You can recognize a chlamydial infection in men by these symptoms
introduction
When speaking of a chlamydial infection, an infection by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis is usually meant. The Chlamydia family also includes Chlamydophila pneumoniae and psittaci. However, these two pathogens occur less often.
Chlamydia lead to infections of the eye and / or the genitourinary system. With the exception of the two rare chlamydia pathogens, they are transmitted during sexual intercourse. All forms are treated with an antibiotic from the tetracycline class. It is also important to treat the sexual partner as well.
Learn more about the symptoms of chlamydial infection in men below.
Read more on the subject at: Chlamydial infection

Typical symptoms of chlamydial infection in men
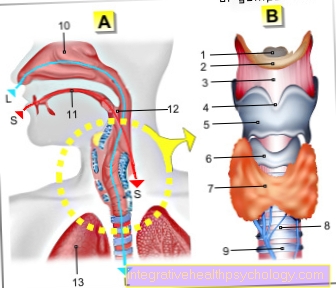
Chlamydia infection can lead to inflammation of the urethra, epididymis and prostate inflammation in men. The classic symptoms of these diseases are:
Symptoms of urethritis:
-
Burning sensation in the urethra
-
Purulent discharge from the penis ("Bonjour drops")
Symptoms of epididymitis:
-
Redness, swelling, and warmth of the testicle
-
Pain in the testicle
-
difficult, painful urination
-
possibly fever
Symptoms of prostate inflammation:
-
Pain in the anus
-
Painful bowel movements
-
difficult, painful urination
-
possibly fever and chills
An asymptomatic course of a chlamydial infection in men is also possible.
discharge
In the context of urethritis caused by chlamydia, discharge from the penis can occur in the context of urethritis. The discharge traditionally occurs in the morning before urination and is therefore also called “Bonjour drops”. The discharge can be watery or purulent.
Burning sensation when urinating
A burning sensation when urinating is a typical symptom of chlamydial infection. This occurs in the context of urethritis. In addition to the burning sensation, epididymis or prostate inflammation can also lead to pain and difficult urination.
Read more on the subject at: Burning sensation when urinating
Testicular swelling
Testicular swelling is a classic symptom of epididymitis as part of chlamydial infection in men. In addition to the swelling, there are other signs of inflammation such as redness, overheating and pain in the testicle area. There may also be swelling of the lymph nodes, especially in the groin. Another sign of epididymitis is the ease of pain relief when you lift your testicles. This is called the positive Prehn sign.
Read more on the subject at: Testicular swelling
fever
Fever is not necessarily a classic symptom of a chlamydial infection in men. However, it can occur as part of an inflammation of the epididymis or prostate. In addition to the fever, other flu-like symptoms such as Headache and body aches, chills, and fatigue occur.
Pain in the abdomen
As the chlamydia ascend to the prostate or epididymis, pain in the abdomen can occur. In men, however, this is not a classic symptom of chlamydial infection. Abdominal pain is more likely to occur in women with chlamydial infection as part of inflammation of the ovaries or fallopian tubes.
Read more on the subject at: Symptoms of chlamydial infection in women
Painful intercourse
If you have an acute chlamydial infection, pain during intercourse is not typical. However, they can occur in the context of chronic inflammation of the prostate or urethra. Pain during sexual intercourse is more of a typical symptom of a chlamydial infection in women.
In men, pain during intercourse is more a symptom of a narrowing of the foreskin.
Conjunctivitis
Some sub-forms of chlamydia can lead to conjunctivitis. One form of conjunctivitis is called trachoma. It occurs only very rarely in Germany, but it is particularly widespread in the subtropics and tropics. The infection takes place through a smear infection from person to person. If left untreated, it leads to conjunctivitis on both sides and increased tearing, leading to corneal injuries and even blindness.
Another form of conjunctivitis caused by chlamydia is paratrachoma. Here the chlamydia are transmitted via the hands by smear infection. It comes to a purulent, slimy conjunctivitis, which usually occurs on both sides. The paratracheoma usually heals without complications.
Read more on the subject at: Conjunctivitis
lung infection
The two rare chlamydial pathogens Chlamydophila pneumoniae and psittaci can lead to pneumonia. Chlamydophila pneumoniae usually leads to atypical pneumonia with a gradual onset, a slight fever and a dry cough.
Chlamydophila psittaci leads to the so-called parrot disease. The pathogens are transmitted via feather dust or bird droppings. There are flu-like symptoms and atypical pneumonia with dry cough. To avoid complications such as To prevent heart muscle inflammation, antibiotic therapy should definitely be used.
Read more on the subject at: Signs of pneumonia
Swelling of the lymph nodes
Lymph node swelling as part of a chlamydial infection in men can occur, but is not one of the typical symptoms. This clinical picture is called lymph granuloma inguinale. Epididymitis can also lead to swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. These can then possibly be felt as hardened lumps by the person concerned or lead to pain in the groin area.
Read more on the subject at: Lymph node swelling in the groin
Joint pain
An acute chlamydial infection usually does not cause joint pain. However, one complication of chlamydial infection is reactive arthritis. This joint inflammation occurs after a few days to weeks and primarily affects the joints of the leg and here particularly often the knee joint. In addition to joint pain, fever and pain in the adjacent muscle tendons can also occur. Conjunctivitis or inflammation of the iris of the eye are also possible symptoms of this reactive arthritis.
Read more on the subject at: Joint pain
Bleeding after intercourse
Bleeding after intercourse is not a classic symptom of chlamydial infection in men. Bleeding from infection can occur in women as part of an inflammation of the lining of the uterus caused by chlamydia.
Odor formation
A chlamydial infection can lead to discharge from the penis, as described above. This discharge can also have an unpleasant smell. Typically, however, this is a symptom in women, as there is more discharge here.
How long is the incubation period?
The incubation period, i.e. the time between infection and the appearance of symptoms, is one to three weeks for Chlamydia trachomatis. The incubation period for the other chlamydia pathogens is one to four weeks.
Can a man have chlamydia without symptoms?
Many men develop chlamydia and do not develop any symptoms. This is also known as asymptomatic infection. The absence of symptoms and therefore the absence of therapy can lead to the spread of chlamydia.
Can you get symptoms after years?
The incubation period for chlamydia is around one to four weeks. After this time there will be symptoms or, in the case of an asymptomatic infection, none. It is not possible for symptoms to appear years after infection.