Heat therapy
introduction
In most of its forms of application, heat therapy belongs to the field of physiotherapy and belongs to the class of thermotherapy. Typically, non-inflammatory conditions and pain are treated with heat. This heat can be generated by a wide variety of sources.
Various therapeutic effects are ascribed to heat. This includes improved blood circulation, an increase in metabolic activity, muscle relaxation, pain relief and better elasticity of the connective tissue. It is used in classical western medicine as well as in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and natural healing methods.

Reasons for heat therapy
Heat therapy is very versatile. In classical western medicine it is primarily used to relieve pain. Heat therapy is often used for orthopedic complaints. Muscle tension (for example on the back) is a common reason for heat therapy. Joint problems that have no inflammatory cause are also treated with heat therapy.
Heat therapy can also be used for overuse damage to the muscles, such as a muscle strain.
Heat therapy is also very important in meditation and relaxation. Many massage therapies, especially from Asia, are combined with heat therapies. Circulatory problems can also be a reason for heat therapy. The warmth causes the blood vessels to expand, which improves the blood flow to the tissue behind them.
In addition, heat therapy in the body can have therapeutic effects similar to those of a fever. Due to the increased temperature, foreign substances such as pathogens are inhibited in their function. In this way, heat therapy can also strengthen the body's defenses.
Find out all about the topic here: Pain.
How does heat therapy work?
In heat therapy, there is usually a carrier medium that is heated, stores this heat and passes it on to the body during the treatment. Such a heat source is usually used locally to relieve pain or tension. Heat-storing materials such as hot stones can be used as a carrier medium. Often the heat is used in hydrotherapy. You work with warm water, which can be put on a towel, just like with the hot roll. But a warm foot or arm bath is also a form of heat therapy.
Using infrared radiation or hot air, the heat can be transferred to the body without a real carrier medium. Rather, the heat energy is given off to the body in the form of beneficial radiation.
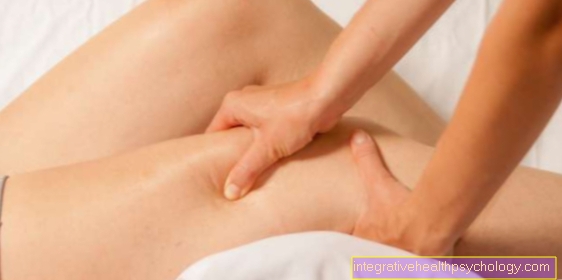
As a rule, heat therapy is combined with relaxing procedures such as massage. This intensifies the effect of the local heat therapy, at the same time it also triggers mental relaxation, whereby the heat therapy can unfold its effect on the entire body.
The mud pack
A mud pack consists of the mud heated to around 50 ° C. This is valuable volcanic soil that, when mixed with liquid, has a slightly mushy consistency. This warm mud pack is spread over the affected parts of the body. Then you wrap the body parts, for example with a film. In this way, the fango remains directly on the skin, the heat can act longer and penetrate deeper body layers.
The volcanic soil often contains additional healing substances. Not only can deeper problems be treated with the heat, but also superficial skin diseases such as eczema or psoriasis improve under the mud pack.
The hot air
During the therapy with hot air, heated air is brought to the body. In contrast to many other heat therapies, hot air is a contactless therapy.
Due to the permanent contact with the hot air, the heat not only reaches the superficial layers of the skin, it can also penetrate deeper tissues and relax muscles and tendons there, for example. Hot air therapy is usually a very mild heat therapy procedure. A treatment usually takes about 30 minutes.
The hot role
The hot roll usually consists of a few towels that are rolled up tightly. Then they are half, two-thirds or whole immersed in hot water. This hot roll is rolled out by the therapist onto the body parts to be treated. As a rule, slight pressure is applied.
The treatment with the hot roller consists of a mixture of pressure and heat. This combination leads to a local improvement in blood circulation. This increases the metabolic activity of the muscles and improves the relaxation of the muscles.
The infrared radiation
From a physical point of view, infrared is radiation that has a slightly larger wavelength than the light that is visible to us humans. This infrared radiation gives off its energy to the body in the form of heat. It is often used in the form of an infrared sauna. This warms the entire body.
However, infrared can also be used locally, usually with special lamps. These are switched on slightly above the affected part of the body, so that, for example, in the case of back pain, the entire back is irradiated with careful heat.
Infrared lamps can also be used with babies. They like to hang them over the changing table so that the little ones feel comfortable while changing and are not exposed to the cold.
The ultrasound machine
Most people know ultrasound devices as devices for diagnostics. In heat therapy with ultrasound, slightly larger wavelengths (smaller frequencies) are used. These penetrate the tissue and give off their energy there in the form of heat. In this way, even deeper tissue layers can be heated. As with all heat applications, this leads to an increase in blood flow and thus an improvement in metabolism.
Also read the article: Ultrasound for diagnosis.
Consequences of heat therapy
Heat therapy leads to an increase in blood flow both locally (limited to one part of the body) and systemic (affecting the entire body). The body receives the signal from the warmth to expand the blood vessels, so that the blood can reach the smallest capillaries.
The improved blood circulation enables the body to increase its metabolic activity. With the increase in blood flow, the tissue is provided with more nutrients, and at the same time waste products of the metabolism can be removed more quickly. For example, the healing of muscle injuries can be significantly promoted. The tissue is also supplied with more energy and can therefore basically work better.
In the joints, the heat therapy affects not only the muscles. The synovial fluid is also positively influenced by the heat: The heat therapy reduces the viscosity (“toughness”) of the synovial fluid and thus leads to improved movement in the joint. At the same time, the warmth makes the connective tissue more elastic, which also improves joint mobility.
The massage, which is often carried out in addition, creates a further stimulus for strengthening the blood circulation on the treated areas of the body. This additionally increases the effect of the heat. At the same time, the warmth also has a relaxing effect on the entire body, which can calm the soul and spirit.
Find out more about the topic here: general physiotherapy.
What are the contraindications?
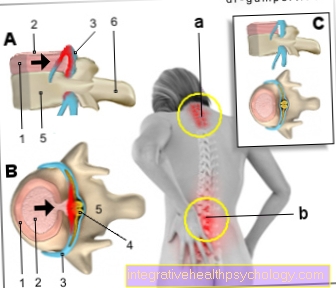
Contraindications to heat therapy are all kinds of inflammatory processes. Typical signs of this are redness, swelling and overheating of the painful area.
Heat therapy should not be used for systemic inflammations such as acute infections, fever, but also for inflammatory rheumatism (in acute flare-ups). Since warmth leads to a strong expansion of the vessels and thus significantly lowers the blood pressure in the meantime, caution is also advised with circulatory problems. Heat therapy is contraindicated in the case of severe circulatory disorders (some of which are already associated with tissue damage).
Also read the article: Circulatory disorders.










.jpg)