Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis)
What is a pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis)?
Pinworms (Enterobius vermicularis from the species of roundworms) are parasites that only affect humans.
They live and reproduce in the human colon and lay their eggs on the skin around the anus.
Pinworms are between 2 mm (males) and around 10 mm (females), are thread-shaped and characteristically white.
The size of the eggs is in the micrometer range and can hardly be seen with the human eye. The clinical picture of pinworm infestation is called enterobiosis.
Read more on the subject under: Parasites in the intestine
.jpg)
How is the transmission route?
The life cycle of the pinworm takes place within the human digestive system. After mating, the females migrate to the anus at night and lay their eggs on the anal skin.
These stick there and cause severe itching.
By scratching, the eggs get onto the infected person's hands and can be distributed. There is either repeated infection by bringing the hands to one's own mouth or transmission to other people by leaving the eggs on objects, door handles etc. when touched (so-called fecal-oral route of infection).
Contagion through inhalation of whirled up egg-containing dust has also been described in isolated cases, since the eggs can survive for up to two weeks.
Causes of Illness
There is no specific cause for the infection with pinworms.
It is one of the most common parasitic diseases in humans. According to the doctrine, 50% of all people get enterobiosis once in their life, the number of infected people is over a billion.
An infection with pinworms says nothing about a person's immune system, anyone can get sick.
In general, the spread among children is significantly more common than among adults (see below).
Poor hand hygiene can be regarded as the only cause of the spread of pinworms. The hands are the carrier from where the eggs are laid to the entry point into the body.
Thorough hand washing after using the toilet can interrupt this cycle of infection and prevent other people from being infected.
Diagnosis of enterobiosis
The anal itching serves as a guide to diagnosing pinworm infestation (enterobiosis or oxyuriasis).
A so-called adhesive tape preparation is then made from the anus. A kind of scotch tape is stuck on the anus and removed again to provide evidence of worm eggs.
This tape preparation is then examined microscopically to reveal the eggs.
This is considered to be definitive evidence of the pinworm infection diagnosis. A stool sample is often used instead of the tape to detect the eggs or worms themselves.
Furthermore, eosinophilia is often found in the blood, an increase in certain white blood cells that react specifically to parasites.
An increase in IgE antibodies can also indicate an infection with parasites.
Read more on the subject under: worms in the intestine
Why do they like to appear in children?
Children do not yet have a particularly pronounced hygiene behavior. Washing hands after going to the toilet is often forgotten or even unwelcome, the hands often end up in the mouth, an itch is simply given in and scratched, even if the itchy area is on the buttocks.
The nocturnal itching of the anus is particularly tricky, where it is unconsciously scratched during sleep and the eggs are ingested. It is also easier to spread it in kindergartens and day-care centers, as not every child can be checked for hand washing after using the toilet.
They play together, touch the same toy and the worms spread unhindered. The children bring the worms home with them, where the family can also become infected.
How long is the incubation period?
The incubation period is quite long and is five to six weeks, which corresponds to the development of sexually mature worms from the laid eggs.
Pinworms have several larval stages that they go through after hatching. Infection usually occurs with the eggs, and the worms then develop as they pass through the digestive system and stay in the intestines where they mate.
The first symptoms (usually itching) occur when eggs are laid on the anus.
What can be signs of pinworm infestation?
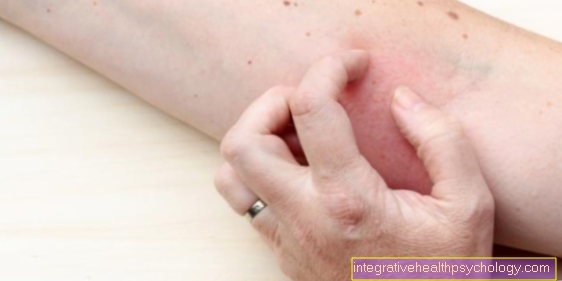
The typical symptom of pinworm infestation is anal itching, which is triggered by the eggs that have been laid.
The worms can often be seen in the stool with the naked eye. They appear as pointed, light white, up to 12 mm long, thread-like structures.
The smaller males die after mating and are excreted in the stool. They are only up to 5 mm long and therefore easier to miss.
The larger females can also be excreted alive and are therefore sometimes noticeable by movement in the stool.
Concomitant symptoms
The classic symptom of itching of the anus in pinworm infestation can be accompanied by other symptoms.
Especially in children, behavioral problems and growth delays can occur in the course of the disease.
Due to the itching at night, the children sleep worse, which is shown by abnormal behavior resulting from overtiredness during the day. Abdominal pain can also occur less frequently (see below).
A more common phenomenon in pinworm infestation, on the other hand, is the spread of the infection to the genital area in girls.
The eggs can also be distributed to the vulva when using the toilet, where worms can also hatch. These lead to inflammation of the vulva and vagina and can be detected there macroscopically or microscopically.
itching
Itching is the characteristic symptom of pinworm infestation, which usually leads the infected to the doctor.
It occurs mainly at night and in the anal region.
The itching leads to the worm eggs being absorbed by the fingers and is responsible for further distribution or infection.
Pain
If the infection lasts for a long time and the worms continue to multiply in the intestine, inflammation can occur there.
These lead to abdominal pain and cramps, which can express themselves like appendicitis up to fulminant peritonitis (peritonitis).
Such gradients are, however, quite rare. In children, such inflammation can in turn lead to inhibition of growth.
Read more on the subject under: Peritonitis
Treatment and therapy
Pinworm infestation should always be treated with medication if possible. A number of anti-parasitic substances are available for this purpose (see below).
Additional measures can also be taken. These usually serve to prevent the further spread and infection of other family members. Underwear with a tight waistband may prevent the anus from scratching at night. Shortened fingernails also help to reduce the absorption and distribution of the eggs.
If a pinworm infestation is known, careful hand hygiene should be observed during treatment and for about two weeks afterwards. Used towels, bed linen and clothing should be washed at at least 60 °. Possibly contaminated surfaces and objects can be cleaned of adhering eggs by washing them with hot water.
It is also advisable to shower in the morning after getting up, before the eggs that were laid overnight can be distributed. These measures minimize the risk of repeated self-infection and of infecting others.
Read more on the subject at:
- Medicines for worms
- Parasite cure
What drugs are used for treatment?
Medicines that are effective against roundworms, such as pinworm, are called anthelmintics.
The most commonly prescribed active ingredients are mebendazole (e.g. Vermox) and pyrantel (e.g. Helmex). Tiabendazole, piperazine derivatives and pyrvinium can also be used.
All active ingredients kill both the adult worms and their larval stages. Usually a single dose is given, which should be taken repeatedly after two weeks to really get rid of the worms.
It is recommended that close family members also be treated, e.g. B. the parents of affected children, even if they do not yet notice any symptoms. Most active ingredients mainly work in the intestine and are hardly absorbed, but side effects can occasionally occur.
Are there any over-the-counter medications?
The active ingredient Pyrvinium (e.g. Molevac) can be obtained from pharmacies without a prescription.
It only works against the pinworm, whereas the other substances have a broader spectrum of activity and can also be used for other worm diseases. Mebendazole, pyrantel and others require a prescription and must be prescribed by a doctor.
If a worm infestation is suspected, however, therapy should not be carried out on one's own initiative. Confirmation of the suspected diagnosis and adjustment of therapy to the extent of the infestation and other factors such as age and body weight are necessary.
Can Homeopathy Help?
According to current scientific studies, the effectiveness of homeopathic therapies has not been proven.
Since the worms spread without adequate therapy and other people can be infected, drug therapy is always recommended.
If desired, homeopathic remedies can also be used.
However, they are not a substitute for treatment with anthelmintics
Pinworms During Pregnancy - Is It That Dangerous?
An infestation with pinworms during pregnancy is not necessarily a threat. The worms stay in the intestines and pose no threat to the unborn child.
Only in the case of massive infestation and inflammation in the intestine can the worm infestation have a negative effect on pregnancy.
Infection of the newborn through eggs sticking in the anal / genital region is also possible at birth.
Therefore, in the event of an infection with pinworms during pregnancy, therapy should be with an antihelminthic. Not all active ingredients are suitable for pregnant women. However, pyrvinium, mebendazole, and noclosamide are listed as usable in pregnancy.
However, a suitable therapy should be discussed with a doctor.








.jpg)