Abscess on the ear
introduction
An abscess is an encapsulated collection of pus in a cavity that is caused by inflammation and can theoretically appear anywhere on the body. They are painful red nodules that are usually accompanied by swelling and reddening of the surrounding tissue. Typically abscesses can be found on the face, neck, buttocks and genital area and thus also in front of, behind and on the ear.

Depending on where an abscess occurs and how big it becomes, it can be harmless or, in the worst case, cause damage to important organs or blood poisoning (sepsis) to lead. Pus is made up of dead cells, bacteria, and white blood cells, which are defense cells of the immune system. A cavity is formed through the pus, an abscess cavity, which is surrounded by a capsule.
Causes of an Abscess in the Ear
Bacteria are almost always the trigger for the formation of an abscess. Most often it is an infection with bacteria that are part of the natural skin flora. These get into the body through a poorly cared for wound or through the smallest skin injuries. An abscess on the ear can develop as a result of an operation, an injection or a small wound in the area of the ear. But even without an apparent external cause, an abscess can form on the ear. A general immune deficiency, such as that found in diabetes mellitus, increases the risk of developing an abscess.
One of the most common causes of an abscess on the ear is a complication of acute otitis media, mastoiditis. This is an acute inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone (Mastoid process), a protruding bone behind the ear. The inflammation leads to the formation of abscesses, usually originating from an inflamed mucous membrane in connection with the involvement of the bone (melting of the bone). Around the third or fourth week after an otitis media, the abscess becomes noticeable as a tender swelling behind the ear.
An abscess on the ear can also be due to an inflammation of the ear canal (External otitis) arise. This is an inflammation of the skin in the external ear canal caused by bacteria or fungi. Such inflammation of the ear canal can often be observed after swimming, which has led to the name "swimmer's ear". If contaminated water gets into the ear and there is also the slightest damage to the skin of the ear canal (e.g. due to improper cleaning of the ear with cotton swabs), an infection can occur.
Ear wax has an antibacterial effect and should not be removed too often, as it can then no longer perform its protective function. An abscess can develop on the ear as a result of inflammation and lead to further complications such as spreading the inflammation to the bones or nerve paralysis.
Boils in the ear area are just as common and can develop into abscesses. A boil is a painful inflammation of the hair follicle and the surrounding tissue. Boils occur on the ear, for example, when the skin is injured when shaving or when hair is removed from the ear.
Read more on the subject at: Inflammation of the sebum - this must be observed!
Symptoms of an abscess in the ear
Depending on where the abscess is on the ear, different symptoms can occur. In mastoiditis, for example, after an initial improvement or after an acute otitis media, there is renewed earache, sensitivity to pressure behind the ear and swelling, which is associated with protruding the auricle.
Skin abscesses around the ear can look like enlarged pimples, characterized by reddening and swelling of the tissue. Usually there is pain and a feeling of tension from the swelling, and there is also pronounced tenderness. For example, pain can be triggered by pressure on the cartilaginous elevation in front of the auditory canal (tragus) or when the auricle is pulled.
An abscess on the ear can also lead to pronounced itching, discharge from the ear or hearing loss can occur. In many cases, the abscess causes pain when chewing or even when speaking. It can also lead to painful and enlarged palpable lymph nodes on the neck. An abscess on the ear can also severely impair general well-being with a fever.
diagnosis
To determine the diagnosis of an abscess on the ear, the Medical history collected (anamnese). For example, it is important for the doctor to learn how Ear cleaned and which hygiene products are used. cotton swab should basically not for cleaning of the ear.
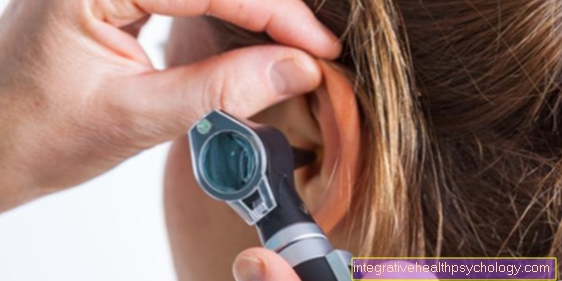
The Ear is examined (inspection) and examined for redness, swelling and pain points. These are the typical signs of inflammation and are usually found in an abscess. Even if the abscess is located outside the ear, the ear canal is usually examined with an ear mirror (Otoscope) examined to rule out any involvement of the eardrum. In some cases it makes sense to have a Smear from the abscess to take by the ear in order to determine the causative pathogen in laboratory medicine and to be able to use drugs in a targeted manner.
Treatment of an abscess in the ear
An abscess in the area of the ears, on the head or on the neck poses a particular risk, which is why they should never be treated yourself, but rather belong in the hands of a doctor. The close proximity of such an abscess to the brain can, if improperly treated, lead to the bacteria entering the brain and, for example, bacterial meningitis (meningitis) cause.
Ointment for an abscess in the ear
In general, if you have an abscess on the ear, you should first consult a doctor instead of causing greater damage through self-treatment. The person concerned can obtain advice on how to proceed from the doctor.
With a smaller abscess, a so-called pull ointment can provide relief. As the name suggests, the ointment pulls out the pus and inflammation. It can have an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, circulatory and antibacterial effect. It also inhibits the formation of sebum.
Depending on the preparation, different active ingredients can be contained in the pull ointments. Sulfonated shale oil is often used. This is contained, for example, in the active ingredient ammonium bituminosulfate. This is also known as the Ichthammolum. The active ingredient ensures that the abscess empties itself after a few days.
Depending on the severity and individual factors, different concentrations and dosages are effective.
Even if some ointments are available over the counter in pharmacies or on the Internet, you are strongly advised to contact a doctor. This can assess whether treatment with an ointment is sufficient or whether other measures need to be taken.
Read more about this under Treat an abscess with an ointment.
If it is a small abscess on the ear and depending on where it is exactly, the doctor may recommend a pull ointment. These ointments contain active ingredients from shale oil and help the abscess to mature so that it can empty itself. The doctor will then thoroughly clean the small crater and cover it with a plaster, after which the abscess on the ear should heal in a few days. A larger abscess on the ear must be opened in a small surgical procedure so that the pus can drain away.
As a rule, the affected person immediately feels a feeling of relief and a significant reduction in pain when the pus cavity is opened, as the pain caused by the strong pressure on the surrounding tissue suddenly decreases. A strip of gauze soaked in an antibacterial solution is often placed in the wound. This acts as a drainage through which any remaining pus can drain away and the wound can slowly heal from below. Mastoiditis usually requires surgery. A so-called Mastoidectomy carried out. The bone behind the ear is exposed, reamed and the pus is removed.
Since abscesses can form again even after they have completely healed, the attending physician should be consulted again if the pain does not go away, the area around the wound is swollen or red, or the wound fills with pus again.
Read more on the topic: Abscess treatment
When do you need antibiotics for an abscess in the ear?
Since an abscess on the ear is a bacterial infection, antibiotic treatment is obvious. But since the abscess is surrounded by a capsule, it is often difficult or insufficient for the active substance of an antibiotic to reach the site. Treatment with antibiotics alone is rarely sufficient. Additional measures are usually required.
If there is a fever associated with the abscess in the ear, antibiotics must be used. A fever is a sign that the bacteria are already in the blood. There is a risk of blood poisoning. If a fever occurs, an immediate doctor's visit is essential.
These home remedies will help with an abscess in the ear
There are several home remedy recommendations. According to some voices, peppermint, camphor and coffee should be avoided. In contrast, aloe vera, chamomile, hay flower and arnica can have a supportive effect. In some cases, applying a tincture of proplist locally can aid the healing process. Some authors advise drinking nettle tea.
Furthermore, warmth supports the healing process. This can be in the form of a red light lamp or in the form of compresses. There are various suggestions and experiences with warm compresses. Some authors recommend compresses with pure hot water, others recommend compresses with chamomile or calendula, and still others recommend compresses with hot milk.
As home remedies, shredded raisins, a crushed cabbage leaf, fenugreek seeds, warmed slices of onion or garlic or burdock leaves seem to be helpful in some cases. In some cases, in addition to other measures, homeopathic remedies can have a supportive effect. For example, Traumeel® S tablets are recommended in combination with 5 drops of Notakehl D 5. As a rule, these should be taken 4 times a day for 2 days.
Read more about this under Home remedies for an abscess.
Special features in children
In children, one should be even more careful with an abscess on the ear. Since the blood-brain barrier is different and works differently than in adults, this can have fatal consequences. The blood-brain barrier is even more permeable because a protective transporter, the P-glycoprotein, is not yet fully developed. This can mean that certain pathogens can reach the brain more quickly. The risk of complications is higher.
In addition, children often pay less attention to hygienic measures when playing and romping. Younger children cannot yet understand that they must not touch or "pinch open" the abscess. The pathogen can spread faster and the abscess can heal more poorly.
In addition, certain medications must not yet be taken by children. Only 20% of all drugs are approved for children. In addition, a surgical procedure is often a traumatic event for children and parents. However, if adequate medical support and advice is used early on, the healing of an abscess on the ear in children is usually without complications.
Read more on the subject at: Earache in children
Abscess on the earlobe
An abscess can develop through an inflamed earring hole on the earlobe. But it can also form at this point for no reason. The procedure and measures are similar to other parts of the ear.
Of course, no earrings or earrings should be worn during the time of the abscess. First of all, the abscess on the earlobe should be examined by a doctor. The use of home remedies in addition to other measures can be discussed with the doctor.
Adhering to hygiene measures is the basis for the effectiveness of the treatment. In no case should it be pressed against the abscess on the earlobe. This should not be touched at all. If this is accidentally done, hands should be washed thoroughly. As long as the abscess is present on the earlobe, bathing should be avoided. Otherwise the pathogen could be spread further.
The abscess should be carefully cleaned according to the doctor's instructions. When this empties, a plaster should be applied. It is important that this is changed regularly and then your hands should always be washed thoroughly. The pillowcase and towels should be changed regularly, at best daily. Both should be washed separately at at least 90 °.
Of course, the towel or pillow case should not be shared with anyone else. If hats or hoods are worn, the earlobe should be protected with a plaster. If a fever occurs, a doctor should always be contacted immediately.
Read more on the subject at: Inflammation of the ear lobes
forecast
Basically, abscesses on the ear have one good prognosis, but only if they are handled properly. With the correct therapy, an abscess on the ear will heal within a few days.
However, some factors can make the healing process take longer. Especially in the face area and on the ear you should no way Press around on the abscess, as this will burst the abscess capsule and the pathogens can be transported to the brain. The flow of blood from the face and brain is closely related and the pathogens can be spread Meningitis (Meningitis).
In addition, a Expand the abscess on the ear and spread to the cartilage and bones. It can also cause an abscess of the parotid gland. Especially in people with diabetes but also rarely in other people, inflammation of the surrounding bone can occur, a so-called External otitis maligna.
prophylaxis
Basically you can Abscesses all over at the body arise. In the ear, for example, they arise through too little or through excessive hygiene measures. The ear should Not With cotton swab be cleaned, but always gently rinsed with water. After showering or swimming, the ear may become Prevention of infections and abscesses be blown dry.
Abscesses also occur more frequently immunocompromised people on. For this reason it is recommended that the Susceptibility to infection generally too reduce. For example, people suffering from diabetes should ensure that their blood sugar levels are maintained well over the long term. Basically, excessive nicotine and alcohol consumption should be avoided.














.jpg)