Syndactyly of the hand
- Split hand
- Spoon hand
Connection / fusion of two fingers, when all fingers are affected, it is called a spoon hand.
Syndactyly is more common with Apert syndrome.
definition
Syndactyly of the hand is a bony or connective tissue connection between two fingers. In this condition, there is no space between the fingers. This disease is congenital.
Epidemiology
Hand syndactyly is a relatively common condition. It is the most common congenital malformation of the hand. Syndactyly is found to occur in 1 in 1000/5000 newborns. A developmental disorder in the 5th-7th Embryonic week is discussed.
In most cases, no cause of the disease can be identified, genetic hereditary diseases are less common (approx. 20% of all cases). Genetic diseases in which syndactyly occurs
-
Aarskog syndrome
-
Adams-Oliver Syndrome
-
Fraser Syndrome
-
Pfeiffer syndrome (acrocephalo syndactyly syndrome) and
-
Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome
The most common is the connection between the middle and ring fingers.
Appointment with a hand specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me at:
- - orthopedics
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, appointments can only be made with private health insurers. I ask for understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at -
to form
Basically one differentiates
- the soft tissue syndactyly
- bony syndactyly
In soft tissue syndactyly, the fingers are only connected to one another by skin and connective tissue. In bony syndactyly, the finger bones are also connected to one another.
Furthermore, one differentiates the extent of the connection of the fingers with one another. There are three degrees of severity:
- partially (partially)
- almost entirely (subtotal)
- completely (total)
In most cases, only two fingers are connected (simple syndactyly). If several fingers of one hand are affected, one speaks of multiple syndactyly. If all fingers of one hand are affected, a so-called spoon hand forms. If such a malformation is present, a genetic disease (Apert syndrome) is suspected.
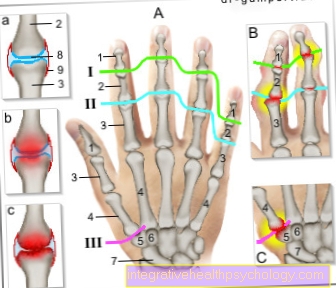
X-ray of an infant's hand with syndactyly
The red row of numbers shows the rays of the hand. The ray 4 has merged with the 5, so the number 5 is missing.
The fingers (blue row of numbers) are laid out normally from 1 to 5.
diagnosis
As a rule, syndactyly is a so-called eye diagnosis that is immediately apparent when you look at it.
In order to confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray of the hand should always be taken. On the basis of the X-ray image, a bony syndactyly can be distinguished from a soft tissue syndactyly.
In exceptional cases, a Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI of the hand) give more information about the soft tissue structures of the fingers. Since in this examination the infant in anesthesia must be placed, since the hand must be kept absolutely still during the examination, information obtained through the examination must be weighed against the risk.
therapy
A syndactyly of the hand should be operationally separated in order to ensure good function of the hand taking into account the existing risks. However, the shape and location (affected fingers) should be included in the indication for the operation, so that a general statement is not possible.
With fingers of the same length, this operation usually takes place in the second year of life, sometimes later. One waits for this timeframe, as a sufficient size of the fingers reduces the operational risks.
The operation is only carried out in the first year of life if the fingers are of unequal length, since permanent growth damage can be expected at a later date.
Most of the time, the changes also affect the nerves and blood vessels (arteries and veins). This must be taken into account during the separation operation and nerves, as well as vessels, must be carefully separated.
The difficulty of the operation is to re-use the separated fingers skin to cover. Overall, too little skin is available. It is important that the ends of the skin are sutured together without tension so that no excessive scars can form. Areas that cannot be covered with skin must be covered with skin grafts from other areas of the body.
Due to the risk of complications, especially circulatory disorders, only two fingers can be separated during an operation. Are several fingers connected to each other (multiple syndactyly), must follow the operations one after the other, six months apart.
Because of the complex operation, the operation time is usually more than 3 hours.
Risks of the operation
If the blood vessel supply cannot be completely separated, this can lead to impaired wound healing after the operation. In rare cases, the blood circulation can be so bad that the finger dies or has to be amputated before it becomes infected.
If the nerves are only simply laid on, the separated fingers can become numb after the separation.
If excessive scars form after the operation, the inability to fully stretch the operated fingers (flexion contracture) occurs as the patient grows.
Furthermore, as part of the growth, the webs between the fingers can grow again towards the fingertips. This restricts the function of the fingers again. Another operation (relapse operation) must follow.