peppermint
Synonyms in a broader sense
Vegetable synonyms: peppermint belongs to the mint family (Lamiaceae), like lemon balm or sage. They are also called feverfew, cat's weed, prominzen or taster, as well as garden mint or English mint.
Latin name: Mentha piperitae
English: peppermint
Explanation / definition

Peppermint, also called Mentha piperita in Latin, grows as a perennial herb up to 90 cm high. The leaves sit on branched, bare, purple stems. The shape of the leaves is oblong to ovate. The typical menthol scent arises when the leaves are rubbed.
The corolla consists of a purple four-column corolla lobe. The healing power of peppermint is mainly in the leaves. The most important pharmacological, effective ingredients are the essential oils with the main component menthol, as well as the tannins and flavonoids.
Plant description
The peppermint is a bastard of two wild types of mint, the water mint and the spearmint. The medicinally used peppermint is multiplied by cuttings in cultures. There are two harvests a year possible.
The plant grows to a height of 80 cm. Square stem, opposite leaves, elongated and roughly toothed. The pink flowers stand close in spike-like inflorescences.
Wild growing relatives of real peppermint are water mint and horse mint.
Occurrence: The most closely related variety, "Mitcham", comes from England and is grown in our crops.
Summary
The healing power of peppermint was already described by many healers in antiquity.
The essential oils, primarily menthol, as well as the bitter substances and the tannins, contribute to the medicinal properties of the plant.
Peppermint came to England via North Africa and is still known today as spearmint. The typical spearmint smell arises when the leaves are rubbed.
In folk and monastery medicine, peppermint is of great importance because it offers a very wide therapeutic spectrum.
history
The peppermint (Mentha piperita) can now be described as an ancient medicinal plant. It was found in ancient Egyptian graves as a burial object.
In the current culture form, the medicinal plant peppermint was described in England in the 17th century. It is presumably a cross between the brook mint and the corn mint.
The biologist John Ray gave it the name Peppermint in 1696. As early as 1705, the healing properties of peppermint were described by the writer Dale. The leaves and the oil obtained from them were used for medicine.
Manufacturing
The peppermint will cultivated in North America and Europe.
With us is the medicinal plant mainly in Bavaria and Thuringia cultivated. The active substance-rich substances of the medicinal plant peppermint are in the leaves.
To medical application come dried peppermint leaves, as well as that oil, which is obtained from the freshly harvested, flowering branch tips by steam destination. The main ingredient is the essential oil with the main ingredient Menthol.
Indeed only in connection with the other ingredients the peppermint unfolds its specific effect. Flavonoids, tannins, bitter substances and about 60% menthol lead to a healing effect and relief. The leaves are the starting material for medicines. From the leaf extracts the peppermint arise Dragees, tablets and peppermint oil.
ingredients
Tannin, bitter substance, a lot of essential oil with menthol as the main component
Therapy / areas of application / effect
The peppermint is universally applicable.
For us it is of the greatest importance as a natural remedy and medicine.
As a cosmetic, food or household remedy, peppermint can be found in almost every household.
The peppermint leaves were in the Folk medicine
- nausea
- Nausea
- Cycle fluctuations
- Vomiting and at
- Applied to colds
Today there are many scientific studies that prove the effectiveness of peppermint. The medicinal use of the medicinal plant peppermint (Mentha piperitae) is recommended for the symptomatic treatment of
- Indigestion
- Flatulence
- Inflammation of the gastric mucosa
- cramp-like complaints of the gallbladder or biliary tract (e.g. gallstones)
The peppermint oil, which is obtained from the medicinal plant peppermint, has a positive effect when used internally
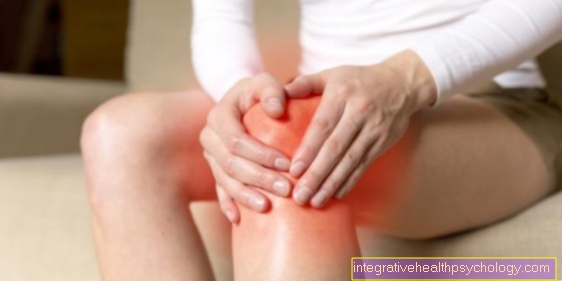
- rheumatic complaints (rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism)
- Tension headache / headache
- Migraine,
- Itching and
- Hives
For external use, the peppermint oil can be used Muscle tension and nerve pain are used.
The antispasmodic and antibacterial effects of peppermint oil and peppermint leaves have been confirmed in clinical trials. Tension headache / headache could be eliminated in studies with peppermint oil when applied externally.
Also at migraine good results can be achieved.
At Upper respiratory tract infections Peppermint oil is placed in a warm water bath. Then the steam is inhaled with a towel over the head. The respiratory tract become free again.
The drug stimulates the flow of bile. The contained menthol is excreted through the bile and here it unfolds its anti-inflammatory effect. Menthol also has an effect on nerve endings that are sensitive to cold.
Side effects and interactions
Peppermint oil is allowed Not on the chest or that Face of babies or toddlers be applied!
Mint tea is made by the high menthol content not well tolerated by children.
Beware of allergies!
At Overdose can it to Inflammation in the digestive tract come. It can also increase with internal application of the peppermint oil heartburn come.
In the pregnancy you should Medicinal plant peppermint use cautiously.
Please talk always before using the medicinal herb peppermint with your doctor !!!
Dosage form and dose
Peppermint is used mainly in tea (next to the chamomile).
Many teas are mixed together and thereby increase the effect. For the Making a tea two to three teaspoons of peppermint leaves are scalded with 150 ml of hot water, let steep for 10 minutes, and drink three times a day.
Peppermint oil is used internally for digestive problems. One takes one to four drops up to three times a day.
At Irritable bowel syndrome in the form of gastro-resistant capsules.
At general Indigestion and fatty foods, Loss of appetite, Menstrual cramps and nausea Drinking a cup of mint tea can do that Relieve discomfort.
External use of peppermint oil:
- for inhalation 3 to four drops in hot water
- for skin problems as an ointment with menthol.
- for tension headaches / headaches, migraines and weather sensitivity as a 10% solution.
- for joint pain (arthralgia), muscle tension and neuralgia (nerve pain)
Manufacturer / trade name
Manufacturers are named as examples and were selected at random. we have with none Manufacturers a personal connection!
Carminativum - Hetterich® 20 ml € 3.74
Carminativum - Hetterich® 100 ml € 12.95
Status: January 2006
Phytopharmaceuticals in Germany
The list of the best-selling herbal preparations led by far the ginkgo:
- ginkgo
- Johannis herbs
- Devil's claw
- Horse chestnuts
- artichoke
- Milk thistle
- Nettle
- Umckaloabo
- Hawthorn
- ivy
A list of all medicinal herbs / medicinal plants that we have already published can be found under: Medicines A-Z.