Inflammation of the bronchi
introduction
The respiratory tract of humans consist of different parts. In the beginning is behind mouth and nose of the throat, to which the Larynx the windpipe (Trachea) connects. It runs approx. 10-12cm downwards and at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra it divides into two main bronchi.
From here they branch out further and further to the Alveoli.

The Inflammation of the bronchi, technically as bronchitis or in the case of involvement of the trachea Tracheobronchitis is a common respiratory disease and one of the most common causes of a doctor visit. In the inflammation of the bronchi a distinction must be made between the acute bronchitisas one often suffers in winter or autumn, and the chronic inflammation. One speaks of chronic inflammation of the bronchi if in 2 consecutive years for coughing with sputum for at least 3 months consists.
The chronic inflammation of the bronchi is considered a preliminary stage for another independent disease that occurs predominantly in smokers: the chronic obstructive (= constricting) lung disease (COPD, for chronical obstructive pulmonary disease).
Symptoms
The symptoms of a bronchitis are diverse and often not very specific. Classically, an acute inflammation of the bronchi initially stands cough in the foreground, often called barking is described. As in over 90% of cases, the inflammation is through Viruses caused is that to cough first dry and scratching.
After a few days the disease turns into a secretory phase over while in response to the inflammation increased mucus is formed in the bronchi, the light yellow-whitish impressed as expectoration. Bacterial inflammation of the bronchi usually causes a secretion at the beginning of the symptoms, which is coughed up with. Especially when the windpipe with is concerned, the patients complain of an extremely unpleasant one burning pain in the throat and below.
This comes through the persistent irritation caused by the inflammation and the cough and is sometimes called convulsive described. If the cough is particularly pronounced, small amounts of blood can be found in the sputum. These are mostly harmless, but should be clarified. If the Larynx is a rough, hoarse voice another symptom.
In addition to these symptoms, there are those typical of an infection General symptoms added. These include Exhaustion and fatigue, those affected are weakened overall. fever occurs not infrequently. How long the acute inflammation of the bronchi lasts depends on the pathogen and the patient's condition.
The easy one Chronic bronchitis expresses itself to a similar extent, but without fatigue and fever, but mainly through the cough. The frequent occurrence is also included here repeated slight inflammations of the bronchi become evident in a relatively short time. In the COPD the obstructive, i.e. narrowed, component is in the foreground. This means that in addition to the inflammation, the bronchi are permanently narrowed and produce mucus. This chronic inflammation of the bronchi is classified according to severity Grade I to IV assigned.
Typical for patients with COPD is coughing with Expectoration, especially in the morning after sleeping. There is also a more or less pronounced one shortness of breathwhich initially occurs during exercise and causes complaints in later stages even at rest. The shortness of breath is also caused by a permanent Overinflation of the lungs. If there is a permanent lack of oxygen, the skin can turn blue, especially on the lips and fingers.
causes
The causes that lead to inflammation of the bronchi are different for different diseases. The commonplace acute bronchitis is caused by a large number of pathogenic agents. Over 90% of the cases are viral. The most common viruses that cause inflammation of the bronchi are adenoviruses or rhinoviruses, which are also responsible for the typical cold. Furthermore, influenza viruses in the context of the real flu or parainfluenza viruses are known to cause inflammation of the bronchi.
For more information, we recommend our website to: Viral Bronchitis - You Should Know That!
Rare causes of acute bronchitis are e.g. measles. The incubation period, which describes the time between infection and the onset of symptoms, is 2-3 days in the case of viral genesis. The remaining 10% of acute bronchial infections are bacterial, the best-known representatives being mycoplasma or Bordatella pertussis, the causative agent of whooping cough.
The whooping cough has, however, decreased significantly thanks to consistent vaccination programs.
There is also the possibility of getting a bacterial superinfection in addition to a virus infection. The infection occurs independently of the pathogen via droplet infection. The smallest droplets that get into the air through the airways when coughing or sneezing, for example, are sufficient to transmit enough pathogens for infection.
These droplets then get into the next person's bronchi, adhere to the wall and cause inflammation there. A weakened immune system favors the occurrence of the disease, and previous diseases of the lungs themselves also increase the risk of acute bronchitis.
For the development of chronic inflammation of the bronchi and COPD, which can be described as a consequence of chronic bronchitis, the inhalation of harmful substances applies in particular. Cigarette smoking is by far the leading cause.
90% of all COPD patients are or were smokers. The smoke contains a multitude of toxins that directly damage the tissue, especially the small bronchi, and provoke inflammation. By swelling, increased mucus production and especially by remodeling the bronchial wall, these airways narrow and cause the typical symptoms.
Industrial dusts or other toxic gases are rarely responsible.
diagnosis

The diagnosis bronchitis belongs to the most common diagnoses in general practice. There are various ways of detecting acute bronchial inflammation. The symptoms of the person affected give some clues. Of the barking coughwho mostly with Pain goes along suggests an inflammation of the bronchi. The question of expectoration as well as the duration of the complaints give further clues.
The symptoms persist many days to weeks further investigations are indicated, as the acute inflammation of the bronchi usually occurs quickly and subsides after a week. This is followed by the anamnesis Listening to the lungs with the stethoscope.
Here the doctor may like a sharp breath sound Pipes or Hum hear what signs of narrowing are.
The other complaints like Exhaustion and fever are caused by a variety of diseases, but they fit the clinical picture of bronchitis. Usually this clinical diagnosis is sufficient.
In addition, a X-ray image further help the lungs.
A pathogen detection from the coughed up mucus is not necessary in most cases. Only in the case of persistent or very severe complaints should a Pathogen can be determined in order to be able to treat in a targeted manner.
In the COPD stand next to the positive smoking history, as well as listening with whistles and hums, apparatus-based processes focus, with which one can precisely determine the lung function and determine the current stage of the disease.
At a so-called Spirometer one lets the patient perform certain breathing maneuvers with which various parameters such as Lung capacity, resistance and Tidal volume to be determined. A key value is the so-called 1 second capacitywhere the patient should breathe in as deeply as possible and then exhale as forcefully as possible. With the criteria cough, sputum, 1-second capacity and the general resilience before there is shortness of breath, the patient is in one of the 4 stages divided, the fourth being the final stage.
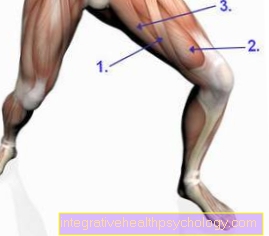
Figure bronchi

- Bronchiole
cartilage-free small bronchus -
Bronchiolus - Branch of the pulmonary artery -
Pulmonary artery - End bronchiole -
Respiratory bronchiolus - Alveolar duct -
Alveolar duct - Alveolar septum -
Interalveolar septum - Elastic fiber basket
of the alveoli -
Fibrae elasticae - Pulmonary capillary network -
Rete capillare - Branch of a pulmonary vein -
Pulmonary vein
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
therapy
The therapy the acute inflammation of the bronchi looks primarily bed rest before since the disease mostly self-limiting is. In addition adequate drinking and possibly that Inhaling herbal tea steam. To support you can Expectorant how ACC are used that have the Coughing up facilitate the secretion.
Against the cough can Cough syrups with the active ingredient Codeine have a soothing effect. Also plant-based funds like Bronchipret are given in addition.
Most of the time Viruses are responsible for the inflammation of the bronchi, antibiotics help here Not. However, they can be used against bacterial infections and should then be prescribed. To Pain relief can means like Ibuprofen or Paracetamol can be used.
The therapy of chronic bronchitis moreover consists mainly in avoiding the pollutant in order to prevent the occurrence of the COPD to prevent. Therapy for this disease is more complicated and diverse. One has to distinguish between Long-term therapy and the measures at a acute deterioration.
Depending on the stage, various active ingredients with different mechanisms are used. It always stands Avoiding the noxious agent at the beginning, then first of all active ingredients are used that dilate the bronchi, e.g. Salbutamol or Formoterol.
They can be used as needed or as long-term medication, as can the means that the Inhibit slime formation (e.g. ipratropium). The next therapeutic stage in this type of inflammation is the bronchi Cortisone prescribed what the Inhibits inflammation. With acute deterioration can Theophylline are given additionally. In the last stage, almost every patient is given pure oxygen through the nose, which should be inhaled 18 hours a day. If the measures are not sufficient, one must have Lung transplant to be thought about.
forecast
The forecast for easy Inflammation of the bronchi is very good. It is a frequent infectionwhich usually subsides by itself and can be combated by the means mentioned above.
Chronic bronchitis, however, should be considered Warning sign be seen for immediate habit changes, otherwise the risk for that Development of a COPD consists. this is a chronically progressive Disease that is not reversible and, in high stages, leads to considerable loss of quality of life.
prophylaxis
As a precaution you should against a acute inflammation of the bronchi especially a healthy one immune system respect, think highly of. Healthy eating and regular exercise form the basis. In winter and autumn you should because of the accumulation of the disease hygienic measures like washing hands pay more attention. Against some pathogens like influenza or whooping cough there are vaccinations that make the disease unlikely. Against the chronic inflammation of the bronchi and the COPD there is only one thing that can be done prophylactically:
Avoid the harmful ingredients and, most importantly, stop smoking.