Thyroid Removal
definition
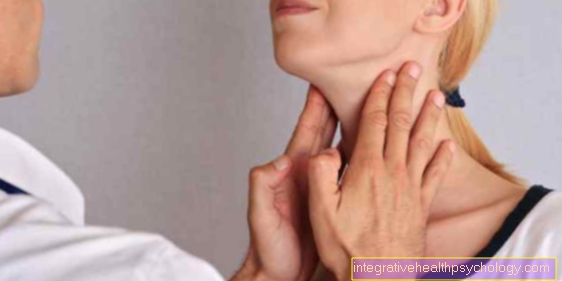
The thyroid lies in the front of the neck directly in front of the windpipe. It consists of 2 lobes and is mainly used for human metabolism as well as for Calcium provision for the bone responsible. This is regulated by the production of certain hormones.
Various diseases that affect the thyroid gland can lead to either one Hyperthyroidism or to one Hypothyroidism to lead. These are mainly noticeable through changes in weight, the sensation of warmth and cold, the heart rate and the level of activity. There are different causes, a so-called surgical removal of the thyroid gland Thyroidectomymake necessary. The thyroid gland can be removed either on one or both sides, depending on whether only one flap or both are responsible for the symptoms.

Causes of Thyroid Removal
There are many different causes in favor of thyroid removal. This can be both benign (benign) as well as malicious (malignant) Be changes. Depending on whether only one side or both sides are affected, a total thyroid removal (Thyroidectomy) or only one side of the thyroid is removed (Hemithyroidectomy).
A Enlargement of the thyroid gland is referred to as Goiter. If the thyroid gland is characterized by nodular changes, the affected part or the whole thyroid gland can be removed in order to prevent recurrence. Even with the autoimmune disease Graves disease the thyroid gland is enlarged and removal may be necessary if the disease is severe.
Common causes of thyroid removal are malignant tumors the thyroid gland. There are different types of Thyroid cancerwho are differently aggressive. The thyroid gland is partially or even completely removed in all types in order to heal the patient.
Many benign tumors do not have to be removed despite the enlargement of the thyroid gland as long as they do not cause symptoms. However, if problems, for example in the form of Shortness of breathif the windpipe is narrowed, or difficulties swallowing occur, should be operated on. Even if the enlargement is a so-called adenoma, surgical removal of the thyroid may be necessary. An adenoma is a tumor that produces hormones itself. This can lead to a Metabolic imbalance come, which can be very dangerous for the person concerned. The operation prevents overproduction.
Operational sequence
The operation of a thyroid gland removal can be done either on one side or on both sides. These operations are performed under general anesthesia. The patient is operated on in the supine position and the head is hyperextended backwards so that the operating area is more accessible. After thorough disinfection, a four to five cm long incision is made on the front of the neck so that the surgeon can clearly see the thyroid gland. During the subsequent removal of the thyroid gland, particular attention must be paid to the recurrent nerve, which is close to the thyroid gland. A so-called neuromonitoring system can be used, which emits warning noises as soon as the nerve is touched by the surgical instrument. If the recurrent nerve is injured, this can lead to temporary hoarseness after the operation. In the case of bilateral injuries, breathing noises or shortness of breath may occur after the operation.
It also has to be on the very small Parathyroid glandsthat are in contact with the thyroid gland should be taken care of during the operation. These should be retained as far as possible, as they are Parathyroid hormone production an important role in the Calcium regulation take over.
The blood vessels of the thyroid are electrically obliterated during the removal so that there is no bleeding. After one or both lobes of the thyroid have been removed, the wound can be closed again. If the bleeding is profuse, it may be necessary to insert drainage tubes into the wound. These are thin tubes that carry the blood and wound secretion to the outside, where it is collected in small bags.
The actual operation takes about two hours with a total removal of the thyroid gland. Together with the preparation, induction of anesthesia and storage, however, about three hours can be included.
Duration of illness
As a rule, you have to stay in the hospital for about two to three days after a thyroid removal. It is allowed to stand up immediately after the operation. The length of the sick leave depends on the type of occupation. While office work can be resumed a few days after the operation, physical work must be avoided for around two weeks. If the patient is free of symptoms and has healed well, the incapacity for work can possibly be reduced by a few days.
Hashimoto
Hashimoto is an autoimmune thyroid disease in which the body antibody produced against its own thyroid tissue and thereby destroys the thyroid. This often causes the symptoms of a Hypothyroidismhow slow heartbeat (Bradycardia), Constipation, fatigue and weight gain. In some cases, however, the disease is symptom-free.
As a result of the destruction, the thyroid gland cannot produce any or fewer thyroid hormones, which is why it may be necessary to take the hormones in tablet form. This often helps to stabilize the patient's metabolism. As a rule, this is a lifelong intake of L-thyroxine necessary.
Graves disease
At Graves disease is it a Autoimmune disease. This means that the body produces antibodies that are directed against structures in its own body. In Graves' disease, antibodies are produced that bind to a receptor in the thyroid tissue and activate it there. The thyroid gland then releases hormones that interfere with the metabolism. This leads to an increase in the general level of activity and is often expressed in Racing heart, high blood pressure, increased sweat and Weight loss. There is also general unrest. Patients often fall from protruding eyes (Exophthalmos) on.
As a therapy, thyroid drugs can be taken, which ensure that the activity of the thyroid gland is reduced. The disease often regresses under this therapy. If this is not the case and Graves' disease leads to symptoms, a thyroid removal may be necessary and useful.
Thyroid Removal During Pregnancy
Thyroid removal, like any other operation, should not be performed during pregnancy if possible. There can always be unexpected complications that can put the baby at risk.
Is there a Graves diseaseSo should women basically advised against pregnancy due to the necessary medication intake, it increases more frequently than normal Early abortions comes. In addition, the antibodies are transferred to the unborn baby, which can have serious effects on the child's growth.
After a thyroid gland has been removed, there are no concerns about pregnancy if the replacement hormone therapy is properly adjusted. Only if the removal was carried out because of a malignant tumor and a therapy with radioactive iodine follows, no pregnancy should occur in the next 6 months.
Consequences of a thyroid removal
After a thyroid removal, some tests must be done to assess the success of the operation. First, it should be checked whether the so-called recurrent nerve (Recurrent laryngeal nerve) was damaged during the operation. Damage would make itself felt as hoarseness in a restricted speech function. However, hoarseness after the operation can also occur temporarily as a result of irritation from the ventilation tube. The calcium level in the blood should also be monitored after the operation in order to check the function of the parathyroid glands. If the calcium level drops very sharply, this indicates damage to the parathyroid glands.
Since the thyroid produces important hormones for the body, these must be replaced after a complete removal. These are triiodothyronine and thyroxine. These should be taken in tablet form after the operation. After about five weeks, the hormone dose is adjusted and individually set using a blood test. If only part of the thyroid has been removed, this is usually not necessary.
After the operation, vigorous physical activity should be avoided as much as possible for the first two weeks to ensure optimal healing of the wound. After about two to three days, the hospital can be left and after about a week the stitches are pulled.