Osteochondrosis dissecans
Synonyms
Bone necrosis, bone death, Ahlbäck's disease, Aseptic bone necrosis, joint mouse, dissecat, osteochondritis dissecans, Osteonecrosis, OD, dissecting osteochondrosis, Osteochondrosis
definition
Osteochondrosis dissecans (OD) is a disease that often occurs in growing age and young adulthood, about 85% of which affects the knee joint. In the course of this disease, bone death near the cartilage occurs, whereby a piece of cartilage located above the affected bone area can detach from its composite (free joint body, jointed mouse, dissecat).

anatomy
The knee joint is formed from the upper and lower leg bones and the kneecap. Osteochondrosis dissecans predominantly affects the joint-forming thighbones (femoral condyles). Usually the lateral part of the inner (medial) femoral condyle is affected, but the outer femoral condyle or the posterior kneecap can also be affected.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
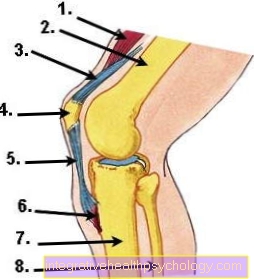
Figure knee joint
- Thigh muscles (Musculsus quadriceps femoris)
- Thigh bone (femur)
- Thigh tendon (quadriceps tendon)
- Kneecap (patella)
- Kneecap tendon (patellar tendon)
- Kneecap tendon attachment (tibial tuberosity)
- Shinbone (tibia)
- Fibula
causes
The cause of the development of osteochondrosis dissecans is largely unknown (ideopathic). One of the existing and most widely accepted theories sees recurring pulse loads on the knee joint as the cause of the development of osteochondrosis dissecans. It should therefore be a mechanical damage to the knee joint, as can occur in sports with recurring stopping or pushing movements. Other theories describe a nutritional and / or circulatory disorder of the knee joint bone, improper loading, ossification disorders and genetic influences. So far, however, no theory has really been able to explain osteochondrosis dissecans.
Symptoms of osteochondritis dissecans
A trend-setting medical history in osteochondrosis dissecans (anamnese) there is not any. More often it is about sporty adolescents and young adults who suffer from the symptoms.
In the early phase of osteochondrosis dissecans there are no characteristic symptoms or complaints. At first nothing is noticed of the increasing bone death. Incidental findings on x-rays of the knee joint are possible.
Later on, patients with osteochondrosis dissecans can suffer from load-dependent knee joint pain. This pain is uncharacteristic and difficult to describe for the patient. Cartilage breakdown products can lead to inflammation of the mucous membranes (Synovitis / synovitis) and joint effusions. If a joint mouse has finally formed, symptoms such as entrapment and blockages in the movement of the knee joint (extension and flexion inhibition) can occur. The joint mouse can damage healthy knee cartilage. Osteochondrosis dissecans disease is counted among the pre-arthrosis, i.e. As a result of this disease, osteoarthritis of the knee (Gonarthrosis) train.
A bilateral disease can exist in about 25%. These do not have to correlate exactly with one another in terms of time.
Read also the topic: Cartilage flake
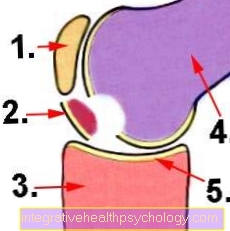
Illustration osteochondrosis dissecans
- Kneecap (patella)
- Joint mouse = free joint body
- Shinbone (tibia)
- Thigh bone (femur)
- Articular cartilage
pathology
So for a largely unknown cause it comes in a circumscribed, cartilage bearing bone area of the knee joint to a creeping bone death. Usually the circumscribed area is no larger than a cherry or plum pit.
More rarely, it can also be several square centimeters. In the very early phases of the disease, only very discrete bone changes can be detected. Later, there is a sharp demarcation between the dying bone tissue and the healthy bone tissue, which can be recognized by bone condensation (sclerosis). The Blood supply is now completely cut off.
By the Bone death the associated cartilage region increasingly loses its bond with its bony substrate. Steps the Osteochondrosis dissecans further on, a piece of cartilage (dissecate) or a piece of cartilage / bone is completely loosened from the rest of the cartilage. An initially connective tissue connection can ultimately no longer hold the dissecate, which leads to the formation of a free joint body. In this case one likes to speak of a jointed mouse. The associated dead bone area is called the mouse bed.
Stages
The Osteochondrosis dissecans is in different stages divided.
These stages mainly serve the Diagnosis and using X-ray examinations proven. For example, if a patient utters Stress-related pain, it can be determined by means of the X-ray examination whether the Osteochondrisos dissecans in one Initial stage located or whether the disease already more advanced is.
Overall, one differentiates three different stages of the diseasewhich are typically run through one after the other. However, a patient may find the first stage less bad and therefore only in the second stage Osteochondrosis dissecans see a doctor. In this case, the disease is diagnosed at stage 2, which does not mean that the first stage has not been passed.
Stage 1 however, is called the so-called Slumber stage because it goes unnoticed by many patients. At this slumber stage, the disease gradually begins. In this first stage it comes due to poor blood circulation to that one Inflammatory process in the bone arises. Here the bone cells are attacked. This first stage of osteochondrosis dissecans is described in medicine as osseous demarcation (Differentiation between destroyed, inflamed bone and healthy bone).
This stage can too divided into 2 stages become. In this case, stage 1 is called incipient inflammatory process viewed, the Bones still normal on X-ray appears and stage 2 of the Osteochondrosis dissecans is that then Stage of visible osseous demarcation. Assuming a total of 3 stages, the slumber stage is now followed by stage 2 of the osteochondrosis dissecans. In this stage 2 you can clearly see in the X-ray that the broken bone is detaching from the healthy bone and no longer supplied with blood will and accordingly no longer viable is.
The Cartilage layer can also affected be and either slightly swollen (edematous) or also have damaged shares.
in the Stage 3 of the Osteochondrosis dissecans then one sees a hole in the area in which the dead piece of bone found (so-called. Mouse bed or empty dissecat bed), the piece of bone itself remains as a dead piece of bone (so-called dissecate or Joint mouse) back.
Authors who assume 4 stages of osteochondrosis dissecans refer to this last stage as stage 4, the above-mentioned stage 2 is then regarded as the third stage.
Exclusion diseases
Exclusion diseases:
The excluded diseases include:
- Meniscal injury
- Patellar tip syndrome
- Chondromatosis
- Tumors
- Rheumatism / rheumatoid arthritis
- Reactive joint inflammation
- Osteochondral fractures (bone / cartilage fractures)
- Ossification disorders
- "Growing pains" / overwork pains
classification
X-ray stages according to Rodegerdts et al. (1979):
- Stage I: slumber stage (detection only possible by MRI)
- Stage II: Clear brightening
- Stage III: demarcation of the OD area by a sclerotic edge zone
- Stage IV: Free joint body
At the ankle
The Osteochondrosis dissecans on the ankle is a rare disease, only roughly 5 percent In all cases the ankle is affected, the disease occurs more often on knee or on Elbow in front. Osteochondrosis dissecans at the ankle is probably caused by repeated ankle injuries, so is through traumatic cartilage and bone damage triggered. Heavy sporting activities in the child or adolescent seem to increase the risk of osteochondrosis dissecans.
At Children with osteochondrosis dissecans usually already one supports six weeks of rest natural healing of the ankle. In adults it is often inevitable under one Ankle surgery (Arthroscopy) a operative re-fixation or one Bone graft perform.
The disease is often first noticed by pain deep down in the upper ankle. The pain typically increases under exertion and subsides at rest. The osteochondrosis dissecans only rarely shows itself as clearly delineated pain or blockages. Sometimes there are no symptoms and the disease is discovered by accident. The condition increases the risk of one Ankle wear (arthrosis) due to damage to bones and cartilage. To avoid this, the treatment of osteochondrosis dissecans on the ankle should start as early as possible.
On the talus
In the case of osteochondrosis dissecans of the ankle, certain areas of the Talus (Ankle bone) affected. The talus is a short bone and part of the ankle joint and the tarsusl. It connects the foot with the leg and lies between the ankle fork (Malleole fork) and the calcaneus (Calcaneus). On the top of the talus is the Trochlea tali (Ankle roll), which is arched in the middle and has prominent side edges. Osteochondrosis dissecans affects them upper edges of the talusthe inner edge being affected more often than the outer. Because the inner edge is the main weight-bearing part of the joint surface, which suggests that the osteochondrosis dissecans on the ankle load-dependent arises.
Osteochondrosis dissecans on the knee

The most common place of expression an osteochondrosis dissecans that is knee (about 75 percent all cases). In most cases, the weight-bearing parts of the joint surfaces are affected, in the knee the lateral (lateral) and medial (inner) condyles on the thigh side.
First and foremost is the bone affected by the disease as the cartilage from the joint is supplied with nutrient-rich synovial fluid. The cause of the death of a bone near the joint under the cartilage is likely one temporary circulatory disorder.
Often the disease is associated with a disorder of movement run and Leap connected. This leads to a short-term rotation in the knee with subsequent impact of the bones involved in the joint.
But also one abnormal meniscus change (e.g. a Disc meniscus) and child rheumatism are discussed in relation to osteochondrosis dissecans of the knee.
The disease mainly affects children, adolescents and young adults, and about twice as many men as women get the disease. In about 70 percent of the cases it is only one Knee joint affected by osteochondrosis dissecans.
The Symptoms can be very different and occur frequently Pain on exercise of the affected knee joint, but also Joint swelling by forming a Joint effusion and Restrictions on movement of the knee joint are described.
If the severity is low or in young, still growing people, the disease can through physical conservation and physiotherapy care be treated. Only when there is no healing or the disease worsens is one Knee arthroscopy required.
The best and safest method of diagnosis is to do one Knee MRI´s.
At the elbow
The Osteochondrosis dissecans of the elbow is likely through one Circulatory disorder part of the Elbow bone conditionally. Another hypothesis is that the osteochondrosis dissecans on the elbow is caused by a Overload response of the bone as a result of extreme and frequent arm movements (e.g. during throwing movements in sports).
In most cases, osteochondrosis dissecans affects the outer roll of the upper arm (Capitulum humeri), but can also be done on the spoke head (Caput radii) or on the inner arm roller (Trochlea humeri) occur.
In the case of osteochondrosis dissecans on the elbow varying degrees of pain felt in the affected elbow, as well Crack or Rub, Blockages or Entanglements occur.
The diagnosis is usually made via a X-ray of the elbow joint, the representation of the elbow is more sensitive Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as they can also represent earlier stages of osteochondrosis dissecans.
Also read our topic: MRI of the elbow
The disease can take very different courses. In some cases the osteochondrosis dissecans runs through the elbow unproblematic and without consequences, so can the disease heavy permanent marks leave. Osteochondrosis of the elbow has a favorable prognosis, the younger the person concerned is when the Growth plate the outer humerus is still open and the smaller the spatial extent of the osteochondrosis dissecans.
The therapy consists in one Sports break, the gift of anti-inflammatory drugs, possibly also one Plaster immobilization for some days. A surgery may become necessary if the osteochondrosis dissecans at the elbow worsens, the affected bone area threatens to detach, or a free joint body (Piece of bone that "floats" freely in the joint) was created.
MRI
A MRI is an imaging technique for displaying Structure and function of tissues and organs in the body. An MRI machine generates very strong magnetic fields with which certain atomic nuclei in the body are excited and an electrical signal is induced. It will no harmful X-rays or other ionizing radiation generated.
An MRI scan is available for Diagnosis of osteochondrosis dissecans most reliable and helps with staging. An X-ray often shows the typical changes long after the actual circulatory disorder, which is why the diagnosis is often made late. Before MRT examinations were possible, the osteochondrosis dissecans was only discovered when the affected piece of cartilage-bone (joint mouse, dissecat) was detached, as this triggered blockages.
Using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the location and size the osteochondrosis dissecans, the Depth expansion and above all precisely measure the involvement of the overlying cartilage. This means that statements about Stability of the affected joint to be hit. The MRI is also very suitable for monitoring the course of the disease, but simple X-ray examinations can also be carried out if necessary.
An MRI should in any case both sides be carried out as the osteochondrosis dissecans in about 40 percent of cases occurs bilaterally.
Read a lot more information under our topics:
- MRI
- MRI knee
- MRI elbow
- Ankle MRI
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis dissecans
To diagnose the Osteochondrosis dissecans includes a detailed survey of the anamnese (Medical history).
The physical exam will reveal other possible diseases (Differential diagnoses) excluded as far as possible.
There is no specific examination technique with which osteochondrosis dissecans can be reliably diagnosed. Recurring blockages in advanced osteochondrosis dissecans caused by a pinched joint mouse are trend-setting. The same phenomenon can also be found in certain forms of meniscus injuries and in free joint bodies of other causes (e.g. chondromatosis).
Imaging diagnosis
The Sonography (Ultrasonic) is a readily available and suitable method for detecting a knee joint effusion. Depending on the location, one free joint body this can also be proven.
The X-ray can be an advanced Osteochondrosis dissecans prove. The standard x-rays a.p. are usually sufficient. (from the front) and on the side. The tunnel recording is also helpful after Frik. The typical changes are most common in the area of the lateral portion of the inner thigh roll (Femoral condyle). The X-ray image does not provide evidence of the initial stages with the onset of bone death. The first signs are an oval bone lightening (dark spot) at the described area, which later becomes a whitish one Edge hem (Sclerotic zone) is limited. The resulting dissecate can eventually become detached from its composite as a whole or in several small parts. This can be recognized by the evidence of free joint bodies and a depression in the knee joint bone.
With the MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) the respective region (e.g. MRI of the knee, MRI of the ankle or MRI of the elbow etc.) is an early diagnosis of the Osteochondrosis dissecans possible. When making a diagnosis, it is also important to exclude almost all other possible diseases. The stage of bone death can be determined by the MRI as well as the Nutritional situation of the dissectate.
The nutritional situation of the dissectate can also be used to predict the extent to which a rejection of the dissectate is to be feared. However, the MRI cannot give an exact time. Dissections that have already been rejected can be reliably detected in the MRI.
The most accurate examination, however, is with one Knee joint endoscopy (arthroscopy) possible if the knee joint is affected. If there is another joint, this can be arthroscoped in the same way (e.g. ankle)
It has the advantage that the stability of the OD area can be safely checked with a hook (see figure: loose OD area, very enlarged) and it can be seen whether the cartilaginous surface structure is still intact or whether it is already damaged. Suitable surgical therapeutic measures can then also be carried out in the same session.
-> Continue to the topic Osteochondrosis dissecans therapy
Complications
The usual surgical complication options apply:
- Infection, bone infection, wound healing disorder
- Nerve injuries
- thrombosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Recurrence / failure of the operation = renewed joint mouse, renewed loosening of the cartilage bone fragment
- Early osteoarthritis
forecast
The Osteochondrosis dissecans is a serious disease for the knee joint. If left untreated, it counts Osteochondrosis dissecans to pre-arthrosis, i.e. those factors that lead to the development of early knee arthrosis (gonarthrosis). Through the above surgical measures, the damage to the knee joint can be reduced to a minimum and the ability to exercise can be regained for the mostly young patients.
The spontaneous course can be waited for, especially in very young patients. A Spontaneous healing is described in up to 50% of cases.
The prognosis is best if the dissection can be prevented by revitalizing the bone area. All other procedures with refixation of the dissection or the introduction of a replacement tissue have a poorer prognosis, since the knee joint reacts very sensitively in the long term to even the smallest irregularities in the cartilaginous surface structure.