Löfgren's Syndrome
Definition - What is Löfgren Syndrome?
Löfgren's syndrome is a name for the acute form of the multi-system disease sarcoid. Löfgren's syndrome often occurs in women between the ages of twenty and forty.
Those affected suffer from characteristic triad of symptoms, including polyarthritis, erythema nodosum (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) and biliary lymphadenopathy (swelling of the lymph nodes on both sides of the lung root).
Since Löfgren's syndrome often heals spontaneously, therapy is not always necessary.
Before continuing with the article, we recommend that you take a quick look at the main topic "Sarcoidosis" and the accompanying symptoms mentioned:
- Sarcoidosis - Symptoms, Causes and Therapy
- Polyarthritis

Causes of Löfgren's Syndrome
The cause of the development of Löfgren's syndrome is not yet known. We know that there is a systemic disorder in which certain immune cells, the T helper cells, are impaired in their function, while B lymphocytes show increased activity.
The immunological overactivity causes the formation of granulomas, nodular tissue changes, in various organs.
There is also a connection with certain HLA antigens. This means that a genetic predisposition is possible.
In addition, there are environmental factors that seem to favor the development of sarcoid. This includes work in agriculture as well as in the metalworking industry.
The impairment of the immune system can harbor numerous reasons. In order to make sure of this, it is advisable to also look at the following articles:
- How does the immune system work?
- Autoimmune Diseases - What is it?
- How can you strengthen the immune system?
I recognize Löfgren's syndrome by these symptoms
Acute sarcoid, Löfgren's syndrome, consists of a characteristic triad of symptoms. Those affected suffer from erythema nodosum, arthritis and biliary lymphadenopathy.
Erythema nodosum is nodular skin changes that are painful to pressure and that initially look reddish and later bluish.
Are you more interested in this topic? You can read more detailed information in our next article: Sarcoid of the skin - causes, symptoms and therapy
Arthritis primarily affects the ankles and causes severe pain when walking.
The biliary lymphadenopathy describes a finding that can be seen on X-rays or in computed tomography. There there is an enlargement of the lymph nodes in the area of the lung hili, i.e. in the areas of the main bronchi and large vascular arteries of the lungs.
In addition, the sick suffer from general symptoms such as fever, poor performance, loss of appetite and fatigue.
You can find detailed information on the symptoms also in relation to sarcoid on our main page: Symptoms of Sarcoid
Course of disease and duration in Löfgren's syndrome
The course of the disease is extremely favorable in Löfgren's syndrome. In around 95% of patients, the disease disappears completely after several months and then heals spontaneously, even without treatment.
The severe initial symptoms, the erythema nodosum, arthritis and swelling of the lymph nodes, usually subside four to six weeks after the onset of the disease and slowly regress.
Occasionally, it takes a year or more for the person to be completely healthy. The course of a chronic sarcoid can, however, vary greatly from person to person and can last for years and recur after healing.
However, Löfgren's syndrome very rarely turns into chronic sarcoid.
Prognosis of Löfgren's Syndrome - How Common Does It Relapse?
There are no figures on the frequency of relapse in Löfgren's syndrome. However, the prognosis for Löfgren's syndrome is very good, as the disease heals spontaneously within several months in more than 90% of patients.
Treatment of Löfgren's Syndrome
Löfgren's syndrome does not always require treatment. The syndrome heals spontaneously in 95% of cases within months, even without therapy.
If symptoms are felt to be very unpleasant, treatment initially consists of anti-inflammatory pain medication such as ibuprofen or acetylsalicylic acid. These medicines lower fever, reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
More severe symptoms can be treated briefly with cortisone. Cortisone has a very strong anti-inflammatory effect and is also the drug of choice for chronic sarcoid.
Cortisone therapy is not uncommon in everyday medical practice. This commitment can be a blessing, but it can also quickly become a nightmare. To learn more about the effects of cortisone, also read:
- Effects of cortisone
- Side effects of cortisone
Risk of infection with Löfgren's syndrome
Löfgren's syndrome is not contagious. The question of whether pathogens are involved in the development of acute sarcoid is the subject of current research. However, no pathogen has so far been found and it is considered certain that Löfgren's syndrome is not contagious.
Diagnosis of Löfgren's Syndrome
Those affected with Löfgren's syndrome typically go to their family doctor as the first point of contact. He or she has a detailed conversation with the person concerned about the symptoms, undertakes a physical examination and takes a blood sample.
Other diagnostics also include x-rays of the lungs, a lung function test, a lung specimen and a biopsy.
Based on the fact that Löfgren's syndrome is a subgroup of the clinical picture of sarcoid, the diagnosis of sarcoid also plays an important role. To do this, read: Diagnosis of sarcoid
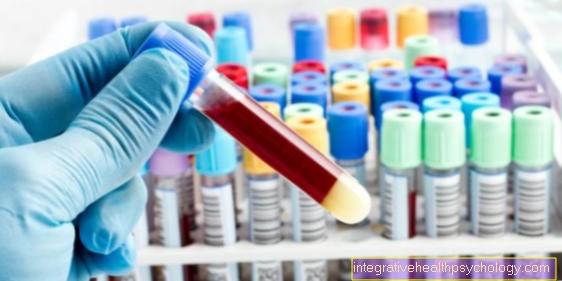
Laboratory values in Löfgren's syndrome
If Löfgren's syndrome is suspected, the treating family doctor will usually take a blood sample. This often shows an accelerated blood sedimentation and a pathological increase in white blood cells (leukocytosis) with an increase in eosinophilic granulocytes.
In serum electrophoresis, a special study of the proteins in the blood serum, an increase in alpha and beta globulins is often found.
In addition, the blood is checked for tuberculosis pathogens in order to rule out tuberculosis as an important differential diagnosis.
The angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), which is typically increased in the chronic form of sarcoid, is also measured.
Tuberculosis is a systemic infectious disease that can also be fatal. In order to be able to determine the exclusion of tuberculosis on the basis of the symptoms, you should also deal with the symptoms of tuberculosis: Signs of tuberculosis
Can you do sports if you have Löfgren syndrome?
In acute Löfgren's syndrome, those affected often suffer from exhaustion, high fever and painful joints. These are complaints that severely limit physical activity.
There is an acute inflammation. This means that you should refrain from exercising. In particular, if you have a fever, you should avoid sporting activities.
Recommendation from the editor
Further important information on the subject of "Löfgren Syndrome" can be found at:
- Diseases of the lungs
- Infectious diseases
- Pneumonia - What's Behind It?
- Sarcoidosis - You Should Know That
- The most important thing about tuberculosis