Cure thyroid cancer
introduction

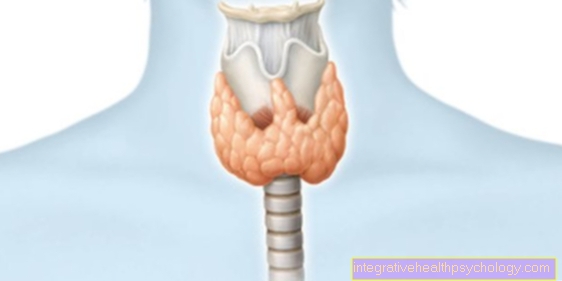
Thyroid cancer can as belt-like and vicious tumor occur. Women are more often more affected by thyroid cancer than men. The disease occurs mainly between the 30 and 60 years of age on, however, is one rather rare Cancer.
The Thyroid cancer therapy depends on the aggressiveness of the cancer and initially includes one surgery. Then a Radiation or radio-iodine therapy be necessary. A chemotherapy has played a subordinate role in the therapy of thyroid cancer until now.
surgery
The goal of surgical removal of the thyroid is that remove cancerous tissues. Depending on the type of thyroid cancer, the operation is more or less extensive. How far advanced the cancer is is also important for the operation. Therefore it can happen that just a rag The thyroid gland needs to be removed if it is a very little cancer acts. With the suspicion that the whole thyroid and / or the adjacent Lymph nodes Are affected or have a greater spread, the thyroid must completely and together with the adjacent lymph nodes (neck area, upper chest) away become.
In rare Cases are the neighboring organs (esophagus, windpipe, Blood vessels) and must be partly removed. It is extreme important for the cure of thyroid cancer remove all tumor cells.
In connection Therefore, additional treatment options, such as a Radioiodine therapy or one Irradiationto be important for the healing of thyroid cancer. The surgery entails that the body no thyroid hormones more can produce itself. So this must be Hormones lifelong over Tablets be taken and the concentrations of the hormones are regularly im blood checked.
Radioiodine therapy
To cure thyroid cancer from remaining tissue and eventual Metastases one uses the treatment with radioactive iodine and makes use of the ability of the thyroid gland, metastases and cancerous tissue Absorb and store iodine.
The radioactive iodine gets through the remaining thyroid tissue absorbed and destroyed then the cancer cells without affecting the other tissues in the body. Radioiodine therapy does not make sense for cancers (medullary, undifferentiated) that do not store iodine. Otherwise the first radioiodine therapy can be used a few weeks after the operation to be started.First, the smallest remnants of the thyroid are destroyed, then the radioactive iodine accumulates in the metastases.
Important is that with radioiodine therapy no other thyroid hormones are substituted, because this would reduce the absorption of radioactive iodine.
Please also read: Metastases in thyroid cancer; Radioiodine therapy
Irradiation
The radiotherapy becomes following the operation or radioiodine therapy performed. The goal is irradiation is that Destruction of remaining tumor cells or the smallest metastases in the tumor region.
Most often the irradiation only for healing used when the tumor has not been completely removed in the previous treatment steps. The radiation also makes that Metastasis growth inhibited. Irradiation has developed significantly in recent years and can now be planned and carried out very precisely using advanced technology and computer programs, which means that the Radiation dose on smallest level and sequelae in other organs have become less frequent.
chemotherapy
So far it plays chemotherapy in thyroid cancer one rather subordinate role. Only the very aggressive and undifferentiated types of thyroid cancer respond to chemotherapy to a certain extent.
Subject of current research is development new drugsthat are based on the signal pathways changed by the cancer. These new active ingredients are the bright spots of hope for cancers that have not yet been cured by standard procedures. Previous studies show one Improvement related to healing of thyroid cancer. Chemotherapy is mainly used if the operation no longer promises a cure and radioiodine therapy is not possible.
Metastases
Initially, the tumor is limited to the thyroid gland. With further growth the tumor breaks through however the Connective tissue capsulethat surrounds the thyroid gland and may affect the adjacent tissue, lymph nodes, annoy, Vessels and other organs are affected.
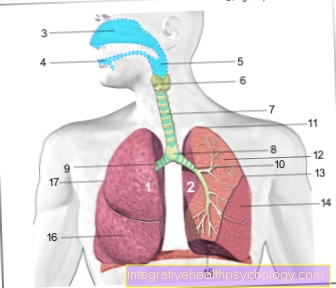
Via the blood and lymphatic systems can they Cancer cells spread throughout the body and also affect other, more distant organs. There then so-called Metastases (Daughter tumors). The most common places for metastases in thyroid cancer are those Lymph nodes in the neck, lungs, liver, brain, and bones.
The Chances of recovery in advanced Thyroid cancer with Distant metastases are bad. In most cases a complete cure is impossible. In rare cases, patients live on for several years despite thyroid cancer and metastases. It can be tried the Surgically remove metastasesto cure the disease. This is often the only option since thyroid cancer little sensitive to chemotherapy is. For most types of cancer, life expectancy is still good, even with metastases. However, metastases from other malignant tumors, such as Skin cancer, Breast cancer or Lung cancer occur.
Life expectancy
Life expectancy after thyroid cancer is generally speaking varies well, however depending on the type of cancer. At the particularly common papillary thyroid cancer life expectancy is best: 85-95% of those affected will survive the next 10 years.
A bit lower is the Life expectancy in which medullary thyroid cancerwhich is much rarer than papillary thyroid cancer. If this cancer no metastases yet has trained lies the Chances of recovery are over 90 percent. Long term seen the chance of survival is between 50 and 60 percent.
A Low life expectancy solves that undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma in which numerous other organs are already affected with metastases at an early stage. Most of the time it is cure this type of cancer hopeless and the person concerned becomes one palliative therapy that tries to enable those affected to lead a symptom-free life. In summary, life expectancy depends on the type of thyroid cancer and the age of the person affected.
The most of those affected however suffer from well curable species of thyroid cancer and have one after consistent therapy and good follow-up care almost normal life expectancy. Thanks to drug-based hormone replacement therapy, even well-adjusted patients do not experience any problems due to a deficiency or excess of hormones.