Intervertebral disc bulge
General
The Band washers connect the Vertebral bodies of the Spine together. They lie between the said vertebral bodies and consist of Fiber cartilage.
It is not a rigid one, but one flexible connectionwhich gives the spine the freedom it needs to move. The human being has 23 intervertebral discs, which consist of one Fiber ring (Anulus fibrosus) and a soft one Gelatinous core (Nucleus pulposus) exist. The intervertebral discs primarily buffer Pressure loads on the spine caused by muscle pull.

The longer the intervertebral discs are (improperly) stressed or damaged, the higher the likelihood of Herniated discs or Intervertebral disc bulges. But also genetic factors, arthrosis and Signs of wear play a role here.
definition
A Intervertebral disc bulge is also called in medical terminology Disc protrusion or "incomplete intervertebral disc prolapse". This event is observed more and more often with increasing age.
The protruding intervertebral disc differs in size and texture from the so-called herniated disc (intervertebral disc prolapse) and must be distinguished from it. At the disc prolapse parts of the intervertebral disc enter the Spinal canal a. The spinal canal is the bony canal in which the Spinal cord lies.
In contrast to the protruding intervertebral disc, it tears disc prolapse of the Fiber ring (Anulus fibrosus) of the intervertebral disc partially or completely. When the intervertebral disc bulges the Fiber ring just arched outwards and in the worst case only very slightly torn.
In general, there are also differences in the imaging diagnostics.
In the Magnetic resonance imaging of a disc protrusion (short MRI) the vertical diameter of the affected disc is less than or equal to the height of the disc. A Intervertebral disc bulge can be painless. Depending on its location, however, it can also cause pain in the spinal canal, which can also radiate into other parts of the body.
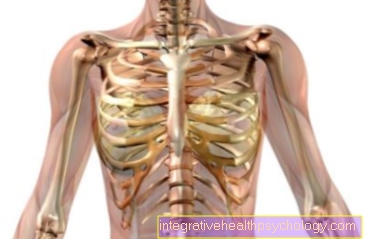
Image of a protruding disc

Intervertebral disc bulge
Disc protrusion
- Spinal nerve -
Spinal nerve - Spinal ganglion -
Ganlion sensorium - W.vertebral body -
Corpus vertebraea - Gelatinous core -
Nucleus pulposus - Fiber ring -
Annulus fibrosus - Intervertebral disc
(Intervertebral disc) -
Discus inter vertebralisa - Thinned fiber ring
A - intervertebral disc
bulging
Vortex from above and from the right
B - healthy disc
C - herniated disc
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Symptoms of a bulging disc
A Intervertebral disc bulge can initially symptom-free be. As a rule, however, it is expressed in Pain at the affected area of the spine. This pain can radiate to other parts of the body. The localization then depends on which part of the spinal cord or which nerves are affected or compressed by the protrusion.
In the case of impairments in the lumbar area of the spine (Lumbar spine) the pain can radiate into the legs, for example, whereas protrusions further up the head may radiate painfully into the arms. According to recent studies, however, the pain is generally more of a result Inflammatory reactions and not from the Compression of nerves.
Rarely can too impaired vegetative functions be. These include, for example Stomach, intestinal and bladder problems. In addition, a protruding intervertebral disc can lead to restricted mobility and stiffening. The lumbar spine is most commonly affected. This is a higher one Weight load exposed than parts of the spine higher up. The cervical spine is also more often affected. The thoracic spine, on the other hand, is almost never affected.
Pain with a bulging disc

A protruding disc can be completely painless, or it can be accompanied by severe pain.
On the one hand, this depends on how quickly the bulge develops; a protruding intervertebral disc can develop without discomfort if it develops over several weeks and months.
The faster the disc bulges, the sooner nerve fibers are compressed. This causes severe pain and possibly even numbness or symptoms of paralysis.
These are described as deep-seated, dull and sometimes burning. The localization of the pain depends on the height of the protruding disc.
If the cervical spine is affected, pain occurs primarily in the neck and arms up to the fingers.
If the thoracic or lumbar spine is affected, patients mainly complain of lower back pain and pain that extends into the legs.
This is due to the fact that the pinched spinal nerves pull into the leg in the case of a protrusion in the lumbar spine or into the arm in the case of a protrusion at the level of the cervical spine.
causes
The causes of a Intervertebral disc bulge are similar to those of one Herniated disc. First of all, it should be made clear how such damage can come about. The cartilaginous intervertebral discs consist of two parts, the fibrous cartilage ring and the gelatinous nucleus.
Usually, intervertebral disc bulges (as well as herniated discs) develop on the floor long-term previous damageso that their number increases with age. Through many years Incorrect loads the water content and thus the elasticity of the gelatinous core can decrease, so that it can no longer perform its function as a pressure cushion properly. As a result, the load on the fiber ring increases enormously over time. A Bulging or even Cracks in the fiber ring result.
Also Muscle weakness the paravertebral muscles and genetic predispositions can play a role in the development of a bulging disc. The paravertebral muscles are precisely those muscles that lie directly on the spine.
It is debated whether Accidents and traumatic injuries Disc bulges or herniated discs. This mostly remains a point of contention in labor courts.
This is another risk factor for changes to the intervertebral disc Obesity dar. Also Sedentary lifestyle and Bad postureas they are often observed with office workers, for example, seem to contribute significantly to the increasing number of disc events. Ultimately seem too Herpes viruses a role in the creation of degenerative changes Playing on the cartilaginous intervertebral discs, which can then cause a protruding disc or a prolapse.
therapy

The treatment of an intervertebral disc bulge is based on the national guidelines for back pain. In general, the therapy is similar to that of a herniated disc. Initially, the therapy is conservative.
Surgical interventions should only be considered if all conservative therapeutic approaches have failed or severe symptoms of paralysis and muscle weakness occur. The latter is more the case with a herniated disc than with a protruding disc, so that a protruding disc can almost always be treated conservatively.
However, it is important to have sufficient patience for the therapy, as these are usually months-long treatment concepts, which also require an adjustment to the general lifestyle. First of all, adequate exercise is required. Relief postures and bed rest are not recommended and do not make progress in therapy. If mobility is restricted due to severe pain, pain therapy is indicated as soon as possible. So-called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are mainly used in pain therapy. These are painkillers that work peripherally (at the point where the pain arises) and also reduce inflammation. This includes, for example, aspirin.
But also muscle relaxants, which relieve tension in the muscles and relax them, as well as centrally effective pain relievers (analgesics) are used. Connective tissue massages, heat and electrotherapy can alleviate the symptoms. However, their scientific usefulness is controversial.
Chronic and subacute pain is treated with the help of physiotherapy exercises and physiotherapy. However, they are not suitable for treating acute pain. Acupuncture represents another therapeutic approach in pain therapy and is also used in the treatment of protruding intervertebral discs.
In some cases, anti-inflammatory agents (such as cortisone) are injected directly into the spine for pain relief. However, such treatment is usually not covered by statutory health insurance. In severe cases, patients can wear a corset to support the spine.
In all of these therapeutic approaches, however, good patient cooperation is essential. These are lengthy therapy concepts that can sometimes take months and depend on the conscientious cooperation of the patient. In so-called back schools, those affected learn to integrate "back-friendly behavior" into their everyday lives. Such courses are offered by health insurance companies, fitness studios, occupational and physiotherapists and physiotherapists. Participants learn how to properly load and relax their backs in everyday life but also at work and how to avoid damaging movements and postures. In addition, specific exercises are carried out to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles in order to strengthen them. The course content also includes relaxation exercises and training in dealing with back pain, stress and health resources.
They contain a comprehensive course concept and are particularly useful for patients who have sedentary jobs or who put too much strain on themselves. Surgical therapy is roughly equivalent to treating a herniated disc. However, due to the numerous risks and the risk of relapse, the indication is very strict. The operation is to be seen as a last resort if no conservative therapy is successful or if there is already severe damage to the spinal cord. Such manifest themselves in paralysis and vegetative dysfunction. Vegetative dysfunction is understood to mean, for example, stomach, intestinal and bladder problems, e.g. urinary retention.
Exercises for a protruding disc in the lumbar spine
The therapy of Disc protrusion in the lumbar region, a protrusion of the intervertebral disc in the direction of the spinal canal with irritation of the nerves running there, is based on conservative measures, consisting of medicinal such as physical Treatment approaches through certain movement exercises.
The main goals are adequate stabilization as well Strengthening the muscles in the lumbar spine area and the greatest possible freedom from pain. Also, the complication is supposed to be a Herniated disc be prevented.
With regular, i.e. daily, back exercises, which are also often referred to as back exercises, you can improve your symptoms. The following exercises, among others, are suitable for treating intervertebral disc protrusion:
- At the Quadruped both hands and knees are on the floor. For about 15 seconds, one arm and the leg on the opposite side are raised in a straight line and held. Alternate sides and repeat the exercise five times each time.
- To Mobilization of the lumbar spine among other things, the so-called Knee wagons. In the supine position, the legs are bent and alternately tilted to the right and left. This position should be maintained for a few seconds and repeated five times on each side.
When treating your intervertebral disc protrusion, it is also important to build up your back muscles through regular exercise, such as swim, Walking, To go biking and gymnastic stretching and strengthening exercises. It is also possible to have your doctor prescribe physiotherapy for you. In general, it is important to do the exercises for treating your disc protrusion continuously, preferably daily, to prevent your symptoms from worsening. Even in everyday life, you should always pay attention to back-friendly work when lifting heavy loads.
OP for a bulging disc
The Intervertebral disc bulge (Protrusion) differs from the clinical picture of Herniated disc (Prolapse) mainly in the size of the protrusion.
In addition, the fiber ring of the intervertebral disc, which keeps it in shape, is not yet torn during the protrusion. For these reasons, the protruding disc is often referred to as an incomplete herniated disc. Since the spinal segment has not yet been severely damaged, a bulging disc is treated in almost all cases conservative.
Here one restricts oneself to adequate pain therapy, as well as the physical therapy. Surgical intervention, on the other hand, is only considered if conservative therapy is unsuccessful or if the symptoms quickly worsen despite therapy. Surgery is the treatment of choice for a herniated disc.
Exercise with a bulging disc
The diagnosis of a bulging disc raises a number of questions for most patients. One of the most frequently asked questions is whether, and if so, how much and which sport can still be practiced. The first question is with a clear "Yes" to answer. Sport actually plays an important role in that Therapy what to do with a herniated disc and avoiding worsening of the symptoms.
With regard to intervertebral disc protrusion, the primary goal of sporting exercises should be to strengthen the back muscles without overloading the back.
On the one hand, this can be done through targeted strength and movement exercises, for example in a fitness studio, ideally under the guidance of trained trainers.
Sports that train the core muscles and improve posture and coordination are also highly recommended.
Above all, this includes endurance sports such as swim (but here especially backstroke and crawl), hike and also Play table tennis.
However, since the restrictions caused by the protruding intervertebral disc are very individual, sports such as To dance, To go biking or Ball sports be perceived as pleasant and helpful.
Sick leave
If pain occurs with a bulging disc, the person concerned will be written off by the attending physician (e.g. the orthopedic surgeon) as long as the pain or other limiting symptoms occur.
How long the sick leave lasts depends on the patient's current complaints, so here no general time frame can be specified.
Furthermore, the length of the sick leave depends on the type of Activity of the person concerned. A physical worker can be on sick leave for a longer period of time than an office worker, for example.
Prophylaxis / prevention
One Intervertebral disc bulge or one disc prolapse you can't in every way prevent.
Genetic factors, Connective tissue weaknesses and also Injuries are not something that can be directly influenced. In some cases, not all of the causes for the development of such disc weaknesses are fully understood.
However, one can help his back and especially that Back muscles through targeted strength and movement exercises strengthen. Such back training can be done well in a gym with trained staff, for example. But you can also do something for your back in everyday life. Sports like to jog, horse riding, To dance and swim are recommended as they put a load on the intervertebral discs in a good way and promote muscle building. Static sitting positions are to be avoided in everyday life and especially at work (e.g. office work). However, there are now some ergonomic solutions that can be used to improve work at the desk, for example.
Please also read our relevant topics:
- How to strengthen the back muscles
and - How to best prevent a herniated disc
Curability
An intervertebral disc bulge becomes predominant conservative treated and usually heals completely within four to six weeks.
Conservative therapy primarily includes adequate pain therapy (mostly in the form of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or diclofenac), as well as muscle relaxants (to relax the muscles) and physical and exercise therapy.
Surgical therapy is less of an option for a bulging disc.
The reason for this is that surgery is not superior to conservative therapy and the risk of new intervertebral disc bulges (recurrences) is increased.
An operation can be useful if there is muscle weakness due to pinched nerve fibers or very severe pain that does not respond to pain therapy.
Disc protrusion of the cervical spine
Intervertebral disc bulges (Protrusion) can in principle occur at any height of the spine. The lower sections of the L.end upwirbelscolumn (Lumbar spine); at the level of Haswirbelscolumn (Cervical spine), on the other hand, intervertebral disc protrusions are rare. The cause of intervertebral disc bulges here, as in other spinal column sections, is often excessive and incorrect loading. However, especially with the cervical spine, there are also accidents (for example a car accident) with a strong acceleration of the head causes a protrusion.
Depending on the extent of the bulging disc, different symptoms can occur as a result. If the cause is due to wear and tear, the protrusion develops only slowly, so that symptoms appear late. These are then mostly characterized by strong ones Pain in the neck and upper back area, which can radiate into the arms and fingers. Furthermore, numbness and tingling feelings in the arms and fingers are typical, as are a headache, especially in the back of the head. Dizziness and ringing in the ears can also occur.
In the case of the cervical spine, the therapy is initially conservative. Avoiding stressful activities such as heavy lifting plays a major role in this. Furthermore, a healthy head and back posture should be ensured. Pain caused by the protruding intervertebral disc is initially usually treated with over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or diclofenac.
Disc protrusion of the lumbar spine
Even if intervertebral disc bulges can occur at any level of the spine, in the majority of cases they arise at the level of the lumbar spine (Lumbar spine). The segment between the Lumbar vertebrae (LWK) 4 and 5 affected. Here, too, the cause is mostly again an incorrect and overloading of the spine, for example by lifting heavy loads. The Lumbar spine is even more affected by this, since leverage and the weight of the lifted load are particularly strong at this point.
The first symptoms eventually appear when the bulging disc compresses nerve fibers, usually the spinal nerves. This then usually initially leads to pain in the body regions supplied by the nerves.
In the case of the lumbar spine, these are mainly the buttocks, as well as the legs and feet, but especially the lateral and front thighs and the back of the feet. In addition, numbness and tingling sensations can occur.
The treatment of the protrusion of the ban disk is in most cases purely conservative. On the one hand, this includes Exercise the lower back muscles, as well as posture training. In addition, lifting heavy loads should be avoided as a matter of urgency. Pain therapy is usually initially carried out with over-the-counter pain relievers, first and foremost Ibuprofen and Diclofenac.
Summary
The protruding disc is one Bulging of the fiber ring (Anulus Fibrosus) of the intervertebral discs in the Spinal canal and occurs increasingly in old age. She will too Disc protrusion called and can show different symptoms.
So it can depending on the location and extent painless or very painful The pain can also radiate to other parts of the body. The causes of such a bulging disc are various and range from genetic factors, over Muscle weakness up to Injuries and for years Incorrect loads.
The treatment of a protruding disc is done with the help of various conservative therapeutic approaches. Above all, this includes adequate pain therapy, which is carried out both medically and in the form of physiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises. The drugs used here are anti-inflammatory (anti-inflammatory drugs) and pain relievers (analgesics) and mostly belong to the class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Further therapeutic approaches are the acupuncture, Heat therapy, electrotherapy and patient training in the form of so-called Back schools. In such back schools, patients learn back-friendly behavior and specifically train the back and the surrounding muscles.
Operations are usually not indicated, but are basically the same as the treatment of a herniated disc (prolapse). The best prophylaxis against a bulging disc is sufficient movement and behavior that is easy on the back. Static sitting positions and incorrect loads such as stooping and lifting heavy loads are to be avoided. Strengthening the back muscles with the help of exercise as well sufficiently changing pressure loads the intervertebral discs are recommended.
















.jpg)