Pubic bone pain
introduction
The pubic bone is part of the hip bone and delimits the groin region and the region of the genital organs. Pubic bone pain (Pubis) often affect athletes, but can also occur during pregnancy or in everyday life.

causes
There are many causes of pubic bone pain and some of them can be very gender-specific.
Pubic bone inflammation can occur in athletes. This inflammation causes severe pain in the pubic bone and can arise in a number of ways. On the one hand, if the pubic bone is heavily stressed, for example when playing soccer or sprinting, micro-fractures in the pubic bonePubis) come. These small cracks (also called fatigue fractures) by no means cause instability of the entire hip, but they do cause severe pain in the pubic bone. In addition, new bones are formed to compensate for the small micro-lesions. This can lead to a painful but not infectious inflammation. It is important not to continue training with such pain, as the inflammation affects the inner thigh muscles (the so-called Adductors) or even spread to the abdominal muscles and cause even greater pain there.
Another cause of pubic bone inflammation and thus pain in the pubic bone can be an imbalance in the pubic symphysis, which consists of fibrous cartilagePubic symphysis) be. Numerous muscles are attached to the pubic symphysis, especially the inner thigh muscles (the Adductor group). If an incorrect load occurs in people who are very active in sport, the pubic symphysis can be irritated. This leads to pain and inflammation in the surrounding pubic bone. This pain in the pubic bone is often only diagnosed when the thigh or abdominal muscles are also affected.
There is also gender-specific pain in the pubic bone. In men, inflammation of the prostate (Prostatitis) lead to pain in the pubic bone, among other things. With prostatitis it is mostly caused by gram negative bacteria or Escheria coli (E.coli) painful inflammation. The pain occurs mainly after urinating or after an orgasm. The pain is often limited to the groin area, but can reach the pubic bone. Since the prostate corresponds to the anus (anus) is very close, there is also severe pain when defecating.
Another gender-specific cause of pubic bone pain is pregnancy. The paired pubic bones surround the cartilaginous pubic symphysis and thus represent the foremost and lowest boundary of the pelvis. During pregnancy, the pubic symphysis is stretched further and further. However, since this consists of very tight fiber cartilage, tension quickly occurs on the surrounding pubic bone or the two paired pubic bones (Pubis). However, it can also be the case that the pubic symphysis is loosened too much due to the hormones exposed during pregnancy. This is due to the two hormones progesterone and relaxin. Both occur more frequently during pregnancy and ensure that the cartilage of the pubic symphysis is more easily stretchable in order to make childbirth as easy as possible. However, the pubic symphysis may be loosened too much. This allows the pubic bone to slip easily. This pain in and around the pubic bone can radiate into the back or the thigh muscles and is particularly noticeable when climbing stairs.
You might also be interested in these topics:
- Inflammation of the bone skin on the coccyx
- Pubic branch fracture
- Painful bowel movements
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Tendinitis of the adductors
Tendon inflammation of the adductors occurs when the adductors, i.e. the muscles on the inside of the thigh, are subjected to excessive stress. This is more common in sports, such as playing soccer. This leads to typical pain in the inner thigh, which can radiate to the groin and pubic bone. They mainly occur during physical activity.
If the pain in the groin is also severe, a possible hernia should be clarified. Adductor tendinitis can be treated with drugs that reduce the inflammation and physical therapy.
More information can be found here:
- Tendonitis on the thigh
Inguinal ligament inflammation
Inguinal ligament inflammation typically causes pain in the groin and pubic bone area.
The inguinal ligament is the connection between the intestinal and pubic bones and can be affected by various causes. Often there is an overstretching of the inguinal ligament due to incorrect loading. There is pain that, depending on the severity of the inflammation, can radiate into different areas and is intensified by pressure. If the inguinal ligament is overstretched, the therapy consists of physical rest and, if necessary, physiotherapy.
Periosteum inflammation
Periosteum inflammation can rarely affect the pubic bone.
The reason for this is usually excessive or incorrect loading of surrounding muscles, for example an incorrect sitting posture, which can inflame the periosteum. This usually causes very severe pain. These can typically be precisely localized, i.e. they occur specifically at a certain point. They also get worse when you apply pressure. The pain usually only occurs when a certain movement is performed and can last for several months, but can be contained by various medications.
Read more about this:
- This is how long periosteum inflammation lasts
Inflammation of the symphysis
Inflammation of the symphysis affects the pubic symphysis and can lead to severe pain in and around the pubic bone.
The causes are very diverse and include an incorrect load in certain sports, as well as fractures or the formation of cysts, i.e. pockets of tissue. This leads to pain that is aggravated by pressure and is often accompanied by swelling. If there is also a fever, there may be an infection that must be treated as soon as possible. Otherwise, therapy consists of anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy.
rheumatism
A rarer cause of pubic bone pain is rheumatism.
The so-called rheumatoid arthritis typically affects, among other things, the hip joint. More rarely, inflammation occurs in the area of the symphysis that connects the two pubic bones. In the case of pronounced rheumatic inflammation of the hip joint, however, pain can also occur when sitting for a long time, which can accordingly occur in the area of the pubic bone.
Also read our other pages on this topic:
- Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Therapy of rheumatoid arthritis
Inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia can cause pubic bone pain. This is mostly due to the radiation of the pain, although an inguinal hernia is often not associated with severe discomfort. Occasionally there is a strain on the inguinal ligament, which extends to the pubic bone. The pain mostly occurs when there is strong strain or pressure in the groin area.
Depending on the type and severity of the inguinal hernia, it does not always have to be operated on, but should always be treated by a doctor.
You might be interested in these topics:
- Pain in an inguinal hernia
- Symptoms of an inguinal hernia
pregnancy
As a cartilaginous connection of the bony, anterior pelvic ring, the pubic symphysis (Pubic symphysis) exposed to enormous stresses during pregnancy.
The increasing body weight of the unborn child causes increasing pressure in the abdomen and pelvis.
The hormonal changes in the structure of the cartilage joint during pregnancy are essential for the process of approaching birth. The rising estrogen level in the blood leads to a loosening and softening of the fibrous cartilage in the course of pregnancy, which means that the pelvic ring can be more flexible and wider during the birth and the passage of the child can be made easier.
Another hormone (relaxin) also ensures increased elasticity in the otherwise very tight ligaments, which strengthen and secure the pubic symphysis. However, it can happen that this loosening process leads to pain in the pubic area, which is especially pronounced when walking, climbing stairs and lying on the side.
These symptoms are observed in 50% of all pregnant women. Possible risk factors that promote painful joint loosening are back problems, joint diseases (arthrosis / arthritis) and injuries to the hip that existed before pregnancy.
For more detailed information on this topic, read our next article under: Pubic bone pain in pregnancy
Pubic bone fracture
A pubic bone fracture is rare and is usually the result of a serious injury, such as a car accident.
The fracture results in a great loss of pelvic stability and is very painful. Since a pubic bone fracture is often an injury to the internal organs in the pelvic area, this must be treated immediately in a hospital. Depending on the extent of the break, it may take some time for the pubic bone to recover from the fracture and for the pain to go away.
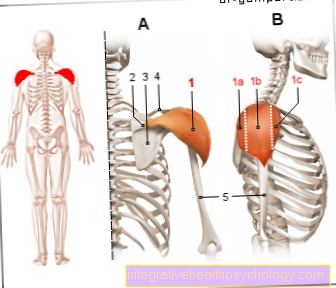
Illustration pubic bone pain

Pubic bone pain
- Iliac bone - Os ilium
- Appendix -
Appendix vermiformis - Ischium - ischium
- Pubic bone - Pubis
(1st + 3rd + 4th = hip bone -
Os coxae) - Pubic symphysis -
Pubic symphysis - Lumbar muscle -
Psoas major muscle - Sacrum - Sacrum
- Long Dresser -
Adductor longus muscle - Short donners -
Adductor brevis muscle - Comb muscle -
Muscle pectineus
Causes of pubic bone pain:
A - inflammation of the prostate
at the man (Prostatitis)
B - diseases of the internal
Genital organs (in women)
C - pregnancy -
Stretching, loosening the
Pubic symphysis
D - pubic bone inflammation -
for athletes (soccer, sprint)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Symptoms
Pubic bone pain usually does not occur alone but with Concomitant symptoms.
The symptoms occur after physical exertion up and shine right into the Thigh muscles, so one can assume an inflammation of the pubic bone.
Are the accompanying symptoms, however increased pain when urinating and after the Sexual intercourse, can a Prostatitis (Inflammation of the prostate) should be considered.
At pregnant women on the other hand, the symptoms occur mainly when Climb stairs or at jerky hip movements on.
Pain above the pubic bone
There are many possible causes for pain above the pubic bone.
Possible triggers that are responsible for the pain in both sexes are, for example, inflammation of the pubic bone itself, which radiates into the area above it. A disease of the bladder, for example in the case of severe cystitis, can be noticeable as pain above the pubic bone. This often results in pain when urinating, passing discolored urine and fever. Inflammation of the cecum called appendicitis can manifest itself as pain above the pubic bone. A disease of the colon can also be the cause of the pain.
In men, pain above the pubic bone can be caused by inflammation of the prostate. In women, for example, inflammation of the uterus is an option. Other diseases of the uterus or ovaries can also cause the pain.
Unilateral pain
If the pain is not clearly felt in the center behind the pubic bone, but may radiate either to the left or right towards the groin or lower abdomen, various abdominal diseases must also be taken into account as the cause.
If the pain is more on the left side and is of a burning or aching character, the most common inflammation is colon wall sacs (Diverticulitis) the trigger. The migration of kidney or urinary stones in one of the two ureters, which run in the area of the left and right lower abdomen towards the urinary bladder, can lead to left or right lower abdominal or pubic pains.
The presence of inguinal hernias (Hernias), can possibly - depending on the location - cause pain in the right or left lower abdomen, and always when there is an entrapment of abdominal organs in the hernial orifice.
In women, attention should also always be paid to possible diseases of the internal genital organs, which are anatomically located in the lower abdominal area. Inflammation of the left or right ovary and / or fallopian tube (Adnexitis, salpingitis, oophoritis), Ovarian cysts, or a pregnancy outside the uterus in the fallopian tube (extrauterine pregnancy), left or right lower abdominal pain.
The most common cause of right-sided pelvic pain is inflammation of the appendix on the appendix (appendicitis). Due to the many different positional variations of the appendix or appendix, however, the pain does not always have to be felt exactly in the right lower abdomen, but can also be shifted further to the left or into the right upper abdomen.
Especially at the beginning of appendicitis, pain in the lower navel region is possible, which only shifts to the right as the disease progresses.
In addition, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis can always lead to uncharacteristic abdominal complaints that can be felt in the lower abdomen on both the left and right sides.
Finally, the classic cystitis should always be considered, which can lead to pain above the symphysis, especially at the end of urination. Under certain circumstances, however, this pain can shift slightly to the right or left side of the lower abdomen if the bladder inflammation increases and the ureters react as well.
Groin pain
If the pain is not limited to the pubic area, but may also radiate towards the groin (or hips or perineal area), various diseases must be considered as the cause.
On the one hand, the so-called athlete bar (Pubalgia athletica) in which the chronically incorrect or overloaded abdominal / trunk muscles attached to the anterior pelvic ring can cause tearing groin and pubic pain.
On the other hand, inflammation of the pubic bone (Osteitis pubis) or the pubic symphysis (Symphysitis), which are irritated as a result of permanent overload (high athletic stress, anatomical malpositions) and can lead to the pain symptoms mentioned above.
In the same way, an inguinal hernia, simple strains of the pelvic, abdominal or hip muscles, irritation or pinching of nerves running in the groin area, as well as swollen inguinal lymph nodes as part of an infection / inflammation, urinary stones or fallopian tube or testicular diseases can lead to the groin - and pubic bone pain.
Read more on the topic:
- Drag in the bar
Differences between men and women
In addition to various causes, which can cause pain symptoms in the pubic area equally in both sexes, there are also gender-specific triggers.
The most important diseases in men that can lead to painful, burning / boring / stabbing / pulling discomfort behind the pubic bone include certain prostate ailments.
These can also cause tearing in the testicle. Inflammation of the prostate (Prostatitis), which around 10% of all men get sick with once in their life, can - regardless of whether it is acute or chronic - lead to pain in the pubic and / or groin area in addition to painful and frequent urination Urinating, ejaculating, or intensifying during bowel movements. The most common causes of this inflammatory prostate disease are the gram-negative rod bacteria Escherichia coli, which rise to the prostate via the urinary tract. In addition, however, it can also lead to an abacterial, permanent inflammation of the prostate (abacterial prostatitis; Protatodynia), which usually leads to a chronic pain syndrome in the pelvis. This clinical picture predominantly affects men between 25 and 45 years of age and is classified as psychosomatic. The symptoms are similar to those of bacterial prostatitis, the cause of the development of these diseases has not yet been clarified. However, a history of traumatic damage to the prostate leading to inflammatory and swelling changes is suspected.
The sex-specific pubic bone pain in women primarily includes so-called symphysis pain, which can occur especially during an existing pregnancy and is caused by the loosening of the pubic symphysis.
The pubic symphysis is a cartilaginous connection that holds the front part of the pelvic ring together and reacts to hormonal changes in women during pregnancy. The increasing levels of estrogen and relaxin in the blood loosen and soften this cartilage structure as well as the ligaments surrounding it, which leads to the widening of the pubic symphysis and thus to the enlargement of the pelvic diameter in the course of preparation for the birth.
The pain over the pubic bone is primarily dependent on movement, is worse, among other things, in the lateral position and can radiate into the sacrum or the thighs.
diagnosis
An important diagnostic procedure is the anamnesis, so that Patient-doctor conversation. Here the doctor can find out, for example, whether the patient might too much exercise operates and can therefore conclude that the pain in the pubic bone is from a overload originates. One is also important roentgen- or MRI-admission. Any micro-breaks can be recognized and diagnosed. Is there any suspicion Prostatitis (Inflammation of the prostate), the doctor can use a rectal procedure to feel the prostate and identify any discrepancies.
therapy
The Therapy for pubic inflammation takes place first conservative. First the patient should be his stop sporting activities to give the bone time to recover and to let the pain in the pubic bone subside. Therapy is also carried out with anti-inflammatory drugs how nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or with Corticosteroids.
If the pain in the pubic bone is not too severe, you can also use a physical therapy kick off. This primarily serves to strengthen the surrounding area belly- and Pelvic floor muscles. In addition, the Muscles of the thigh be trained, especially the inner ones Adductor group.
In the worst case, only one can help surgerywhich involves removing the inflamed tissue.
The Therapy for prostatitis is done using Antibiotics. Different antibiotics can be considered depending on the bacterium. Since the severe pain in the pubic area leads to cramping of the pelvic floor muscles, additional antispasmodic and pain relievers are recommended.
Therapy of pubic bone pain in the pregnancy takes place without medication. Instead, the patient gets one orthopedic support beltsl or may be additional Physiotherapy units visit. This should at least reduce the pain. However, you should also try to avoid painful movements in everyday life as much as possible.
prophylaxis
Most people find it easy to avoid pain in the pubic bone, since such pain is especially common when High-performance sport and here especially at Footballers arise. For athletes, the only prophylaxis is one adequate warm-up training attached to stretching. In addition, movements that are too abrupt (suddenly stopping or turning your hips) should be avoided.
Unfortunately, prostatitis is difficult to prevent, as is the pain in the pubic bone during pregnancy.
forecast
The forecast for pubic bone pain is mostly very good. However, many athletes do not rest completely after an inflammation, so the inflammation may return quickly or not go away at all. In the worst case, a surgery help, which, however, has very good prognoses.
Also a very prostatitis has a good prognosis as long as it is only acute and not chronic. At a chronic inflammation of the prostate help Antibiotics no more and there are no drugs that give a cure forever.
Does it come during the pregnancy pain in the pubic bone, this can mostly be compensated quite well. Nevertheless, the person concerned should have one Caesarean section think about it, otherwise the pubic bone may shift significantly, which can lead to pubic bone pain even after pregnancy.