Sciatic nerve
Synonyms
Sciatica, sciatic nerve, hip nerve, ischial nerve
Medical: Sciatic nerve
English: sciatic nerve, sciatic nerve
Definition and introduction
The sciatic nerve is the longest peripheral nerve in humans. At the same time, it is the largest and thickest nerve with a cross-section of about 1 x 1.5 cm. Together with several nerves, it comes from a plexus of nerves, the lumbar sacrum nerve plexus (plexus lumbosacralis), which supplies the leg and the buttocks region. In its course towards the foot, it divides in the area of the thigh before the hollow of the knee into two further branches, the fibula nerve and the tibial nerve. Each of these two nerves is further divided into two branches. In addition to fibers for the movement of muscles (Motor skills), the nerve carries fibers for the sensation (sensitivity).
Origin of the sciatic nerve

Of the Sciatic nerve comes from a neural network of the spinal column or spinal cord segments in the lumbar and sacrum area (Spine). This lumbar sacrum nerve plexus (Lumbosacral plexus) provides both parts of the lumbar plexus (Lumbar plexus) and sacrum (Sacral plexus) for the motor and sensitive care of the entire leg including buttocks and hips.
The sciatic nerve comes from the sacrum. This sacrum plexus includes:
- the gluteal upper nerve (Superior gluteus nerve)
- the lower gluteal nerve (Inferior gluteus nerve)
- the sciatic nerve with its two branches common fibula nerve (Nervus fibularis (= peroneus) communis) and tibial nerve (Tibial nerve)
- the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve)
- the pubic nerve (Pudendal nerve)
In contrast, the lumbar plexus is responsible for the motor functions of the lower part of the abdominal wall muscles and some thigh muscles. In addition, the sensitivity of the skin of the lower abdomen, the genitals and the anterior thigh region is enabled. The lumbar plexus consists of six nerves and their branches.
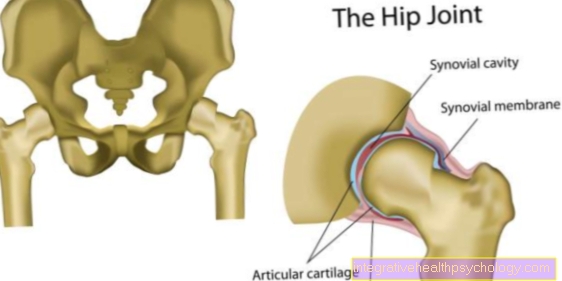
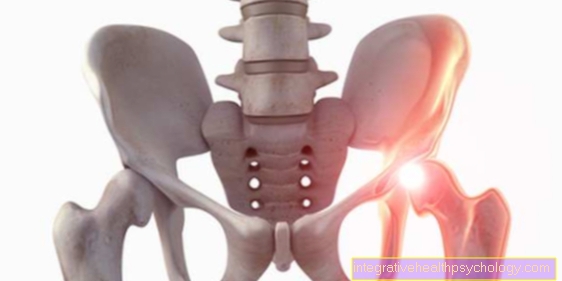
Figure sciatic nerve

- Sciatic nerve -
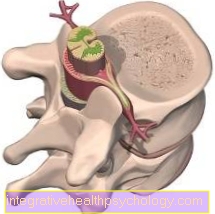
Sciatic nerve - Warping disc
- Disc prolapse -
Nucleus pulposus prolapse - Gelatinous core -
Nucleus pulposus
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Overview and classification
The sciatic nerve divides in the knee area into:
- the tibial nerve (Tibial nerve)
- and the common fibula nerve (Common fibular nerve)
The common fibula nerve divides on the lower leg into a superficial and a deep branch (Superficial and deep fibular nerves). The tibial nerve only divides on the inside ankle into two more branches (Medial and lateral plantar nerves) to supply the foot muscles.
One further subdivides fibers of movement (motor part) and fibers for the sensation (sensory fibers), which run together in a nerve and are then given off as branches to the respective supply area.
Anatomy and course of the sciatic nerve
Of the Sciatic nerve comes from a plexus of nerves in the lumbar regionSacrum-Area (Lumbosacral plexus). First he pulls under the largest gluteus muscle (Gluteus maximus muscle) through the large ischial hole (Greater sciatic foramen). This is a point of passage for important supply structures of the leg and hip, limited in the pelvic area by bones, ligaments and muscles. This large passage is through a pear-shaped muscle (Piriformis muscle) into two smaller openings (Formamen suprapiriform and foramen infrapiriform) divided. The sciatic nerve pulls through the lower opening (Infrapiriform foramen). Then it runs along the back of the thigh between the hamstrings (Sciocrural muscles). Shortly before reaching the hollow of the knee (Popliteal fossa) the sciatic nerve divides into two branches, the common fibula nerve (Common fibular nerve) and the tibial nerve (Tibial nerve), on.
Anatomy and course of the fibula and tibial nerves
The two branches continue to pull along the lower leg towards the foot. The common fibula nerve winds around the head of the fibula bone (Head fibulae) and then runs to the front of the Lower leg. It drills through the long fibula muscle (Musculus fibularis longus) and then divides again into a superficial and deep branch (Superficial and deep fibular nerves).
The tibial nerve runs through the hollow of the knee to the lower leg. There it runs between the superficial and deep flexor muscles of the lower leg. At the inner ankle, this nerve divides into two branches (Medial and lateral plantar nerves) in order to then treat the foot.
Physiology (motor skills)
Of the Sciatic nerve is responsible for the movement of the thigh flexors. This includes:
- the hemi-tendon muscle (Semitendinosus muscle)
- the hemi-diaphragm muscle (Semimembranosus muscle)
- the biceps muscle of the thigh (Biceps femoris muscle)
These muscles arise from that Ischium (Os ischii) and put on the lower leg (Crus) on the side. Accordingly, they cause im Knee joint a flexion and a slight rotation. in the hip joint On the one hand, they are responsible for stabilizing the pelvis, on the other hand, they work in synergy with other muscles to bring it closer (Adduction) and routes (Extension) of the leg or hip.
In addition, the sciatic nerve moves part of a muscle from another muscle group in the thigh, the so-called. Adductors. This muscle is the superficial part of the large muscle leading to it (Adductor magnus muscle).
The common fibula nerve as well as the tibial nerve and its branches are responsible for supplying the entire lower leg and foot muscles with nerve fibers.
Physiology (sensitivity)
The sensitive supply area of the sciatic nerve affects the lower leg (Crus) and the foot (Pes). The nerve gives off several branches of the skin (Cutaneous nerve) to enable the sensation. The skin branches of the common fibula nerve and its branches sensitively innervate the lateral calf area and the back of the foot. In contrast, the skin branches of the tibial nerve and its branches supply the skin the inner part of the calf and the sole of the foot.
course
Of the Sciatic nerve arises from the Spinal cord segments L4 to S3 and then runs as biggest nerve of the human body first through the so-called Piriform foramen, in order to between the flexors (Flexors) and adductors in the direction Hollow of the knee (Popliteal fossa).
Then the sciatic nerve divides into his two lower leg branches the Tibial nerve and the Fibular nerve on. These two nerves then pull in Towards the foot.
At the Thigh the nerve runs along with the Vessels of the thigh, at the Lower leg the nerves only partially run with the vessels. A sensitive branch of the nerve runs on one of the lower leg bones. This nerve is the sensitive nerve that is responsible for the Fall asleep of the foot is responsible for sitting with legs crossed. It comes to a so-called Compartment syndrome in the calf muscles, for example through Overuse and one following swelling, the branch of the sciatic nerve that runs along here can also be damaged.
Damage to the sciatic nerve
Of the Sciatic nerve can become trapped in the ischial hole through a fracture (similar to an inguinal hernia) and cause pain. It can also cause paralysis and pain Broken bones or Contortions e.g. come as part of a trauma. Also intramuscular injections e.g. in the buttocks can lead to nerve damage, especially if they are not performed properly. In addition, inflammation can also be the cause of damage. Not infrequently the sciatic nerve is also with disc prolapse affected. The pain is also known as sciatica. As Lumbago (lumbago) become Back pain understood without charisma in the leg. If the pain occurs in combination, this is called Lumboischialgia designated.
Damage to the fibula nerve
Disorders of the common fibula nerve can be recognized by gait disorders and foot malpositions. If the nerve is damaged before it divides into its two terminal branches, the inward rotation (pronation) and the stretching (extension) of the lower leg section can be paralyzed or weakened. The result is an equinus-clubfoot position (Pes equinovarus). If an injury occurs beyond the branch, an isolated failure or disruption of the branch and the muscles it controls is impressive, depending on the damaged terminal branch. If the deep branch is affected (nervus fibularis profundus), the result is a disturbance of the stretching (extension), which is called equinus foot or dorsiflexion weakness (pes equinus). This leads to a gait disorder (stepper gait), in which increased flexion in the hip and knee joint is necessary so that the tip of the foot does not drag on the floor when walking. On the other hand, damage to the superficial branch (nervus fibularis superficialis) appears in a disturbance of inward rotation (pronation). In addition to the motor failures, there can also be disturbances of sensation.
Damage to the tibial nerve
Damage to the shin nerve or its terminal branches usually results in paralysis of the short foot muscles and / or in sensory disturbances up to pain. The so-called Tarsal tunnel syndrome can occur due to compression through an anatomical constriction in the course of the nerve on the medial malleolus.
Sciatic nerve inflamed in pregnancy
Violent Sciatic pain in the field of Lumbar spinethat radiate down the buttocks to the leg and foot are a typical symptom of a inflamed sciatic nerve during the pregnancy.
In most cases this pain occurs only on one half of the body, it is extremely rare that the sciatic nerve is inflamed on both sides.
Even during pregnancy, the affected person can experience the symptoms through severe to cough or Sneezetrigger while bending and / or lifting the affected leg.
Also, it often happens Numbness sensations, Tingling and / or Signs of paralysis the affected half of the body.
During the pregnancy there is a great risk of the sciatic nerve becoming inflamed.
On the one hand, this is due to the fact that many anatomical structures are shifted in the course of the child's growth and can thus press on the nerve. On the other hand, it can child even one enormous pressure on the Sciatic nerve exercise and in this way trigger the typical symptoms.
The gluteal muscles, which are particularly stressed during pregnancy, are also related to the development of a Sciatic nerve - inflammation.
As the weight distribution is shifted more and more forwards (ventrally) as the child grows, the muscles of the buttocks are forced to build up more strength to keep the body upright.
In those cases in which the gluteal muscles can be identified as the cause of the inflammation, various forms of heat therapy such as heat gels and / or compresses help to provide relief for the women concerned.
They also turn out to be light massages and targeted stretching as enormously pain-reducing. It is not only not necessary to take it easy, it is even counterproductive. Light, careful movement is considered one of the best approaches to treating an inflamed sciatic nerve during pregnancy.
When taking Painkillers and or anti-inflammatory preparations Always seek the advice of a doctor, as many drugs are allowed during an existing one pregnancy not be taken.
Please also read our relevant topic: Lumboischialgia in pregnancy
Sciatic nerve pain
If the Sciatic nerve (Sciatic nerve) trapped or ignited there will be pain either strong stabbing and can be inclusive or rather dull. The pain can be either radiate into the leg or located directly over the lesion site of the sciatic nerve in the buttocks are located.
Depending on the type of lesion of the nerve, inflammatory or entrapment, the pain can be either occur suddenly or yourself develop slowly. The intensity of the pain can also be so high that the Movement restricted because the leg almost automatically assumes a relieving position. In the Relieving posture if the pain usually decreases a little, it can even decrease completely. However, the pain often returns when the reliever posture is given up. As a measure against the pain of an entrapment, the person affected can use it lay on your back and the legs in 90 ° angle in the knee Put it in a hunched position to stretch the sciatic nerve and relieve the pain.
The pain can also severely limit the quality of life of those affected because the pain is also frequent Restrictions in movement of the leg can lead to. Those affected should feel at ease with their Family doctor imagine that this disease also leads to a Sick leave can come.
These pains are in the Rarely is an emergency, however, the pain should be treated so that the person affected can move freely as soon as possible.
The pain can of course die different intensities accept and also will individually very different perceived. For some people, even slight pain can cause severe impairment of quality of life. In other affected people, however, even severe pain only causes a slight reduction in quality of life. Of course, the principle applies that nobody has to suffer pain.
To the correct dosage of pain medication patients should follow their Contact a doctor or pharmacist.
Sciatic nerve irritated
The most common irritation of the sciatica occurs at the Nerve root. There can be various causes for the irritation.
Starting with one Herniated disc of the lumbar spine up to one severe entrapment of the sciatic nerve, the causes may lie.
At a Herniated disc of the lumbar spine, the pain comes from the segment in which the intervertebral disc has herniated. In the case of a herniated disc, the Intervertebral disc, as Damper between the vertebral bodies serves on the spinal canal or the nerve roots of the nerve. This pressure on the nerve root irritates the nerve and creates a sharp pain, which is also called Symptoms can shoot into the leg. The pain can die Severely restrict the freedom of movement of the leg, depending on which nerve root, whether sensory or motor, was damaged, it can also Paralysis of the leg come.
There one Irritation of the sciatic nerve can also be caused by a herniated disc, of course, the same also apply here Risk factors. These factors include degenerative Changes in the spine, a permanent heavy load on the spine through, for example, heavy physical work, one wrong posture especially with sedentary activities and obesity (Obesity).
Can against the pain Painkiller be taken, but they should not be used permanently. On the other hand, you can Muscle relaxants are used to relieve tension and thus also correct a bad posture that has irritated the nerve.
After the symptoms have subsided, the Back muscles to train and strengthen to avoid further irritation. If symptoms of the sciatic nerve occur more frequently, the therapy can also operational respectively. However, conservative therapy should be tried before the operation.
Exercises for problems with the sciatic nerve
Around Prevent pain in the sciatic region, offers itself regular training of the back and glutes on. The exercises should regularly must also be carried out when performing the exercises on both sides equally to be completed.
It is a good first exercise to slowly raise and lower the leg while standingIt is optimal if the leg is between two repetitions not discontinued becomes. Initially, this exercise should be done with ten repetitions per side and three sets.
In the second exercise, the starting position is in Supine position. The bent knees should point towards the shoulder be pulled while the back remains flat. Here, too, the exercises should be performed equally on both sides. At the end of the exercise, the knees should be pulled towards the shoulders at the same time.
One of the most important exercises in everyday life is one straight posture on. When lifting heavy objects you should always make sure that you are bearing the weight off the knees lifts and does not burden the back.
Pinched sciatic nerve
Of the Sciatic nerve (Sciatic nerve) can get jammed even with minor, clumsy movements. In the Entrapment of the sciatic nerve the pain occurs suddenly and is mostly im lower back localized. Because the sciatic nerve is a nerve is that both sensitive as motor Has qualities, both qualities can be damaged in the event of entrapment. This means that in the case of a sensitive disorder, in addition to the pain Sensory disturbances can occur on the leg. If the injury also has a motor component, it can too Paralysis in the leg come.
Depending on root cause Various measures can remedy entrapment:
- In some cases the entrapment can already be through Exercisesthat relax the muscles.
- But if the entrapment comes from a Blockage in the sacroiliac joint, can the Adjustment by a physiotherapist or one chiropractor already be helpful.
- But sometimes the sciatic nerve is pinched relatively firm and deepso that the pain without medical therapy is no longer so easy to fix. At first you can try at this moment to deal with the pain from the outside, for example Voltaren® ointment to meet. If external therapy for the pain is not enough, those affected can too Painkillers with the active ingredients Ibuprofen or Acetylsalycilic acid, such as Aspirin® take in. Those affected who decide to take the pain pills for a long time should also take one Stomach protection To fall back on.
Since the entrapment in many cases again resolved quickly can be stay usually no consequential damage the entrapment exist. Nonetheless, the entrapment of the sciatic nerve is very painful and should be be treated quicklyin order to improve the situation of those affected as quickly as possible.
As prophylaxis it makes sense regular exercises to strengthen the back muscles to graduate and a straight, back-friendly working posture to take.
An entrapment of the sciatic nerve can occur for various reasons: On the one hand, people are with something weaker back muscles predestined to suffer entrapment of the sciatic nerve. For another are Pregnant women also in a risk group for entrapment of the sciatic nerve, especially in the last trimester of pregnancy additional stress on the back comes.