Exercise after donating blood
introduction
Many people regularly donate blood to help others and to earn some pocket money. Athletes in particular ask themselves after a blood donation what happens with direct sports.
When donating blood, about half a liter of blood is withdrawn from the body, which may have an impact on physical performance.

When can you do sport again after donating blood?
Athletes who donate blood more often may wonder how long to wait before returning to exercise. Many athletes don't take a break and endurance athletes in particular often run a smaller or larger lap on the same day.
There is nothing to be said against a sporting training session on the same day. However, there are a few tips to keep in mind. Before the blood donation is carried out one should enough liquid take in the form of mineral water and juices. This replenishes the mineral and nutrient balance in the blood. In addition, after a blood donation you should first renounced coffee and alcohol as these substances tend to dehydrate the body.
Every person feels differently fit, tired or dull after a blood donation. Therefore, your own perception of your performance level is also decisive for completing a sports unit on the same day or not. It is recommended, however To refrain from high sporting loads for one to two daysuntil the blood balance is restored.
The topic is a bit more serious for competitive athletes, as they train in a different performance area. The body is completely switched to high performance and every blood platelet is needed for the transport of nutrients to the muscles. If the amount of blood is reduced by donating blood, the body is automatically in a lower performance state. If you are still training on the same day and the body has no chance to recover from the blood donation, this can in extreme cases lead to a Overtraining to lead. The athlete trains and does not get fitter, but continues to lose performance. The muscles and organs are not supplied with nutrients as is normally the case.
Competitive athletes should therefore talk to a doctor about how and when they can resume normal training after a blood donation.
What are the risks of exercising after donating blood?
After a blood donation, a high level of physical activity should not necessarily be carried out on the same day. If you don't heed this advice, you run the risk Circulatory disorders to provoke. In bad cases this can lead to a Circulatory weakness or even lead to a circulatory collapse. However, this is only known in individual cases and cannot be generalized.
Exercising after a blood donation can also cause pain in the affected arm. The puncture site can bleed again or, in the worst case, become infected. Therefore, some consideration should be given to the arm from which the blood was drawn.
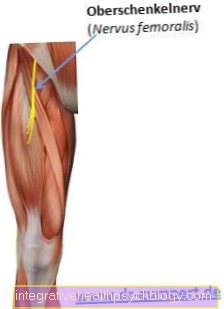
Nerve irritation can also occur in the area of the puncture site, which can lead to a feeling of numbness. In very rare and extreme cases, permanent nerve damage can occur.
How does the blood donation affect performance?
After a blood donation, the plasma and white blood cells regress quite quickly, but it can take 4-8 weeks for the red blood cells to regenerate. Therefore, an effect of the blood donation on the performance of the body can be clearly deduced.
Straight Competitive athlete should therefore under no circumstances donate blood within four weeks before a competition. Anyone who does not follow this advice must expect that the body will not be able to regenerate itself optimally after exercise. In addition, the poor regeneration also tends to reduce the athlete's level of performance in the long term rather than increase it.
The influence of blood donation on the body's performance cannot be dismissed and should not be underestimated. If you are not sure about the length of a sports break, you can do yours Ask doctor for help.
Circulatory problems
In some people it happens that after a blood donation the blood circulation drops significantly and in rare cases even collapses for a short time. This is usually a direct result of the blood donation in combination with external and internal influences on the donor.
People in general to one low blood pressure tend to be particularly susceptible to circulatory problems after a blood donation. This effect is then intensified during exercise, as the body's need for blood increases. In combination with low blood pressure (due to blood donation and generally low blood pressure) this can lead to a circulatory collapse or at least to circulatory problems.










.jpg)