fever remains high after two days, if other symptoms such as pain, constipation, vomiting or bleeding occur, you should consult a doctor at the latest.
Care should also be taken with infants or children who are prone to febrile seizures and with pregnancy.
Please also read the article: Homeopathy for fever
Diagnosing the underlying cause
In order to find out the cause of a fever after an operation, a detailed medical history is necessary. In this conversation, questions will be clarified, such as whether there were major blood transfusions during the operation.
Blood and urine samples are other important diagnostic tools.
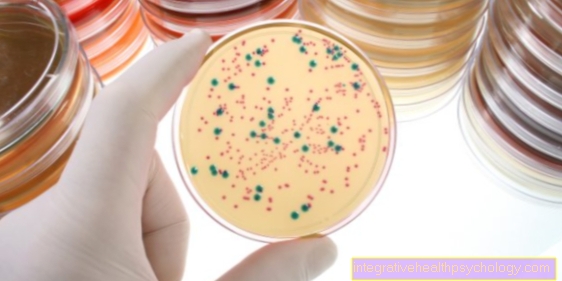
For example, inflammation parameters and blood cultures can reveal bacterial infections.
Depending on the procedure, imaging techniques can be used. An ultrasound examination is painless and can be carried out quickly.
For example, an abscess caused by an operation can be shown well.
If pneumonia is suspected, a chest x-ray can confirm the suspicion.
If an anastomotic leak (leaky connections between anatomical structures) is suspected, a CT (computer tomogram) is useful.
The last resort is a renewed surgical opening of the operating area, the so-called surgical exploration.
Blood count
Taking a blood sample is an important method to clarify the cause of postoperative fever. The inflammation markers CRP (C-reactive protein), ESR (sedimentation rate) and leukocytes are determined.
The blood count can show a bacterial or viral infection. Other possible causes such as thrombosis or blood poisoning can also be identified in this way.
Ultrasonic
An ultrasound examination is painless and can be used in many ways.
For example, you can scan the abdomen to check after the operation whether that is the cause of the fever. The ultrasound device can show increased water retention and air. '
It is a good diagnostic tool that works without radiation and is therefore neither harmful nor painful for the patient.
MRI
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging technique that can examine different parts of the body, joints and organs.
This can also be used to depict organs that lie in the depths.
The MRI machine works with radio wave pulses. This means that no dangerous rays like X-ray or CT are used. Magnetic resonance imaging is a very good, safe examination method to look for the cause of a fever if the operating area is larger or deeper in the body.
Please also read the articles: Procedure for an MRI, MRI for claustrophobia - What are the options?
Fever despite antibiotics
If you suffer from a fever despite taking an antibiotic, there are various possible causes. Basically, antibiotics only work against bacteria. For example, if there is a wound infection after an operation, antibiotics can only take effect if bacteria are actually responsible for them.
In most cases it is bacteria that infect wounds, but pathogens such as viruses or parasites are rarely found.
If there is a bacterial infection after the operation, for example a wound infection, and the antibiotic does not work, it may be the wrong antibiotic. Not all bacteria respond to the same antibiotics. That is why there are different antibiotics that work against different bacteria.
In addition, bacteria can become resistant to certain antibiotics if they are used frequently. In order to choose the right antibiotic for a fever, an antibiogram should be performed before therapy. This is a laboratory test used to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics.
Read more on the subject at: Fever despite antibiotics - what to do?
Recommendations from the editorial team:
- Febrile convulsion - what is it?
- Fix body aches
- How to treat fever correctly
- Chills - What To Do?
- Calf wrap against fever