Vertebral fracture
Synonyms
Vertebral fracture, vertebral body fracture, fracture of the vertebral body, compression fracture, compression fracture, flexion fracture, bursting fracture, dislocation fracture, spinous process fracture, transverse process fracture, fracture vertebral body, fracture vertebra

Definition of vertebral fracture
At a Vertebral fracture it is a fracture of a vertebra of the Spine.
In most cases it is the result of an accident (traumatic vertebral fracture) or osteoporosis-related Vertebral fracture. A vertebral fracture can cause the Spinous process, the vertebral body or the Vertebral arch affect.
This can be the case with an unstable vertebral fracture Spinal cord be at risk from displaced bone fragments.
Causes of a vertebral fracture
The following causes can lead to a vertebral fracture:
- Direct violence (fall, blow, impact, impact, etc.)
- Indirect force (axial compression, hyperextension, over-bending, rotational bending, etc.)
- Pathological fractures (osteoporosis, tumors, etc.)
In the case of direct force, the vertebral body is directly injured by the external force.
Example: Fall on the stairs with direct impact of a vertebral body on the step.
In the case of indirect force, the external force is passed on and the vertebral body is injured indirectly.
Example: Plunge into shallow water with compression of the cervical spine.
It is characteristic of pathological fractures of the spine that a minor injury without significant force development is sufficient to fracture a previously damaged vertebral body.
Example: vertebral fractures without an adequate accident event (Spontaneous fractures) in osteoporosis.
Read more on the topic: What kind of pain occurs with osteoporosis?
Symptoms of a vertebral fracture
Depending on the localization of the fracture, there is pain over the injured vertebral body and the adjacent spinal column sections. The pain intensity can be very different. If the vertebral body is only slightly indented, a fracture can easily be overlooked due to minor discomfort. Larger injuries, on the other hand, can be associated with considerable pain symptoms.
In the event of a spinal cord injury (Transection, spinal contus) can be the typical symptoms of a Paraplegia enter:
- Failure of voluntary motor skills and reflex behavior below the damage
- Loss of surface and depth sensitivity
- Dysfunction of the bladder, rectum, potency
- Changes in skin blood flow, trophism and sweat secretion
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Figure spine

- Transverse process
- outgoing nerve
- Vertebral bodies
- Spinous process
- Spinal cord
Vertebral fracture due to osteoporosis

Cover and base plate collapse (sintering fracture) in osteoporosis with the formation of short-range kyphosis (rounded back). If several vertebral bodies break in this way, the so-called "widow's hump" is created, which is characterized by a pronounced rounded back.
Read more on this topic at: Vertebral fracture due to osteoporosis

Vertebral fracture (vertebral fracture)
- Transverse process -
Transverse process - Spinous process -
Spinous process - Upper articular process -
Superior articular process - Lower articular process -
Inferior articular process - Spinal nerve -
Spinal nerve - Spinal cord -
Medula spinalis - Gelatinous core - Nucleus pulposus
- Vertebral arch - Arcus vertebrae
- Fiber ring - Annulus fibrosus
- Vertebral bodies - Corpus vertebrae
- First thoracic vertebra -
Vertebra thoracica I - Twelfth thoracic vertebra -
Vertebra thoracica XII - First lumbar vertebra -
Vertebra lumbalis I - Fifth lumbar vertebra -
Vertebra lumbalis V
a - cervical spine (cervical spine)
b - thoracic spine (BWS)
c - lumbar spine (lumbar spine)
A - vertebral fracture (spinous process,
Vertebral bodies) from above
B - vertebral fracture (spinous process,
Vertebral body) from the right
C - Most common area of the
Vertebral fracture
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Diagnosing a vertebral fracture
The diagnosis of a vertebral fracture comprises various aspects, which are briefly presented here.
1. Clinical examination and medical history
When diagnosing a vertebral fracture, they are clinical examination and anamnesis the first steps. It is essential for the examiner to know how the break came about. Therefore, it is asked whether it was a fall or an accident or another potentially triggering event gave. Furthermore are Pre-existing conditions related to the skeletal system as a osteoporosis or a Bone tumor significant. Certain medications can also cause bone instability, so too Medication history is very important. The doctor also clarifies whether it is too Signs of paralysis, one Numbness or Problems passing urine or bowel movements came. That can be evidence of a Spinal cord damage be.
For the clinical examination, the Spine examined for knocking and tenderness. The doctor continues to look Deformities, palpable Bone levels or one Restriction of movement. In addition, the Motor skills and sensitivity of the patient are checked. If an unstable break is suspected, for example after an accident situation, this is counterproductive, so that diagnostic imaging is more likely to be used there.
2. Diagnostic imaging
There is a X-ray of the spine in two planes in which fracture signs can be seen. For example See bone fragments or other radiological abnormalities. In the event of an accident that is likely to have other accompanying injuries, a Computed Tomography (CT) to quickly detect any life-threatening injuries. The CT is also used to assess Vertebral fractures in the transition area between the cervical spine and thoracic spine and is always driven when there is a nerve failure. A Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine MRI is only made in rare cases as it takes too long for an accident situation. However, it is definitely useful for surgical planning or if there is a suspicion of damage to nerves, blood vessels, ligaments and soft tissues.
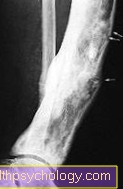
X-ray of a lumbar fracture

The lumbar spine is green.
A cover plate impression fracture can be seen on the red LWK 3.
The sacrum can be seen below in blue.
therapy
corset
A vertebral fracture can be a difficult situation depending on the extent. are several vertebral bodies broken, can the spine unstable and there is a risk that parts of the vertebral body will split off and possibly that Spinal cord injured. Rapid treatment is therefore necessary. To the first Therapeutic measures belong Painkiller and the corset.
Until an operation can be performed, the corset is worn as an orthosis around the Spine to calm down. This is to prevent the break from worsening or becoming important Nerve tracts get hurt. After an operative treatment of the vertebral fracture, a follow-up treatment is carried out, often initially with a corset. Then it should prevent a wrong move or one too high load provokes another injury.
A corset also protects the spine and promotes the healing process. At the same time is targeted through physiotherapy trained the movement and slowly increased the load again.
surgery

To surgery it occurs either with unstable fractures or with stable fractures with severe pain, paralysis or Urinary and fecal incontinence disorders. This often leads to complications of stable fractures osteoporosis.
The objectives of the operation are:
- the Elimination of fractions which, if applicable, on annoy, Spinal cord or Vessels to press
- reconstruction the normal shape of the spine
- the stabilization the spine after the break
If the bones are healthy, in most cases it is sufficient to have the vertebral bodies Fix plates and screws and straighten up. The operations are usually carried out in two steps.
- First, the broken vertebrae are screwed to the neighboring vertebrae from behind and then straightened up again. If necessary, the Spinal canal opened wider when constricted or freed nerve and vascular structures from the constriction.
- In the second step of the operation, the broken vertebrae and the Band washers removed and a Vertebral replacement introduced.
Usually the operation is done in general anesthetic. At the beginning, the patient lies on his stomach so that the operation can be performed from behind in the first step. The patient is then placed on his side and the front part of the spine with a Access through the chest or abdominal cavity reached.
Other methods are that Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty. This is minimally invasive procedures, which is often used for more stable fractures. In these procedures, under constant x-ray control worked, here the patient is in the prone position.
In the Vertebroplasty a hollow needle is inserted into the vertebra with the fracture. Then through the needle cement applied to the site with high pressure. The cement is used for this Bone fragments reconnect after the cement has hardened.
In the Vertebroplastic one is enough local anesthesia off, with the Kyphoplasty a general anesthetic is necessary.
In kyphoplasty, a balloon pushed into the vertebral body and then inflated. This method realigns the vertebra and you can now start pouring cement.
Both treatment techniques should be maximal four to six weeks after the vertebral fracture has occurred.
To Complications During the procedure, it can happen if the cement emerges from the vertebral body when the cement is introduced. This is particularly a problem with Vertebroplastyin which the cement is injected at high pressure. The cement can flow into the spinal canal or even into the blood vessels, causing serious vascular occlusions and other complications (Cement embolism) cause.
Another problem is that heaped Follow-up fractures arise in adjacent vertebral body segments due to the very hard cement.
Alternatively, you now have the Elastoplasty use. In elastoplasty, the principle of the procedure is identical, but instead of cement, elastic is used silicone as an injection material. The silicone is much closer to the bone structure than the very hard cement.
Another minimally invasive procedure puts the application through Endoscopy . With this method, a 1.5-2 cm skin incision set through which four plastic sleeves are inserted between the ribs. It is possible to look inside the body via two monitors.
Operating instruments such as knives are inserted with three sleeves. In order to get a better overview during the operation, the affected lung side is not ventilated during the operation. Vertebral fragments and intervertebral discs can be removed using special surgical instruments such as forceps, milling cutters and punches.
There is also a relief when the Spinal canal possible. The Vertebral body replacement, usually a titanium basket or a bone chip inserted. In addition, a titanium plate is screwed on to ensure increased stability. A computer-aided operation navigation system makes it possible to work very precisely and to control all steps.
In the case of very severe vertebral fractures, usually only the remains to stabilize the spine Stiffening of the spine, the so-called Spinal fusion. Parts of the vertebra or the whole vertebra are removed from the spine and, if necessary, through a Cage replaced. This is a basket made of different materials, mostly titanium. In addition, the vertebrae above and below are connected to one another by plates and screws.
After the operation is the Aftercare very important. Here is only one for now bed rest of a few days necessary. Sometimes after surgery is wearing one Corsets For operations on the cervical spine, there is a treatment with a neck brace after the operation (Cervical brace) for a few weeks.
There are also special ones Rehabilitation programs after the operation. After the operation you should bend over and carry loads over 5 kg be avoided, at least in the first few months. The break then usually heals 6-9 months out. The metal reconstructions are usually kept for a year or some of them remain in the body for a lifetime.
When using minimally invasive procedures like the Vertebroplasty, Kyphoplasty and Endoscopy is it a little different. Here the spine can immediately after the operation because the bone cement becomes very hard and provides the necessary stability. The patient only has to stay in the clinic for a few days and no special rehabilitation is required. In addition, the pain and blood loss after the operation are significantly less than with more invasive procedures and the patient recovers from the operation much faster. One has an increased cosmetic effect in particular with the endoscopy procedure, where hardly any scars arise.
Read more on the topic: Therapy of a vertebral fracture
Vertebral fracture prognosis
A Vertebral fracture leads to a permanent change in the vertebral body and thus also its function. In contrast to others bone Once the bone has been compressed, it cannot straighten up again.
It is practically impossible to predict whether problems will develop from this. The resulting healing in a malformed shape can permanently overload neighboring areas.
If the vertebral fracture has caused nerve damage, the extent of the damage and the time until the damage could be repaired are decisive for the prognosis.
Slight nerve irritation almost always regresses, with cross-sectional symptoms the prognosis is unfavorable, but a complete recovery is conceivable here too.
Is an osteoporosis-related Vertebral fracture before, is the Osteoporosis therapy of crucial importance, since without therapy there is a risk of further fractures in other vertebral bodies.
Healing of the vertebral fracture
The cure vertebral fracture depends largely on the extent of the injury. are multiple vertebral bodies affected and at the same time also the supporting ligaments of the Spine injured, it can be a complicated fracture, which can often bring further complications with it.
Will the break operational Treated with screws and stiffeners, the healing process takes time six to eight weeks. By means of an operation, the broken vertebral body is often connected from the front and back with rods to the neighboring vertebral bodies and so initially stiffened and protected. As a result, the entire spine is initially secured and also stable under load.
Nevertheless, the wounds and also the break points have to heal until full loading is possible again. In severe cases, when the vertebral body can no longer be built up, it is partially or completely replaced. At this point the spine is stiff. The healing time is then up to half a year or even longer, depending on the location and age of the patient. It may be that despite good healing too Pain and decreased mobility stay back.
In the case of uncomplicated fractures, healing usually goes very well and without any consequential damage. Surgical treatment is not always necessary for this, but one is enough conservative therapy out. This usually includes adequate rest and immobilization Orthosis, like one corset. So the healing can take place without disturbances.
Duration of the vertebral fracture
The Duration the healing of a vertebral fracture can vary greatly. Many factors like Age, The extent of the injury and the subsequent treatment affect recovery.
A stable fracture of the vertebra, which often occurs in the course of overload and osteoporosis usually does not endanger the Nerve fibers of the spinal cord. It still causes pain for the patient and movement is also significantly restricted. These vertebral fractures are usually conservative at first, that is without surgery treated. In addition to a pronounced and sometimes longer bed rest the symptoms will be with Painkillers treated. In the further course of this, the physiotherapy facilitated. By means of targeted physiotherapy, the patient receives instructions on how to behave in a way that is gentle on the back for several weeks and learns exercises like in the back school to train the muscles at home. After 2 - 4 weeks, these exercises are then carried out on an outpatient basis. In some cases it will also be wearing one Corsets recommended for 6 - 8 weeks. It prevents incorrect movements from being made and at the same time allows the fracture to heal in peace.
At Cervical vertebrae fractures is a Cervical brace (Ruff) necessary. So it can 2 - 3 months take up the Spine is fully resilient again.
At unstable fractures on the other hand, there is a risk that parts of the breakage Nerve root in the Spinal canal constrict and thereby neurological deficits like Paralysis consequences. Therefore, a surgery recommended. In such an operation, the unstable vertebral body is bridged and sometimes also stiffened. This will cause a possible narrowing of the annoy prevented. Metal plates and / or screws are often used for stabilization, which is why a longer healing phase connects. Nevertheless, movement can be resumed after a few days of bed rest, as the spine is stable enough for everyday stress.
Only at Cervical vertebrae fractures is also a Cervical brace applied. After a week, the patient can leave the clinic. Further treatment then usually takes place in a specialized rehabilitation center. The breaks are after approx Completely healed in 6 to 9 months. Usually the screws and metal plates are left for a year in the body, but in some cases for a lifetime.
Consequences of the vertebral fracture
The consequences of a vertebral fracture can be very different for those affected. you are depending on the type of fracture, the cause and the general condition of the patient.
Stable breaks can usually be treated conservatively, that is, without a surgical measure. These can also prove to be very few symptoms represent. For example, the pain is not at all or only very slight. But that doesn't have to be the case there even stable fractures can cause severe pain. The conservative therapy can last up to several weeks and includes physiotherapy, pain medication and supportive measures such as the application of a corset. Despite such measures, the patient may experience pain that is refractory to therapy, which in the worst case can take a chronic course.
In patients with a unstable vertebral fracture is a Surgery inevitable. Such an operation can be a long-lasting one bed rest entail. In any case, the surgical wound must be spared so that the stability of the operated vertebra is not endangered. Vertebral fractures can in the worst case to paralysis or sensitive paresthesia up to numbness of a body part lead when the spinal cord or nerve roots are damaged. In the most extreme case, a Paraplegia result. Severe paralysis, even with successful surgery, can be irreversible if the damage to the spinal cord or nerves is too great.
Localization of the vertebral fracture
In most cases the lower one Thoracic spine and upper Lumbar spine (Lumbar spine) affected. In about 20% of the cases there are more than one Vertebral bodies affected.
classification
The classification of the vertebral fracture:
For the first two cervical vertebrae (Atlas and Axis) there are separate classifications of the vertebral body fracture, which should not be mentioned here.
The most important feature of vertebral body fractures is the division into stable and unstable fractures.
While the stable vertebral fracture does not pose a threat to the spinal cord, unstable vertebral body fractures endanger the spinal cord from movable fracture fragments (fractions).
The question of spinal stability after an injury is decided by the consequences of the injury to the rear spinal structures:
- Posterior edge of the vertebral body and disc wall
- Vertebral arch and articular processes
- Posterior spinal ligament complex
According to Magerl (1980), primarily stable spinal injuries (A) are as follows:
Compression or compression of the vertebral cancellous bone with intact ligament and joint connections and possibly slightly injured intervertebral discs. This usually results in the typical wedge vortex. There is no injury to the posterior wall of the vertebral body. Despite immediate loading and mobilization, no increase in deformation and no displacement of fracture fragments are to be expected.
In contrast, in the case of primarily unstable spinal injuries (B), at least two out of three stability elements (anterior vertebral body, posterior vertebral body, posterior spinal ligament complex) are injured. There is a risk of increasing deformation and displacement of fracture fragments.
Read more on the topic: AO classification














-braun.jpg)