Lidocaine
What is lidocaine?
Lidocaine (Trade name e.g. Xylocain®) is a local anesthetic, a so-called local anesthetic.
It is very quick and effective and is used very often. Applied to the skin or mucous membrane, lidocaine quickly and effectively relieves pain, itching and burning. Lidocaine is often given in order to be able to sew smaller wounds painlessly and to perform surgical treatments.
It can also be administered against cardiac arrhythmias and has a few other areas of application.

Use of lidocaine
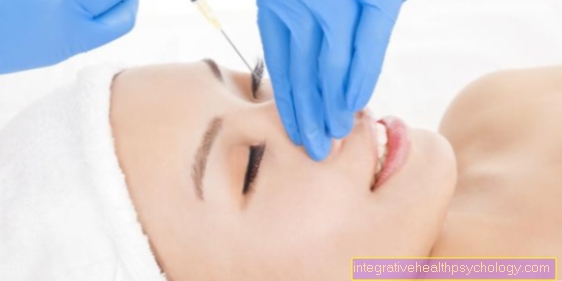
As an anesthetic, lidocaine can either be injected under the skin to numb a smaller area, for example so that a laceration or cut can be sewn.
Lidocaine can also be injected directly into the vicinity of a nerve, thus numbing a larger area and preventing pain transmission and pain perception from this nerve. This is why this type of anesthesia is also called conduction anesthesia.
This is used for minor operations on the extremities, e.g. the treatment of an under-spoke fracture (Radius fracture), in question. But even with spinal anesthesia (Spinal anesthesia) lidocaine is used to numb the nerve root of the spinal cord. It is used in obstetrics to reduce labor pain (Epidural anesthesia).
Lidocaine has to act for about three minutes and then has an anesthetic effect for up to three hours, depending on the dose.
Lidocaine is very often used by dentists to numb the roots of the tooth, and local anesthesia is also carried out using a lidocaine syringe.
In the case of painful inflammation in the mouth and throat or a sore throat, lidocaine can be used as a spray or lozenge to provide relief.
Lidocaine can also be applied locally in the oral cavity to numb teething pain in babies.
Lidocaine is not only available as an injection solution, but also as sprays, ointments or drops. The application of lidocaine for superficial anesthesia on the skin is in principle possible anywhere and is used, for example, as a plaster for pain relief in painful infectious diseases, such as after a herpes zoster disease.
Lidocaine can also be given as a suppository to relieve the symptoms of hemorrhoids.
The drug is also used in an attack of gout, in an acute flare-up of the vertebral disease, ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis) and for inflammatory rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Even with an acute cluster headache attack, lidocaine can be given in the form of a nasal spray into the nostril of the side affected by the headache. This can provide pain relief within a few minutes.
Ointments or creams containing lidocaine, called 'delay creams', can be used by men to suppress premature ejaculation. These are available without a prescription and the effects last up to 60 minutes.
Lidocaine is also used for interventions on the heart that can lead to cardiac arrhythmias. For example, during a coronary angiography, a catheter examination of the coronary arteries, lidocaine is injected into the vein beforehand in order to prevent the risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Lidocaine works particularly well against rapid cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation.
Lidocaine with adrenaline
Lidocaine can be used in conjunction with adrenaline. There are ready-made preparations for this which contain both active ingredients. These mixed preparations should generally only be used by doctors and have clearly limited indications, while pure lidocaine has many areas of application.
The mixed preparations are only used in the area of local anesthesia. Here the adrenaline acts as a vasoconstrictor, which means that the lidocaine is absorbed and broken down more slowly. This means that relatively low doses of lidocaine are available over a longer period of time and the duration of the operation can be extended without further anesthesia.
The adrenaline contained in the mixed preparations results in further contraindications. These particularly affect patients who already have diseases of the cardiovascular system. Patients who take antidepressants, known as MAOIs, should also not receive any of these mixed preparations, as the breakdown of adrenaline is restricted in these patients. There are no studies on the mixed preparations of adrenaline and lidocaine for children. Therefore it is recommended to use other local anesthetics. The mixed preparations are injection solutions.
Maximum dose of lidocaine
The maximum dose for an average adult is 200 mg single dose of lidocaine without adrenaline and 500 mg single dose with adrenaline. However, these are only guidelines, as many factors play a role in the individual maximum dose. The most important thing here is the weight of the person affected. Liver function is also crucial, as lidocaine is broken down by the liver. Furthermore, the uptake of lidocaine depends on the dosage form. It is therefore difficult to make a general statement about the maximum dose.
Lidocaine for pain management
Almost all possible uses of lidocaine are aimed at relieving pain. In most cases this is a local pain relief. Sprays, plasters, gels, ointments, injections, mouthwashes and other options are suitable as dosage forms. The type of application varies depending on the location and type of injury or inflammation. One advantage of pain therapy with lidocaine is that it works quickly.
Lidocaine can also be used for pain therapy during and shortly after operations. It does this through the bloodstream. Lidocaine is not officially approved for this.
Lidocaine for migraines
In the case of migraines, topical application of lidocaine via a nasogastric tube can both stop the acute attack and prevent further attacks in the following days. This is done by numbing a nerve knot in the area of the root of the nose, the so-called pterygopalatine ganglion.
This anesthetic works longer than the lidocaine itself can be detected, as the nerve node acts as a kind of reset button for migraines. The circulation is therefore interrupted once and the migraine attacks become less frequent at first. However, even this migraine therapy is not a cure.
Read more on this topic at: Therapy for migraines, homeopathy for migraines
Lidocaine for hemorrhoids
Lidocaine can be used in various dosage forms to treat pain caused by hemorrhoids. One possibility is the administration of suppositories, another form is an ointment. It is also possible to use hemotamps, which are a type of soaked tampons. It is important that all dosage forms are used correctly. Regardless of the dosage form, it should be remembered that lidocaine can only relieve pain and does not lead to the cure of hemorrhoids. Most drugs that contain lidocaine for pain relief from hemorrhoids are available over the counter in pharmacies.
Read more on this topic at:
- Home remedies for hemorrhoids,
- How To Treat Hemorrhoids Successfully,
- Hemorrhoids - How to Get Rid of Hemorrhoids Using Homeopathy
How lidocaine works
Lidocaine acts as a local anesthetic on our nerves. A nerve picks up a stimulus such as pressure or temperature via a large number of nerve endings and forwards this signal to the spinal cord or brain, where we perceive the stimulus as pain, for example. This forwarding takes place with the help of minerals like potassium and sodium.
Lidocaine influences the sodium channels and thus prevents the stimulus from being transmitted. Thus, for the moment that lidocaine is active, the pain cannot be perceived, the area is numb.
Such sodium channels are also found in the heart, where they are important for the heart rate and the heart rhythm. If lidocaine blocks these channels in the heart, the heartbeat slows down and the rhythm can normalize. This is used in the use of lidocaine for cardiac arrhythmias.
Lidocaine as a drug
Lidocaine is not known as a drug in isolation because, unlike cocaine, it does not cause intoxication and does not contain any addictive components. However, drug dealers use lidocaine to stretch cocaine. This is done because the purity of cocaine is often tested by a feeling of numbness when wiping the gums, and the addition of lidocaine means that the consumer is presented with a particularly pure substance. In addition, the taste of lidocaine is just as bitter as the taste of cocaine and is therefore not recognizable to the consumer. Due to the undesirable side effects of lidocaine, such as cardiac arrhythmias, such an admixture can be life-threatening for the consumer. There is an increasing number of deaths from cardiac arrest caused by a lidocaine overdose, especially among users who use cocaine intravenously. However, because cocaine has similar side effects, it is difficult to distinguish which deaths are due to the diluent lidocaine and which are due to the cocaine itself. About a third of the cocaine samples found contain lidocaine.
When should lidocaine not be used?
Local anesthesia is usually a very gentle way of eliminating pain. However, lidocaine should not be given if the patient already has heart failure or low blood pressure. Certain cardiac arrhythmias (such as grade II AV block), shock, epilepsy, and heart attacks are also contraindications to the use of lidocaine.
Lidocaine can cause allergic reactions and must not be used if you are already hypersensitive to lidocaine or a similar active ingredient.
In addition, infections at the site of local anesthesia are a contraindication for lidocaine. Patients with severe kidney or liver disease should only receive lidocaine in exceptional cases, as it can lead to increased drug concentrations in the blood.
During pregnancy, lidocaine should only be used as an injection solution in exceptional cases and under medical supervision, as it can harm the child via the placenta. Superficial use is harmless during pregnancy.
Read more about Local anesthetics in pregnancy
Lidocaine can also be used while breastfeeding, but it should not be applied to the breastfeeding breast.
An external application of lidocaine as a cream, gel or ointment is harmless in children and may be used. If lidocaine is to be injected, however, this should only be done in children under medical supervision.
There are special restrictions on the use of lidocaine on the spinal cord. Particular caution is required here in patients with bleeding disorders, increased intracranial pressure or reduced blood volume.
Side effects of lidocaine
Adverse effects after using lidocaine do not have to occur, but they can occur with different frequency depending on the dosage form. Lidocaine is usually well tolerated, with occasional pain in the legs or a sudden drop in blood pressure upon injection.
Rare side effects can include restlessness and seizures; some patients report a numb tongue, dizziness, or drowsiness. If ringing in the ears occurs, this is an early sign of lidocaine overdose and should be treated. Cardiac arrhythmias can occur during lidocaine therapy and allergic reactions such as hives, shortness of breath and circulatory disorders are also side effects of lidocaine.
The drug should not get in the eyes or open wounds. In this case, it must be washed out thoroughly with water immediately.
When using it in the mouth and throat, it should be noted that lidocaine causes a feeling of numbness and thus increases the risk of bite injuries. In addition, there is a risk of swallowing, especially in children, as lidocaine impairs swallowing.
Read more on the topic: Side effects of local anesthesia
Allergy to lidocaine
In contrast to undesirable side effects, which often result from overdosing, allergic reactions show up even with very small amounts of the drug. In many cases, an allergy to lidocaine manifests itself in relatively harmless symptoms, such as reddening of the skin and local swelling. In rare cases, however, an allergic shock (anaphylactic shock) can also occur from lidocaine.
It is therefore recommended to carry out a sensitivity test (allergy test) in people who are prone to allergies. Since lidocaine preparations contain other substances in many dosage forms, a possible allergy to these additives should also be considered. In the case of a known allergy, other local anesthetics with the ending -cain should also be avoided.
Read more on this topic at: Allergy diagnostics
Lidocaine interactions
Lidocaine can be administered in different dosage forms. Interactions with other active ingredients usually only occur when a lidocaine solution is injected, local application forms would have to be used for a very long time and in high doses to cause interactions.
Drugs that affect the heart rhythm (such as calcium channel blockers and antiarrhythmics) may increase or decrease the effect of lidocaine on the heart's action. The effect of lidocaine can be increased by taking antihypertensive drugs (e.g. beta blockers) at the same time, while anti-epileptic drugs can decrease the effectiveness of lidocaine.
Dosage forms of lidocaine
spray
When used as a spray, the skin and mucous membrane can be effectively numbed with lidocaine. Spray can be used especially in the ear, nose and throat area to reduce sensitivity. By spraying into the pharynx, examinations can be carried out in this area without immediately causing the patient to gag. Small interventions such as cutting the eardrum (Paracentesis) can usually be carried out without problems and painlessly after using lidocaine pump spray.
Furthermore, the spray can be used as a support for gels and plasters in order to strengthen their effect for a short time. The spray can also be used to relieve pain when cleaning abrasions or to relieve pain from superficial burns.
A slight burning sensation on the skin immediately after spraying is harmless and usually disappears quickly, at the latest when the numbing effect occurs. The spray must not be used in children under two years of age because of the menthol content, as it can cause severe irritation to the airways. Likewise, the lidocaine spray must not be used to anesthetize the eyes.
You can find a lot more information under our topic: Lidocaine spray
band Aid
You can also take advantage of the effects of lidocaine with patches. Many people suffer from permanent pain in a certain area of the skin after being infected with the herpes zoster virus. A patch with lidocaine can continuously relieve pain over a longer period of time by continuously releasing a small amount of lidocaine from the patch to the skin. A patch with a concentration of 5% is available in Europe. The duration of action here is around 12 hours, then the patch must be removed. After a patch-free break of 12 hours, another patch can be applied. Here, too, the maximum dose must be observed, especially if several plasters are applied at the same time (maximum permitted amount: 3 plasters at the same time).
If the amounts are too large, there is a risk of serious side effects on the cardiovascular system, as a certain amount always gets into the body. A plaster must not be used on wounds or mucous membranes, as the amount of lidocaine that gets into the body increases enormously. Caution is advised here with people who are particularly sensitive to lidocaine in the body. These include patients with impaired liver and kidney function. Because of the harmful metabolic products of lidocaine, long-term use is only recommended if absolutely necessary and should be discussed in detail with the attending physician.
You can also read our article on the subject: Lidocaine patch
gel
Lidocaine in gel form is particularly suitable for the local treatment of painful wounds or inflammation of the oral mucosa or the gums. The lidocaine contained in the gel temporarily numbs the affected areas of the mucous membrane, making it possible, for example, to eat or drink painlessly.
For teething infants, the gels are available in extra child-friendly doses to make teething more bearable. Some gels available on the market also contain anti-inflammatory and soothing natural ingredients such as sage or chamomile. Since the duration of action is very short due to the continuous production of saliva, more frequent use is necessary, but the recommended maximum dose should always be observed in order to avoid side effects.
- Lidocaine gel
Cream / ointment
Lidocaine can be used as a cream or ointment to temporarily numb a wide variety of parts of the body. A cream is simply said to be an ointment that is slightly thinner due to its higher water content. The area covered with cream will be temporarily numb and neither pain nor other sensations can be felt. After applying cream, even minor superficial interventions on the skin are possible (e.g. taking samples from birthmarks).
In children or other fearful patients, applying lidocaine before the need for needle pricks can make them painless. For this, however, a thick layer of cream is necessary, which is attached with a covering bandage. The duration of the anesthesia is then about 1-2 hours. Another area of application of the cream is the treatment of painful skin changes in the anal area such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures (= painful tears in the mucous membrane in the anal area).
More information on the use of Lidocaine as an ointment read here.
syringe
Lidocaine, as an anesthetic in a syringe, is mainly used by dentists to numb the nerves in the mouth area during surgery. After injection, the effects begin to set in after 10-15 minutes and last for 1-1.5 hours. After this time, however, the feeling does not come back suddenly, but very slowly.
As described for the patches, lidocaine should only be used carefully in patients with heart disease, as accidental injection into a vessel can cause a large amount of lidocaine to enter the body and cause side effects. What is an unintended side effect with plasters and local anesthesia is even desired for certain types of cardiac arrhythmias and so lidocaine is even injected directly into a vessel as the drug of choice.
Read more on the subject at: Local anesthesia at the dentist
powder
Lidocaine as a powder is used more in the drug scene than in medicine, although there is a ready-made powder from a supplier on the German pharmaceutical market. In the drug scene, lidocaine in powder form is often used to stretch cocaine or heroin, as the powder looks the same on the outside and is also similar in taste to coke. What is missing, however, is the intoxicating component, the kick.
In the last few years in particular, increasingly high doses of lidocaine have been discovered in the drug powder, as it is cheaper than the more expensive cocaine or heroin. The high doses, however, have the side effects already described, so that the admixture has often led to deaths due to lidocaine overdoses.
Suppositories
Lidocaine can also be given in suppository form. Here, the effect of lidocaine is used as a local anesthetic to soothe painful or itchy areas in the area of the anus. These include hemorrhoids, cracks in the anus, minor injuries and abscesses, and rectitis. Lidocaine can also be used as a suppository before and after painful examinations in the anus area. Unless otherwise prescribed, the normal dose is one suppository containing 60 mg lidocaine twice a day. There are different manufacturers and preparations, which is why the approvals for different applications sometimes differ.
Read more on this topic at:
- Home remedies for hemorrhoids,
- How To Treat Hemorrhoids Successfully,
- Hemorrhoids - How to Get Rid of Hemorrhoids Using Homeopathy
- Pain in the anus
Mouthwash
Another way to administer lidocaine is a mouthwash solution. Here too, the analgesic and numbing effect of lidocaine is used. The mouthwash solution is used for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa such as mucositis. This inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs particularly in patients who are receiving chemotherapy or radiation and can represent a great burden for the patient. Lidocaine helps to calm the pain and promotes the healing of the mucous membrane. The effect only lasts for about half an hour and is therefore often used so that the patient can eat without pain.
Read more on this topic at: Inflammation in the mouth, inflammation in the corner of the mouth
Lozenges
Lidocaine is used very frequently as a lozenge to numb and relieve pain in the case of sore throats or inflammation of the gums. The lozenges are over-the-counter and have a maximum dose of eight tablets per day.Overdoses are not known with this dosage form. In addition to lidocaine, the tablets often contain antibacterial and disinfecting substances. So far there are no studies on whether the drug can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Read more on this topic at: Sore throat - get rid of it quickly !, Inflammation of the gums with pus
Lidocaine in condoms
In low doses, lidocaine in condoms can delay the time until ejaculation and is therefore suitable for treating men who suffer from premature ejaculation. This is done by numbing the tip of the penis and thus reducing feeling perception. These numbing condoms are available over the counter in drugstores. Anesthesia of the partner is not excluded.
Lidocaine as a lubricant
Lidocaine is mainly used as a lubricant in urology. It is used for painless and injury-free insertion of urine catheters and endoscopes into the urethra. The effects set in five to ten minutes after administration and last for 20 to 30 minutes. Antibacterial substances are usually added to the lidocaine in order to avoid infections during the catheter installation. Another area of application is endotracheal intubation, for example as part of anesthesia during operations. Here too, lidocaine is used to ensure intubation is as injury-free as possible.