Signs of a herniated disc
General
A disc prolapse represents a common occurrence in the population Spinal disease represent. The Signs that there is a herniated disc can do this very different be. They are largely determined by the localization and the extent of the disease.
Depending on the height of the spine the herniated disc is irritates different nerves and thus causes different complaints at different locations. In general, the complaints are usually caused by a Impairment of certain nerves and compression of the nerve roots evoked. Depending on how strong the irritation of the nerve is, it can different symptoms come. Usually it is mostly about Pain such as Disorders of the perception of sensitivity such as motor dysfunction. Existing signs of a herniated disc should always be clarified by a doctor in order to avoid serious complications of the disease.

Symptoms of a herniated disc
In general, the signs of a herniated disc can vary greatly from person to person. Depending on the height of the spine at which the incident is located, there are different localizations of the complaints. The more the nerves are affected by individual parts of the spine, the more pronounced are the symptoms that are typically associated with the incident.
The foreground of a herniated disc is usually severe pain. These can appear on the back itself as well as radiate into other parts of the body. Sensitivity disorders and paresthesia are also common. This can manifest itself as numbness or tingling on the skin.
The tingling sensation from the herniated disc can also radiate into different parts of the body. If the affected nerves are more severely impaired, motor dysfunction can also occur. These can take the form of a decrease in the strength of certain muscles (muscle weakness) or even paralysis.
You can find detailed information about the symptoms of a herniated disc at:
- Symptoms of a herniated disc
- Symptoms of a herniated disc in the leg
- Poor falls asleep
Appointment with a specialist for a herniated disc?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
A herniated disc is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
Therefore, treating a herniated disc requires a lot of experience.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
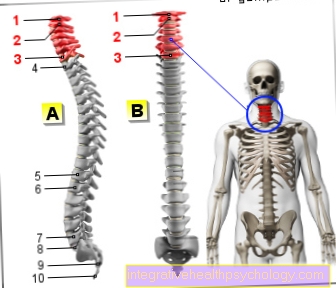
Signs of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine
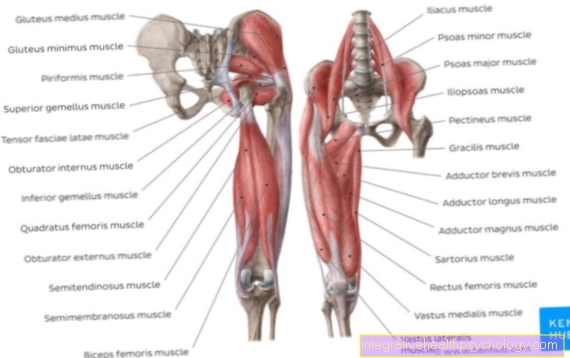
Most herniated discs occur in the lumbar spine area (Lumbar spine) on. Very often the moment and the movement at which the herniated disc occurs can be remembered. Sudden pain that occurs in direct connection with increased exertion and poor posture of the back are typical signs of a prolapse of the lumbar spine.
Symptoms that occur with a herniated disc at this level are characteristic of nerve irritation at the level of the lumbar spine. Pain in the lower back that is difficult to isolate is typical of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine. The pain also often radiates to a leg and foot. Sensory disturbances in both the leg and the foot suggest a herniated disc at the level of the lumbar spine. In the event of motor malfunctions, lifting the toes is no longer possible or only possible to a limited extent. If the impairment of the nerves running at the level of the incident is particularly great, the sphincter muscles of the bladder and intestine may be disturbed.
Not sure what is causing your back pain? Find out more in our article:
- How do I distinguish a herniated disc from a lumbago?
Signs of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine in the L4 / L5 area
A Herniated disc in the L4 / L5 area due to overstrain or poor posture can be diagnosed by signs such as sensory disorders or pain. These are expressed in the corresponding area supplied by the spinal nerves L4 or L5, the Dermatome is called.
If the herniated disc (prolapse) compresses the spinal nerve of L4, the sensory disturbance extends along the outside of the back of the thigh over the kneecap (Latin: patella) to the inside of the lower leg. Another sign can be an extinguished one Patellar tendon reflex be. Motor failures also manifest themselves in those affected in a weakened knee extension.
If the herniated disc in L4 / 5 presses on the spinal nerve L5, the sensory disturbance along the rear outer thigh over the outside of the knee and the front of the lower leg to the back of the foot and toes (1st and 2nd) may be suspicious as a sign. In addition, the “tibialis posterior reflex” is typically reduced or extinguished and a typical gait pattern, the “stepper gait”, occurs due to motor failures.
Signs of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine in the L5 / S1 area
The most common localization of a herniated disc is the transition area from the lumbar spine to the sacrum (Latin os sacrum). A herniated disc in the L5 / S1 area leads to typical signs, which are explained below.
If the herniated disc compresses the root or the spinal nerve in the L5 segment, it is also referred to as an L5 syndrome. Classic symptoms are both radiating pain and sensitivity disorders along the dermatome, i.e. the area of the skin that is supplied by the sensitive nerve parts of the spinal nerve L5.
It can therefore be indicative that those affected feel a "strange feeling" as a sign of the sensory disorder along the rear outer thigh over the outside of the knee and the front of the thigh to the back of the foot and toes (1st and 2nd), as these areas Dermatome L5. In addition, a first sign can be that lifting the foot is no longer possible, so the so-called "heel walk" is difficult / not possible. However, this already represents a motor failure because a peripheral nerve (N. fibularis communis), with the spinal nerve parts L4-S2, is damaged. One then speaks of a "dorsiflexion of the big toe" or a "stepper gait". In addition, the weakening or lack of the “tibialis posterior reflex” can be an indication that a herniated disc is present.
If a so-called S1 syndrome occurs in a herniated disc, typical signs are also indicative. On the one hand, there are sensory disorders on the back of the thigh and lower leg up to the outer (lateral) edge of the foot and the toes (3rd to 5th). In comparison to the L5 syndrome, however, “tiptoeing” is more difficult here, since the peripheral nerve (N. tibialis) with spinal nerve components from L4-S2 is damaged and the motor function fails. In addition, testing the Achilles tendon reflex can reveal signs of a herniated disc, which in this case has either gone away or weakened.
In addition to the signs described, severe cases of a herniated disc in L5 / S1 can also lead to bladder and rectal disorders, which give those affected an opportunity to consult a doctor.
Read more on the topic: Herniated Disc: Symptoms in the Leg
Signs of a herniated disc of the thoracic spine
Among the locations of herniated discs, a herniated disc in the thoracic spine is definitely the rarest. Nonetheless, there can also be a prolapse in the thoracic spine, which must be recognized by the appearance of the first signs and after excluding some differential diagnoses.
Above all, the sudden stabbing back pain at the level of the thoracic vertebrae, roughly speaking in the upper back area, is a typical sign of such a herniated disc.The pain does not necessarily have to be related to a stressful event or an overload, as most people initially assume.
The pain is typically transmitted to the chest and, due to its location in this area, can also be called "Intercostal neuralgia“, A nerve irritation of the spinal nerves between the ribs. The pain symptoms often worsen when the trunk muscles are tensed, as is the case with sneezing or coughing.
Typical signs of a herniated disc are, of course, the sensitivity disorders. Depending on the thoracic vertebrae between which the herniated disc occurs, the area of skin in which those affected complain of paresthesia or tingling paresthesia varies. So-called landmarks of the dermatomes in the area of the thoracic vertebrae are the nipples, dermatome Th5, or the navel, dermatome Th10.
In severe cases, a herniated disc in the thoracic spine can lead to bladder and rectal disorders or, in the worst case, to one Paraplegia come. By then, however, other initial signs should have appeared that give reason to see a doctor.
Signs of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
Herniated discs, which at the level of the Cervical spine (Cervical spine) are relative Rare. About 10% of all incidents are localized in the cervical spine. Unlike Herniated discswhich occur in the lower back, damage to the cervical spine is common during a longer time owing to Bad posture. Sudden incidents are rare in this region. However, the signs of a herniated disc in this localization are characteristic of the disease. The pain that occurs is usually both at neck, as well as on poor felt. The Charisma the pain can down to your fingers reach out to hand. It can also Sensory disturbances occur in the course of the damaged nerves. With a strong impairment of the nerve structures it comes to motor disorders. These express themselves in one Loss of strength in muscles on the arm and hand or in severe cases in Paralysis of the arm.
Difficulty swallowing as a sign of a herniated disc of the cervical spine

Cervical herniated discs are actually rather rare. However, if there is a herniated disc in the cervical spine, the occurrence of swallowing difficulties (lat. Dysphagia) can be a sign of many.
The cervical spine syndrome, a complex of symptoms of many complaints in the neck and throat area due to degenerative, functional or post-traumatic causes, makes it difficult for patients to swallow. This can be due to tension in the muscles involved in the act of swallowing or blockages in the nerves.
Most of the time, the first sign is a feeling of lump in your throat, which makes swallowing difficult. Sometimes the difficulty swallowing can also be accompanied by pain, in which case one speaks of "odynophagia" in medicine.
Read more on the topic: Causes of difficulty swallowing and pain when swallowing
Signs of a herniated disc of the cervical spine in the C5 / C6 area
A herniated disc in the C5 / C6 area caused by poor posture or traumatic effects often leads those affected to see a doctor due to the following signs.
If there is a C5 syndrome, there are sensory disorders in the form of tingling sensations in the transition area between the shoulder and upper arm. In addition, an indication of the presence of a herniated disc can be the extinguished or weakened "biceps tendon reflex".
In the case of C6 syndrome, the sensory disturbance extends from the outer elbow area along the outside of the forearm to the thumb and parts of the index finger. In addition to the extinguished biceps tendon reflex, another sign can be another weakened reflex, namely the "radius periosteal reflex".
Affected patients often report a weakened arm lift as the first sign of motor failures.
Signs of a herniated disc of the cervical spine in the C6 / C7 area
After a herniated disc at the level of C6 / 7, there are sensory disorders in the area of the index, middle and ring fingers as well as on the back of the hand.
In addition, there is a weakening of the triceps muscle, which is responsible for stretching the elbow. The triceps reflex is weakened or extinguished in the reflex examination,
Read more about this at: Disc herniation at the level of C6 / 7
Therapy / treatment
At existing signs a herniated disc should be a first A doctor should be consulted, which one the diagnosis of a herniated disc can possibly confirm. The signs and symptoms of a herniated disc are determined by the causal treatment of the incident treated myself. So can with a successful Treatment of the herniated disc It can be assumed that the symptoms that occur as part of the disease will disappear.
There are different possibilities of a herniated disc to treat. Depending on the individual extent and location of the disease and individual factors, the disease can be a conservative as well as operative therapy are used.
In most cases, a herniated disc can be successfully treated with conservative therapies (without surgery). The gift pain reliever drugs in combination with a consistent Physiotherapy for a herniated disc helps to take the discomfort and thereby the Mobility of the spine to obtain.
A operative therapy of the herniated disc is usually carried out when conservative measures have not achieved the desired result. The surgical treatment method can also be used in particularly serious incidents.
Which therapy / treatment is best in individual cases can be discussed with the attending physician.
Read more information at: Treatment of a herniated disc
Summary
There are certain symptoms that are to be interpreted as signs of a herniated disc and should be perceived as such. Characteristic pain, sensory disturbances and abnormal sensations as well as motor failures are typical for a herniated disc. It should be noted that not all symptoms have to appear in order to be able to diagnose a herniated disc as such. The symptoms can be very different from one person to the next. The severity of the symptoms and their localization are directly related to the height of the spine at which the herniated disc occurs. Herniated discs in the lumbar spine are generally the most common, which is why complaints in the lower back as well as in the leg or foot are to be classified as signs of a herniated disc.
You can read more information on this topic in our next article: Is there a herniated disc without pain?