Ear infection
introduction
In general, inflammation of the ears in humans and animals is called otitis. A distinction is made between different forms of otitis, which differ in their localization. The two major subgroups of otitis are otitis media and otitis externa, which are explained in more detail below with regard to their causes, symptoms and therapy.

Ear canal inflammation
External otitis
Synonyms: engl: otitis externa, „Outer ear infection"/ For animals: Ear pressure
Classification according to ICD-10: H60 otitis externa
Definition: In the External otitis is it a Inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous fat (Subcutis) in the area of the outer ear. These include the outer ear canal (Meatus acousticus externus) and the auricle. The causes of this inflammation of the ear canal are Allergies and Microorganisms.
In the External otitis different forms are distinguished.
Below is a list of the different types of inflammation.
Severe ear canal inflammation - otitis externa maligna
Synonyms: External otitis necroticans, Osteomyelitis of the temporal bone; English: malignant otitis externa (MOE)
Definition: This otitis is a Inflammation with severe disease. It is about a necrotizing inflammationwhich on the Skull bones and the Cranial nerves can spread and damage them. Necrotizing means that the tissue dies due to inflammation.
Root cause: Such otitis is the result of one Infection of the external ear canal, especially with the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Usually are immunocompromised patients affected.
Symptoms: A necrotizing otitis is expressed in severe pain of the person concerned. It comes to one Secretion from the external ear canal. Fluid leaks from the ear. In the course of the disease, the inflammation attacks Cranial nerves over. A very concise symptom is that Facial palsy. This damage to the so-called Facial nerve shows up as Disturbance of facial expressions of the patient. Other cranial nerves can also be affected. With this otitis, people are generally not doing well. You are plagued by severe pain and general weakness.
Diagnosis: Are in the blood increased levels of inflammation (e.g. CRP) detectable. In further diagnostics, a Magnetic resonance imaging, one Computed Tomography and a Bone scintigram carried out.
By means of a Trial excision ensures that it is not a carcinoma, i.e. a malignant tumor. Here, a little inflamed tissue is removed and examined pathologically.
Therapy: The therapy of otitis externa maligna depends on the severity of the disease. First of all, there is one daily cleaning of the external ear canal. The inflammation is with the help of Antibiotics fights. These are for one applied locally, that is, they are applied to the inflamed area and on the other hand one takes place systemic gift. The duration of therapy varies between 6 weeks and 6 months, but can also be used in very severe disease up to one year last.
Since it is for damage and Detachment of small bone parts, so-called Bone sequester, can come, surgical removal of this may be necessary. Abscesses on the ear are operationally opened and cleaned.
During therapy, the Inflammation values, for example the CRP, again and again controlled become. This guarantees the success of the therapy. Because with such a disease, the tissue ultimately through Lack of oxygen (Hypoxia) dies (necrotic), if the disease is resistant to therapy, a Oxygen therapy should be considered. In this way, the dying tissue is supplied with oxygen. The oxygen is usually administered using a nasogastric tube. In extreme cases it may be necessary that destroyed bone area or at least parts of it to remove surgically.
Diffuse ear canal inflammation - otitis externa diffusa

Synonyms
Ear canal phlegmon, ear canal eczema; English: diffuse otitis externa
definition
The Otitis externa diffusa, also called ear canal phlegmon or ear canal eczema, is one inflammation of the skin and des Subcutaneous fatty tissue (Subcutis) of the external auditory canal. It will be a dry from one oozing form differed in their clinical symptoms.
causes
This form of otitis is usually one Infection with bacteria or fungi underlying. The most common pathogens are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Proteus. Also one allergy, for example directed against cosmetics or hair shampoo, is a cause of ear canal eczema.
Susceptible the external auditory canal is primarily used for the penetration of such pathogens Clean ears with cotton swabs or fingers. Ask other risk factors Metabolic diseases, again Diabetes mellitus, or a kidnapped chronic otitis media represent.
Symptoms:
Dry form:
The ear canal eczema manifests itself in one Scales of the skin and an unpleasant one itching (Pruritus).
Oozing form:
As in this form of otitis externa diffusa one secretion leaks out of the ear, it is called weeping. These secretions are greasy and are also called fetid designated. That means they smell foul. The unpleasant smell comes through bacterial decomposition products come about, which are Sulfur compounds acts.Secretions from the middle ear are slimy rather than greasy, which allows a distinction to be made.
Other symptoms are severe earachewho are at Pressure on the Reinforce tragus. You can see one on the outside swelling of the ear canal. This swelling is from severe itching accompanied. As a result, the eardrum can also be affected by inflammation (Myringitis). The pre-auricular (located around the auricle) Lymph nodes are swollen and painful.
Diagnosis:
The clinical examination and evaluation of symptoms provides the final diagnosis. To determine the causative germ, are Trade-offs made. So can a suitable antibiotic be prescribed. Furthermore, the patient is on Allergies examined. Ultimately, one happens Examination of the eardrum, as this can also be affected.
Therapy:
Dry form:
The eczema is made with the help of Cortisone ointments treated. For the treatment of tears (Rhagades) becomes Silver nitrate solution (5%) used to this too burn.
Oozing form:
First there is a cleaning of the external ear canal, then one local application of antibiotics. Of course, this only occurs in the case of bacterial infection. The antibiotics are in Ointments or drops applied and only in very rare cases occurs a systemic Gift. A Flushing of the ear canal can be made.
At a Fungal attack, become antifungal ointments or creams placed on the external auditory canal in the form of rods in the ear canal.
Ear canal furuncles - otitis externa circumscripta
Synonyms:
Ear canal furuncles; English: meatal furuncle, circumscribed otitis externa
Definition:
At this extremely painful Inflammation is one inflamed follicle in the external ear canal; they are also known as Ear canal furuncles.
Causes:
Bacterial infections are often the cause of such hair follicle inflammation. The penetration of germs, often Staphylococci, is made by the Clean of the ears or a Scratch favored.
Here's a metabolic disorder like that Diabetes mellitus also a risk factor for the frequent occurrence of such ear canal furuncles.
Symptoms:
Outwardly they impress pre-auricular and retro-auricular (lying around and behind the auricles) Lymph nodes as enlarged. A swelling of the external ear canal is visible. The clinical examination of the ear canal using an ear speculum is painful. The remaining, severe pain are through a pressure on the tragus and that Increased chewing.
Diagnosis:
The clinical examination of the patient provides the diagnosis.
Therapy:
To be treated Alcohol envelopes and with Alcohol-soaked gauze strips placed in the ear. Be against the severe pain Painkiller (Analgesics) prescribed. Also be ointments containing cortisone and antibiotics used for therapy.
Bloody ear canal inflammation - otitis externa bullosa haemorrhagica
Synonym:
Flu otitis
Definition:
This otitis can occur under a flu (Influenza and other viral infections) occur. However, she kicks more common with an otitis media (Otitis media) and one acute inflammation of the eardrum on.
Causes:
The cause are viral pathogens.
Symptoms:
Symptoms include Earache, as well as a Conductive hearing loss.
Also are bloody vesicles in the ear canal and on the eardrum visible. Rare is such an otitis with one Tinnitus or dizziness socialized. This mainly occurs when the Inner ear also affected is. This can lead to a Hearing loss come.
Diagnosis:
The two methods used for diagnostics are the Otoscopy and the Tone threshold audiogram.
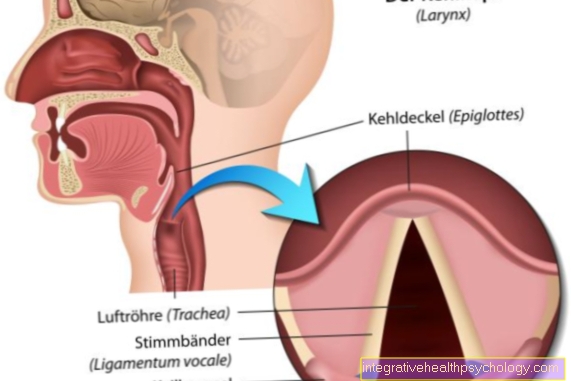
An otoscopy is an examination of the external ear canal and des Eardrum using an otoscope.
The threshold audiogram is used to test the Competence of hearing used.
Therapy:
The treatment is initially carried out by means of a Ventilation tube. This serves the Ventilation of the tympanic cavity and des Eardrum. In addition, a Infusion therapy be prescribed.
Complications of ear canal inflammation
With each form of external otitis there is one risk, that the infection on the surrounding Bones and soft tissues, as well as the Cranial nerves overlaps. Are particularly dangerous then Inflammation of the bone marrow and Cranial nerve failure.
Otitis media
Otitis media
Synonym:
Otitis media
Otitis media is one Inflammation of the middle ear. It can be different shapes the otitis media, which will be discussed in more detail below. We make a difference according to the course of the disease first of all between one acute and one chronic otitis media.
Acute otitis media

Classification according to ICD-10:
H65 Non-purulent Otitis media
H66 Purulent and unspecified otitis media
H67 otitis media diseases classified elsewhere
It is a very painful inflammation of the middle ear mucous membranes, which infectious is.
Causes:
An acute otitis media occurs as part of a bacterial or viral Infection and is a very common disease.
The bacterial acute Middle ear infection is that more frequent Shape. The bacteria get through the Nasopharynx or else the Blood way into the middle ear and continuously settle there.
Viral Middle ear infections usually develop over the Blood way and are associated with Inflammation of the upper airways. A viral infection can be accompanied by a bacterial infection or it can make it easier to break out. Pathogens can occur in an existing Drum perforation also from the outside get into the ear, for example from the bath water while visiting a swimming pool.
In the acute serous Middle ear infection is that Tuba auditiva (Connection between the middle ear and the nasopharynx) by a swelling the mucous membranes under a Respiratory tract infection locked. By lack of ventilation of the middle ear negative pressurewho ultimately become a Tympanic cavity effusion leads. The affected hear worse and complain about a Feeling of pressure.
Diagnosis:
The ear is examined otoscopically (with the ear speculum). Here you first see a reddened, then a dedifferentiated eardrum. It means that no more details can be recognized by the eardrum and it is bulges. It comes to one perforation from which pus emerges. These symptoms sound like after 2 to 3 weeks from.
It can also small blood and fluid-filled blisters (myringitis bullosa) be seen on the eardrum. From them one can serous secretion step out. This is the case with acute serous otitis media.
Symptoms:
An otitis media goes through different phases. The patient is troubled for the first few days severe ear pain, one Hearing loss, fever and throbbing Ringing in the ears. nausea and Vomit can be accompanying symptoms. The pressure on the temple is painful.
While viral infections usually heal here, kick bacterial Infections in the next few days Defense phase a. Meanwhile step through a Eardrum perforation secretion out of the ear and hearing is decreased. A purulent Secret speaks for one bacterial, a serous-bloody Secretion for one viral Infection. Antibiotics can shorten this phase and prevent a rupture of the eardrum. The Fever subsides and after others two to four weeks is over the otitis media.
Therapy:
Middle ear infections can also heal without treatment. Therefore, the first two to three days under medical supervision waited become. As with any medical condition, the patient should be save.
Nasal sprays and anti-inflammatory pain relieverl like Ibuprofen are recommended. In the case of a bacterial infection, a antibiotic that passes through the liquor (e.g. Amoxicillin, Azithromycin, and clarithromycin).
Chronic otitis media
Synonym:
Otitis media chronica
The chronic otitis media includes two diseases; on the one hand the Augmentation of bone, on the other hand the Mucosal expansion. Overall, it concerns chronic inflammation of the middle ear with permanent eardrum perforation, from which pus exit.
Otitis media chronica mesotympanalis
This form of chronic otitis media affects people Mucous membranes. It is a central eardrum defect without inflammation of the bone.
root cause
The cause is usually an interaction repeated infections and one poorly ventilated tuba auditiva. Traumatic or inflammatory diseases and defects in the eardrum can also trigger this.
Symptoms
Those affected suffer from severe earache and purulent discharge out of the ear. Hearing is decreased. The eardrum is preserved on the edge, but in central areas damaged. During a flare-up of inflammation, the lining of the middle ear is red and thickened. Otherwise, it may appear grayish and dry.
therapy
The perforated eardrum is used as part of a so-called Tympanoplasty locked. Have to dry conditions and the ear canal is cleaned and disinfected.
Suppurations be with antibiotic ear drops treated. Care must be taken after treatment that Keep ear dry (Wadding when bathing, no diving or swimming) and the Tuba auditiva through nasal breathing ventilate.
Otitis media chronica epitympanalis
This is inflammatory damage to the edge of the eardrum; the bone is also affected by the inflammation.
causes
The causes are the same as for otitis media chronica mesotympanalis.
Symptoms
As part of the eardrum damage, there is a Hearing loss (conductive hearing loss). The eardrum damage is marginal and it occurs foul-smelling pus from the ear (Otorrhea). At the same time you can Polyps into the ear canal wax.
Since the bones (for example the ossicles) are also affected by the inflammation, it can lead to a Inner ear damage and associated with it neurological failures come. This includes Nausea, dizziness, facial nerve palsy and deafness.
This form of chronic otitis media may pave the way for that Development of a cholesteatoma be.
therapy
First of all, the Ear canal drained and it can be local or systemic Antibiotics applied to an existing Stop suppuration. In any case, there is a operational renovation of the eardrum (tympanoplasty) and a Removal of the cholesteatoma.
Further inflammation of the ears
Auricular perichondritis

Perichondritis is one Inflammation of the cartilage.
causes
Such inflammation is bacterial (accumulated Pseudomonas and Staphylococci) conditionally. You get over Injuries to the auricle (for example during operations or ear piercings) to the cartilage skin.
Symptoms
The auricle is swollen and reddened. The Earlobe but it is not affectedbecause it does not contain cartilage. If the inflammation is advanced, it can Necrosis come, that means tissue dies. Typically, the shape of the ear changes (Cauliflower ear).
Read more on the topic: Auricular pain
therapy
To fight bacterial inflammation, be Oral antibiotics administered. In the late stages of the disease, antibiotic infusions may be necessary. In addition, a surgical removal of the necrotizing cartilage be necessary.










.jpg)