Heart failure
Synonyms in a broader sense
Medical: Heart failure
Heart failure, heart pumping weakness, right heart weakness, left heart weakness
English:
definition
The Heart failure also as Heart failure designated, represents the inability of the heart to adequately oxygenate the organs of the body.
Depending on the cause, a distinction is made between systolic and diastolic heart failure / cardiac insufficiency, as well as some special forms (e.g. "High Output Failure"), see section "Causes".
Anatomically, the insufficient performance of the entire heart ("Global Heart Failure") Differ from the predominant reduction in performance of one of the two heart chambers ("Right heart failure" and "Left heart failure“).

Frequency (epidemiology)
Occurrence of Heart failure in the population. The proportion of sick people (medically: Prevalence) is highest in the older population group: in the age group from 66 to 75 years, an estimated 4-5% suffer from heart failure, while the proportion is around 1% among 25 to 35 year olds.
According to estimates, around 1.2 million people in Germany are affected. Newly ill (medical: Incidence) mostly older people with heart failure / heart failure, i.e. younger people are less likely to be affected. Due to the changing age structure of our society, the frequency of heart failure has increased dramatically over the past 20 years. Men get sick more than twice as often as women.
The severity of the heart failure / heart failure is divided into four stages, which according to the classification by the New York Heart A.ssociation (short NYHA) short as NYHA 1-4 are designated.
This classification is based on the occurrence of symptoms and the physical resilience of the patient:
While in NYHA 1, for example, physical performance is not (yet) restricted and changes compared to healthy people are only detectable under stress with extensive technical diagnostics, in NYHA 3 there is a strong restriction in physical performance in the absence of complaints at rest.
With heart failure / cardiac insufficiency in stage NYHA 4, the affected patients are bedridden and severely restricted both under stress and at rest.
The NYHA 3 and 4 stages of heart failure represent a very serious disease that not only significantly restricts the quality of life, but also has a life expectancy that is roughly comparable to that of cancer.
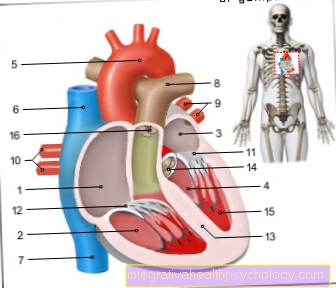
- Right atrial -
Atrium dextrum - Right ventricle -
Ventriculus dexter - Left atrium -
Atrium sinistrum - Left ventricle -
Ventriculus sinister - Aortic arch - Arcus aortae
- Superior vena cava -
Superior vena cava - Lower vena cava -
Inferior vena cava - Pulmonary artery trunk -
Pulmonary trunk - Left pulmonary veins -
Venae pulmonales sinastrae - Right pulmonary veins -
Venae pulmonales dextrae - Mitral valve - Valva mitralis
- Tricuspid valve -
Tricuspid valva - Chamber partition -
Interventricular septum - Aortic valve - Valva aortae
- Papillary muscle -
Papillary muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Causes and origins
The most common causes of heart failure / heart failure are:
- increased blood pressure (arterial hyperonia)
- and atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries called coronary heart disease, or CHD for short.
Read more on the topic: Symptoms of a heart attack
However, there are also a number of other reasons, which can primarily originate from the heart, such as a preceding inflammation of the heart muscle, usually caused by viruses (medical: myocarditis).
But completely different diseases can also be the trigger:
- Medicines or metabolic / toxins damage the heart when taking cytostatic drugs (tumor drugs)
- excessive use of alcohol or cocaine
- Diabetes mellitus (diabetes)
- or renal insufficiency (kidney failure)
lead to a clinical picture called "metabolic-toxic cardiomyopathy" (from Latin cardiomyopathy = suffering of the heart muscle).
In addition, tumors of the adrenal medulla (these are called pheochromocytoma) as well as an over- / or underactive thyroid can contribute to the development of an "endocrine cardiomyopathy" that promotes the development of heart failure.
In the case of the special form of cardiac insufficiency / cardiac insufficiency, known as "high output failure", in contrast to the classic forms, there is not a reduction in cardiac output, but an excessive need for oxygen that is not met by the heart can be.
This is e.g. This is the case with severe anemia (anemia), in which there is not enough blood available for the transport of oxygen and the heart tries to compensate for this by increasing the pumping capacity. Another cause of a "high output failure" is the overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), in which the organs need more oxygen due to the increased metabolic performance.
Classification of heart failure
Is there a Disruption of the filling the ventricles with blood, which e.g. after inflammation of the Heart sac (medical: pericarditis) can be the case, it is a diastolic heart failure (heart failure).
But is that Expectoration of blood a filled heart chamber caused by a contraction disorder of the heart, one speaks of a systolic heart failure.
Complaints / symptoms
The main symptoms of heart failure are:
- Shortness of breath (medical: dyspnea) and
- Edema, the accumulation of fluid in the tissue
Symptoms of heart failure
Symptoms of permanent and chronic heart failure usually develop gradually over the course of the disease.
In contrast, if the heart is weak, the symptoms set in suddenly and with great intensity. The symptoms can also differ depending on whether the left or right half of the heart or even the entire heart are affected.
When the disease affects our left side of the heart, too little blood is pumped into the body's circulation so that organs are insufficiently supplied. Due to the weak heart, there is sometimes a backlog of blood up to the pulmonary vessels. As a result, those affected are less productive and persistent. Many patients complain of dizziness or “black-before-eyes”. Nocturnal shortness of breath, which worsens particularly when lying down, is also typical.
In many cases, this is accompanied by a strong cough. In the event of a sudden cardiac insufficiency with an emphasis on the left, water in the lungs can occur within a short time - pulmonary edema. Severe shortness of breath and “seething” breathing noises are the consequence.
Read about more
- Causes of water in the lungs
- Why does a cough occur when the heart is weak?
In rather rare cases, only the right half of the heart is affected. The oxygen-poor blood that flows back to the heart from the periphery of our body is not pumped to the lungs effectively enough. Due to the massive backwater, blood collects mainly in the neck veins, which are clearly visible to the naked eye.
Depending on the severity and position, increased water retention (Edema) in the area of the ankles, lower legs, thighs or abdomen.
Water retention in the lungs (Pulmonary edema) or in the abdomen ("Ascites“, Ascites) can cause life-threatening conditions in the worst case. Ultimately, the body can store so much water that those affected gain a disproportionate amount of weight in a short time. Since venous blood can back up into the liver or stomach, symptoms such as pressure-sensitive congestive liver are not uncommon. With advanced, right-wing heart failure, those affected often lose their appetite.
Heart failure in the left half of the heart often leads to a so-called “global” heart failure. In addition to the symptoms described, patients suffer from frequent urination at night (Nocturia), faster heart rate or cold sweaty skin.
For the purpose of better comparability, doctors classify the severity of the heart failure in the internationally valid "NYHA classification":
- Stage I: normal physical resilience without symptoms
- Stage II: complaints only with greater stress
- Stage III: complaints even with light exertion
- Stage IV: complaints even at rest
Also read the article on the topic: Heart failure and high blood pressure
Edema as a symptom of heart failure
The second leading symptom of the Heart failure performing Edema are the result of a build-up of blood in the Body circulation:
The blood collects in the right heart, which is no longer working adequately, whose chamber and atrium expand (medical: dilate).
The blood then backs up into the upstream, supplying, Veins and organs. Due to the increased pressure in the vessels of the venous system, fluid is pressed from the blood through the vessel walls into the tissue, comparable to a filter. This manifests itself, for example, with swollen feet.
It should be noted that the exchange of substances between vessels and tissue is generally natural and physiological balance The performing process is the driving force of which is solely the pressure in the vessels and the water-attracting proteins in the tissue (medical: colloid osmotic pressure) represent.
However, the flow of liquid is not always directed from the vessels into the tissue; If the pressure in the vessels is low, but on the other hand the tissue pressure and the protein content in the vessels are high, the reverse phenomenon occurs:
Fluid is taken up by the tissue back into the blood vessels (medical: reabsorbed). Therefore, in the arterial high pressure system of the body, the filtration with the escape of liquid predominates in healthy people, but that no edema as a result, since it is fed back into the body's circulation by the low-pressure venous system.
In the balance sheet, 20 liters of the squeezed tissue fluid are directly recovered; the remaining two liters of the filtrate, which measures an average of 22 liters, reach the so-called. Milk breast duct of the lymphatic system (medical: Thoracic duct) as lymph / Lymph fluid back into the venous system.
This is only with the sick balance Disturbed between leakage and re-absorption (medical: between filtration and reabsorption). In heart failure, the pressure in the venous vessels is the cause of the increased filtration. In the case of damage to the liver - as an example frequently found in western latitudes - the alcoholic one is here Cirrhosis of the liver called - which also typically leads to edema, has a different cause: The increased fluid outflow is caused by the reduced protein content of the blood (medical: colloid osmotic pressure, see above). For fluid accumulation that appears as edema, especially in the dependent body parts such as It occurs in both the damage of the feet liver (Liver cirrhrosis) as well as heart failure (heart failure) when the ability (the so-called capacity) of the lymphatic system, which occurs almost everywhere in the body, is exceeded.
Another consequence of the increased pressure in the venous vessels due to the pumping weakness of the right heart is the backflow of blood stomach, Intestines and liver. This also explains why people with heart failure suffer from symptoms like Loss of appetite, Constipation (constipation) and a feeling of fullness occur, which are not primarily caused by the heart Let the caused (medical: cardiac) cause think.
Severe swelling of the liver caused by congestion (hepatomegaly) can cause pain under the right costal arch and in this case is referred to as "cirrhosis cardiaque" (French).
Frequent, especially nocturnal urination, which is medically called "paroxysmal nocturia", can often be the first indication of a pumping weakness of the heart.
The nocturnal urge to urinate can be explained by the increased reabsorption of fluid, which takes place at night in a lying position, as less fluid is then pressed into the tissue (the pressure of gravity on the vessels in a standing position is eliminated).
Next heart, lung, Gastrointestinal tract and kidney can do that too brain be affected by overstraining the heart: In severe cases, the lack of oxygen leads to symptoms such as
- confusion
- Hallucinations and
- Disorientation
which can range up to delirium. Typical of these so-called cerebral (Latin cerebrum = brain) symptoms is also the as Cheyne Stokes breathing known breathing pattern, for which the constant alternation of increasing and decreasing breathing depth and breathing frequency is characteristic. You can also find more on this topic at: Edema
Diagnosis of heart failure
The most important cornerstone is the detailed questioning of the patient (anamnese). In particular, previous illnesses, such as Heart attacks, the exact course of the symptoms or currently taking drugs are of great importance. In this way, patients who are already using dehydrating drugs ("Water tablets") Take, still be symptom-free even though the heart is already very weak.
This is followed by the physical exam. The doctor pays attention to possible heart murmurs during auscultation ("Wiretapping“), Water retention and congestion of the neck veins.
Certain laboratory values, such as BNP or ANP, may be found in your blood. Every heart failure diagnosis also includes an EKG and a heart ultrasound examination (echocardiography).
During this painless examination, doctors can use ultrasound waves to assess your heart function in three dimensions and in real time. For further clarification, an X-ray of the chest area is also recommended (thorax). In this way, heart size, potential accumulation of fluid in the lungs or congestion of the blood vessels can be assessed. If you have special questions, slice images (MRI, CT), cardiac catheter examinations or biopsies can also be used.
Read more on the topic: Heart MRI, these tests are done when the heart is weak
EKG for heart failure
In the Heart failure diagnostics plays that EKG an important role. The examination can sometimes provide valuable information about possible causes of the disease. These include:
- Previous heart attacks
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Coronary heart disease (CHD)
- Myocardititis
In the course of the heart failure, there is a gradual increase in size of the affected half of the heart, which can be recognized as excessive stress in the EKG. On the basis of e.g. Different types of position, typical signs of enlargement of the heart (signs of hypertrophy) or disorders of the regression of excitation, doctors can draw conclusions about the following pathological phenomena:
- Chronic right heart strain
- Acute right heart strain
- Chronic left heart strain
In addition to the resting ECG, a stress ECG can also provide information about the condition of our heart.
Heart failure in old age
Heart failure is a typical ailment of old age. It is estimated that around 10% of 75 year olds are affected by the disease.
But why is that? Many diseases of our cardiovascular system lead to cardiac insufficiency. Arterial high blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmias and coronary heart diseases are extremely common, especially in the last stages of life.
Often, older people initially do not attribute their symptoms directly to the weak heart, but to other diseases. Only at e.g. increasing shortness of breath and the associated restrictions in everyday life (e.g. Climb stairs) Affected people go to the doctor in old age.
During therapy, the patient's quality of life and well-being should be the main focus! At the same time, other diseases must not be forgotten. For doctors, treating cardiac insufficiency in old age is a particular challenge.
Read more on the topic: Superinfection
Can the weak heart be curable?
According to the latest research, heart failure is still incurable today.
Thanks to intensive efforts, symptoms can be alleviated, the progression of the disease slowed down, and the risk of serious complications reduced. Unfortunately, the disease cannot be stopped or even reversed. In theory, a heart transplant can heal sufferers in the long term. However, since there is an extreme shortage of donor organs, this therapy option is only possible in extremely individual cases. In sum, the prognoses of cardiac insufficiency in the end stage can be compared with a malignant cancer!
In view of the increasing aging of our society and the increasing number of people affected, the efforts of experts and researchers to find a cure for heart failure are increasing. In the future there are great hopes, e.g. put into the transplantation of renewable stem cells or the implantation of special pacemakers.
This topic might interest you: Life expectancy with heart failure