Left ovary pain
introduction
Many women experience ovarian pain at least once in their lifetime. The pain in the ovary can occur both on the right and on the left.
In most cases, the women affected immediately assume a gynecological problem. But in fact, pain that occurs in the area of the left ovary can also originate from other organ systems.
If you have pain in the right ovary, see Pain in the Right Ovary for more information.

In particular, diseases of the colon or rectum can cause corresponding symptoms. In addition, if there is pain in the left ovary, it must be noted that it can be a discomfort without any disease value. During the normal menstrual cycle, especially women of childbearing age can experience pain in the ovaries.
If the pain occurs between the 12th and 14th day of the cycle, the symptoms can in many cases be related to ovulation.
However, ovarian disease is one of the most common causes of ovarian pain. For this reason, women who suffer from persistent symptoms should urgently consult a specialist as soon as possible.
In the event of severe pain on the weekend or on public holidays, you should even go to an emergency medical service or an emergency room. There, with the help of various diagnostic methods, it can be determined whether the pain can be traced back to a gynecological disease or whether the problem is to be found in the gastrointestinal tract.
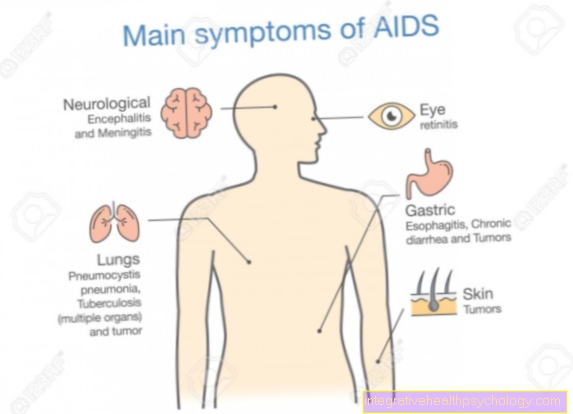
Figure pain in the ovaries

causes
The causes of pain on the left side of the ovary can be varied.
As a rule, the women affected initially assume that pain in the left ovary must be due to a gynecological disease. In fact, gynecological diseases are one of the most common causes of ovarian pain.
In addition, however, it should always be clarified whether there is another reason for the symptoms. Above all, irregularities in the gastrointestinal tract, especially diseases of the large or rectum, can also lead to pain on the left side of the ovary. In addition, the complaints can often be traced back to common, completely harmless, cycle-related causes.
- In women who suffer from ovarian pain between the 12th and 14th day of the menstrual cycle, this may only be an indication that ovulation has occurred. In this context, it must be noted that there are pronounced hormonal fluctuations in the course of the menstrual cycle. The rise in various female sex hormones ensures that one egg cell can mature in an ovary per cycle. From about the 10th day of the menstrual cycle, the so-called luteinizing hormone (in short: LH) and induces ovulation around the 14th day of your cycle. In some women, this process causes what is known as "middle pain" on the left or right of the ovary.
Read more on the subject at: Ovulation pain - In addition, pain to the left or right of the ovary can also be caused by slight contractions of the uterine muscles towards the end of the normal menstrual cycle. In these cases, however, the pain to the left or right of the ovary is usually less intense.
- In the event of severe pain on the left ovary, which increases in intensity as the disease progresses, inflammatory processes should urgently be ruled out. The so-called "adnexitis" (Inflammation of the ovaries) is one of the most common gynecological causes of left ovary pain. Inflammation in the ovaries is typically caused by pathogens that enter the body through the vagina and ascend via the uterus to the fallopian tubes. Affected patients usually have tenderness in the area of the inflamed ovary.
- Another common cause of left ovary pain is what is known as "endometriosis". The term endometriosis refers to growths of the uterine tissue that are deposited in the abdomen. Since these tissue growths also go through the normal menstrual cycle outside of the uterus, the affected women can experience severe, cramp-like pain on the right or left of the ovary.
- Ovarian cancer (Ovarian cancer) is classically painless and does not tend to cause pain on the left ovary. Typically, ovarian tumors are completely asymptomatic in the early stages. Most cancers of the ovary are only noticed by patients when the size of their abdomen increases in advanced stages. For this reason, it can be assumed that an ovarian cancer causing pain in the left ovary has already infiltrated nerve fibers.
- In addition to inflammatory diseases of the ovaries, benign, hormonal ovarian cysts can also cause pain on the left side. A cyst is an unnatural cavity in tissue that is filled with fluid. A cyst in the area of the left or right ovary can be less than several centimeters in size and thus put pressure on the ovary. These cysts can burst (rupture) spontaneously, causing severe pain in the left ovary area.
- Particularly in young, sporty women, rapid, unfavorable movement can also cause such a cyst to twist on its suspension. In these cases one speaks of a so-called twisted ovarian cyst. The affected women experience sudden, severe pain on the right or left ovary. A twisted ovarian cyst is a gynecological emergency that requires immediate medical treatment, as the blood supply to the ovary can be interrupted and in the worst case the ovary dies.
- In addition, the obstruction of the veins supplying the ovary by a blood clot can lead to severe pain on the right or left side of the ovary in the affected women. In this context one speaks of a so-called "ovarian vein thrombosis". It often occurs after the birth in the puerperium. Due to the lack of blood supply, the affected ovary can be permanently damaged within a very short time. The ovarian vein thrombosis can be found much more frequently in the area of the right ovary in a side comparison. A thrombosis that leads to pain on the left side of the ovary is comparatively rare.
- An ectopic pregnancy can also cause pain in the left ovary. Here, the fertilized egg does not implant itself in the uterus, but adheres to the fallopian tube. As the child grows, there is inflammation of the fallopian tube with the risk of rupture. The complications of an ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening, which is why a pregnancy test should always be taken if the left ovary is very painful.
How dangerous is left ovarian pain?
Most often, ovarian pain occurs as part of the natural female cycle during ovulation or in connection with menstrual bleeding. Both are harmless, harmless causes of the pain.
Especially at the fertile age of women, tissue from the uterus can migrate to other organs (Endometriosis), which settle in the ovary and cause period-dependent pain or changed bleeding. However, endometriosis can also lead to changes in fertility, which is why it should be treated in women who want to have children.
Ovarian cysts, which can cause pain with increasing size, do not represent a particular danger at first, but can trigger an acute and potentially life-threatening clinical picture when the stem is rotated. Often an ovarian cyst ruptures, which causes severe pain but is usually a harmless clinical picture without any health consequences. However, the cyst and ovary can also twist when the stem is twisted, cutting off the blood supply to the ovary. In the worst case, this ovary can die, which is why emergency medical treatment is important.
Regardless of age, ascending pathogens can lead to inflammation of the internal genital organs such as the fallopian tubes or ovaries, which leads to acute pain, accompanied by fever or foul-smelling discharge. If this is treated early and adequately, it usually heals without consequences; however, asymptomatic courses also occur which, after a long period of time, lead to adhesions and can be associated with sterility (infertility).
Read more on the subject at: Causes of Infertility
In addition, an ectopic pregnancy can cause acute pain, since the increase in size of the implanted embryo leads to pressure on the walls of the fallopian tube and can even lead to a rupture of the fallopian tube; this is also a life-threatening clinical picture.
However, even after a happy birth, complications such as the occlusion of an ovarian vein by a blood clot can lead to discomfort in the ovaries. The likelihood of a so-called ovarian thrombosis is increased after childbirth due to the generally stronger tendency to clot. With ovarian vein thrombosis, too, there is a risk that the ovary will die, which is why treatment must be carried out quickly.
Diseases of the left intestine can also trigger pain in the ovary area and thus be misinterpreted, so that if the gynecological findings are normal, a consultation with an appropriate specialist should be made.
Read more on the subject under: Abdominal pain on the left side - What do I have?
diagnosis
The diagnosis of pain in the left ovary usually involves several steps.
Above all, the detailed doctor-patient discussion (anamnese) plays a crucial role in this. By precisely describing the existing symptoms, the attending physician can often narrow down the possible cause of the pain. The doctor will also inquire about changes in the discharge, including the smell, amount, and color.
After the doctor-patient interview, an orientating physical examination is usually carried out. During this examination, not only the female genitals, but also the abdomen should be tested. In women who have an inflammation of the left ovary or an ovarian cyst, the abdomen is clearly tense.In addition, the pain on the left ovary can be increased by applying direct pressure on the left groin.
Regardless of whether the attending physician assumes a gynecological or abdominal cause for the development of the pain in the left ovary, an ultrasound examination should be carried out after the physical examination. During this examination, both inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity and a variety of gynecological diseases can be detected. In some cases, it is also useful to supplement the diagnosis with further examination methods.
Inflammatory processes can often be ruled out with a blood test. If there is inflammation that causes pain in the left ovary, the specific inflammation values typically increase. ly an acute increase in white blood cells (Leukocytes) and the C-reactive protein (CRP) can indicate inflammatory processes.
Read more on this topic at: Blood count.
Changes in discharge
There can be a variety of causes for the development of pain in the left ovary. For this reason, typical accompanying symptoms can help to narrow down the possible causes and thus to facilitate diagnosis. Changes in natural discharge can be observed in many of the diseases that can cause pain in the left ovary. The discharge is often changed, especially in infections of the female genital organs.
Patients who suffer from inflammation in the ovaries often notice a change in discharge before the pain occurs. Since bacterial pathogens enter the fallopian tubes via the vagina and uterus in the case of ovarian inflammation, the body tries to remove the germs by stimulating secretion production "flush out". In this condition, the discharge can appear thin or foamy.
Read more on this topic at: Inflammation of the ovaries.
In addition, the discharge from the bacterial infection often turns gray-white in color. The smell of vaginal secretions is also more severe than usual in ovarian inflammation, which leads to pain in the left or right ovary. Most of the affected patients even describe the smell of the discharge as fishy. During the gynecological examination, it is also noticeable that the vaginal environment has an increased pH value of more than 4.5 due to the changed discharge.
In addition, pain in the left or right ovary associated with altered discharge can also indicate an existing pregnancy. Especially in the first weeks of pregnancy, the hormone-induced loosening of the so-called “mother ligaments” can lead to pain in the ovaries. Due to the increasing blood flow to the abdomen, the production and secretion of vaginal secretions are also stimulated. In the case of an existing pregnancy, however, only the consistency of the discharge changes. While some pregnant women observe viscous, clear discharge, other pregnant women may experience increased discharge of milky-white discharge.
Read more on this topic at: Signs of pregnancy.
therapy
The treatment for pain in the left ovary depends largely on the underlying cause. For this reason, women who suffer from persistent or suddenly severe pain on the left ovary should urgently consult a specialist. If the complaints occur on the weekend or on a public holiday, an emergency medical service or even an emergency room may have to be visited.
In the course of a detailed diagnosis, the cause of the pain on the left ovary can be determined and appropriate treatment initiated.
In most cases, inflammatory processes in the ovaries are caused by bacterial pathogens that ascend to the ovary via the vagina. For this reason, antibiotic therapy must be initiated in the affected patients. Depending on the extent of the inflammatory processes, treatment can be either outpatient or inpatient.
If the pain in the left ovary is caused by an ovarian cyst or a twisted ovarian cyst, surgical therapy must be initiated. In this context, however, it must be noted that a cyst in the area of the internal organs does not always require treatment. For this reason, an ovarian cyst is usually only removed if it is causing pain on the right or left ovary. In the case of a twisted ovarian cyst, however, surgical treatment is mandatory. The reason for this is the fact that a possible clamping off of important anatomical structures can impair the affected ovary.
In the case of ovarian cancer, too, treatment consists primarily in the surgical removal of the tissue growth. The aim of the operation is to remove the tumor as completely as possible and in this way to significantly increase the probability of survival. In addition, chemotherapy is followed in many cases after the surgical treatment. The chemotherapeutic agents most frequently used for tumors in the ovarian area are the active ingredients carboplatin and / or paclitaxel. Due to the comparatively high side effects and the significantly lower treatment success, radiation therapy is usually not necessary in patients with ovarian cancer.
Read more on this topic at: Therapy ovarian cancer.
If the pain in the left ovary is not related to a gynecological disease but to an abdominal disease, a referral must be made to an internist. Depending on the underlying disease, this can initiate appropriate treatment.
Pain in the left ovary in various life situations
During the period
Left ovarian pain before or during your period is usually uncomplicated menstrual cramps. In most of the women affected, it can be observed that the symptoms start about one to two days before the start of their menstrual period and peak on the first day of their period.
Read more on this topic at: Menstrual pain.
In general, it can be assumed that any woman can develop left ovarian pain before and / or during her period. In actual fact, however, it can be observed in everyday clinical practice that especially young girls are affected by these complaints. The cause of this uncomplicated pain on the left ovary is the spasmodic contraction (contraction) the uterine muscles. The contractions induced by the hormone progesterone play a key role in the excretion of the rejected uterine lining.
In many cases, pain in the left ovary that occurs before and / or during your period can be relieved by taking hormonal contraceptives (such as the pill) regularly.
Another cause of left ovary pain associated with period is endometriosis. The term endometriosis is a gynecological disease in which scattered uterine cells can be found in the abdomen. Since these cells also go through the natural menstrual cycle outside of the uterus, severe pain in the left or right ovary can occur before and / or during the period.
During ovulation
Pain in the left or right ovary may be related to ovulation (so-called middle pain). In these cases it can be observed that the pain in the ovary occurs between the 12th and 14th day of the cycle. However, since many women have a menstrual cycle of more than 28 days, ovarian pain on the left or right that is related to ovulation can occur much later.
The direct cause of the occurrence of the symptoms is the bursting of the mature follicle. Since an egg cell usually only matures in one ovary during a menstrual cycle, the pain in the ovary is typically one-sided.
Read more about this on our website Ovulation pain.
During pregnancy
Many women often experience pulling or pressure in the groin area during pregnancy. Some women who are pregnant may also experience pain on the left or right ovary. Since these pains are particularly common during the first few weeks of pregnancy, they are the first indication that you are pregnant.
The reason for the development of pain on the left or right ovary in these cases is the increase in pregnancy hormones. In women who have only been pregnant for a few weeks, these induce the stretching of the so-called mother ligaments.
Read more on the topic: Pain in the mother ligaments
In addition, pain in the abdomen, especially in the ovary area, is one of the typical symptoms of late pregnancy. In women who are already in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, the symptoms are caused by the rapid growth of the unborn child. Because the uterus tends to shift a little more to the right in women who are pregnant, ovarian pain can be seen more on the right than on the left. In addition, women who are pregnant and suddenly experience severe pain on the left ovary may have what is known as an ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy is a potentially life-threatening situation that requires immediate medical treatment.
Read more on this topic at: Ovarian pain during pregnancy.
Additional pain on the right side
Almost every cause of pain on the left ovary can cause discomfort on both sides.
For some of the most common reasons for the occurrence of such symptoms, however, it is atypical that the ovaries are affected simultaneously on the left and right. For this reason, it can be assumed that ovulation, for example, does not usually lead to pain in the left and right ovaries.
The typical middle pain that occurs between the 12th and 14th day of the menstrual cycle is caused by the bursting of the follicle. Since an egg cell normally only matures in one ovary per cycle, ovarian pain usually does not occur on the left and right at the same time.
Inflammatory processes that affect the left and right ovaries at the same time are more of a rarity. Ovarian pain that occurs simultaneously on the left and right can, for example, indicate the presence of endometriosis. Endometriosis is a common gynecological disease. In affected women, scattered cells of the uterine lining can be found in the area of the abdomen. Since these scattered uterine lining cells also go through the normal menstrual cycle outside of the uterus, pain in the right and left ovaries can occur, especially during periods. Affected patients describe the typical endometriosis-associated pain as particularly severe. For this reason, extensive diagnostics should be initiated if this disease is suspected. Although pain on the left and right ovaries is quite common in patients with endometriosis, it must be taken into account that the disease can under certain circumstances be silent for years.
Read more on this topic at: Endometriosis Symptoms and Ovarian pain on the right side.




.jpg)











-whrend-der-schwangerschaft.jpg)