Candidiasis
Synonyms in a broader sense
Candidiasis, Candidiasis, Candidamycosis, Candidamycosis, Monoliasis, Thrush
Definition of candidiasis
Candidiasis is one Infectious diseasecaused by infection by a Fungus of the genus Candida (mostly Candida albicans) is triggered. One differentiates between an infection that only Skin and / or mucous membranes concerns and a so-called systemic infectionin which other tissues and organs are also affected.

introduction
Candida fungi are Yeasts. This group includes the most common fungus Candida albicans over 150 more, among others Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida glabrata and Candida krusei.
All of them are counted among the facultative pathogenic agents. This means that one Evidence of these fungi Not necessarily with one illness equates to there too many healthy carriers of candida are. Candida albicans can be found in many healthy people (an estimated at 70%) find either superficial on the skin / mucous membrane
or less common also in
- throat
- esophagus
- Gastrointestinal tract
- vagina
These fungi are also found in the environment, both in plants and in animals widespread.
Please also read our article on the genre Mushrooms.
Causes of Candidiasis
However, an infection (regardless of whether it comes from the outside or from your own body flora) only occurs if that Weakened immune system is. This can either be due to a congenital immunodeficiency, in the context of diseases affecting the immune system such as AIDS, cancer, diabetes mellitus or one sepsis or treatment with certain immunosuppressive drugs how Cytostatics or Cortisone be the case.
Risk of infection from candidiasis
The Candida fungi that can cause candidiasis can be transmitted in different ways. On the one hand, this can happen via a smear infection. This means that the fungus is transmitted if it is directly touched by infected people or infected material.
An example of this would be, for example, that a baby can get candidiasis in the mouth if the pacifier is infected. This candidiasis is then known as oral thrush. Oral thrush in babies can also result from the transmission of the Candida fungus during breastfeeding.
Read more on this topic at: How contagious are yeasts?
Another way of infection is through the blood. For example, drug addicts can become infected through infected needles. The fungus can enter the bloodstream directly, even if the patient has been using IV cannulas.
It is important for the infection that a disturbed body defense is the best basis for an infection. Such a weakened body defense can have many causes, for example various underlying diseases such as cancer, AIDS, alcoholism or diabetes mellitus. But pregnancy or various medications such as antibiotics or corticosteroids that are taken for a long time or chemotherapy and immunosuppressants can disrupt the body's own defenses and thus make infection more likely.
Classification of types of candidiasis
1. Mucocutaneous candidiasis, that is, the form that exclusively affects the skin and / or mucous membrane, is also known as thrush, of which several subtypes can be distinguished.
- Oral thrush shows up on the lining of the mouth and throat
- Skin thrush (typically in folds of the skin), for example in the armpits
- Anal area
- strip
- Esophagus (oesophageal candida)
- Intestinal (intestinal candida)
If the thrush is in the genital area, it is called genital thrush, which affects the vagina in women and the glans (also called balanitis) or foreskin in men. Here, infection often occurs through sexual intercourse.
Vaginal thrush is also known under the term "classic thrush". Almost 20% of women have such an infection in the genital area; women with diabetes mellitus, of childbearing age or during pregnancy are particularly at risk.
In men, a narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis) or poor hygiene have a positive effect on the development of a genital inside.
2. Systemic candidiasis occurs when the pathogens manage to spread into deeper tissue layers and gain access to the bloodstream, which can actually only happen in severely weakened patients. In such a case, the fungal infection can affect practically any organ system, whereby the symptoms can also occur in different places and are not organ-specific.
Read more on the topic:
- Yeast infection
- Penile fungus - candidiasis in men
Symptoms of candidiasis
1. Symptoms of mucocutaneous candidiasis
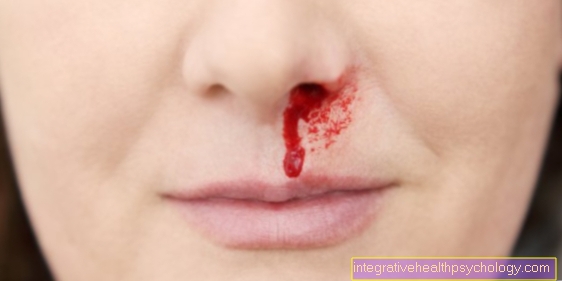
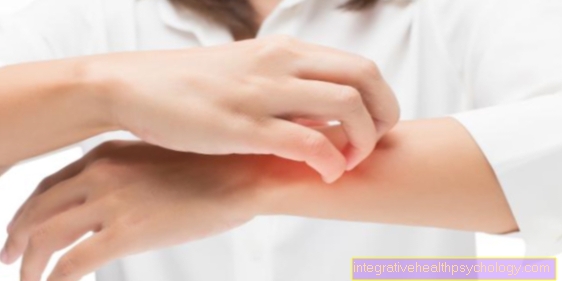
are always local limited. Typically they are affected areas very reddened and there is a pronounced itching. If it is mucous membranes, then arise on the reddened bottom whitish (sometimes yellowish) Toppingsthat can be easily peeled off.
However, this process often leads to Bleeding. If the esophagus Those affected often complain about Pain when swallowing or a burning sensation behind that Sternum. If there is candidiasis of the intestinal mucosa, then there is usually a feeling of fullness, Flatulence and or diarrhea.
In women’s genital thrush, there are also:
- Redness
- Coatings and itching
- whitish-crumbly discharge from the vagina
- Burn
- red pustules or papules (in men)
2. Symptoms of systemic candidiasis
The organs that are more frequently affected include the
- Lungs (candida pneumonia)
- Kidneys
- liver
- spleen
- Central nervous system (CNS, encephalitis)
- Heart valves (endocarditis)
- Eyes (candidal endophthalmitis)
Often times, patients suffer from a fever, which can also be seen through Antibiotics can not lower. At a Blood poisoning due to Candida species (a Candida sepsis) there is permanent or repeated one large number of pathogens in the bloodthat are flushed out throughout the body. As this one serious and sometimes life-threatening clinical picture represents (approximately 70% of these generalized candidiases are fatal), become risk groups (i.e. immunodeficiency) often treated with antifungal therapy as a precaution.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
Superficial candidiasis is usually diagnosed without any problems. Either a Smear from the toppings on the mucous membrane or under a Gastroscopy a tissue sample from the Esophagus or stomach lining taken. In the case of lung involvement, a so-called bronchoalveolar lavage take place in which cell material is obtained by “flushing” the lungs with a saline solution.
The test material containing the pathogen is then examined microscopically and it becomes one Cultivation of Candida carried out on a special culture medium (Sabouraud agar). In addition, in some cases (depending on the localization of systemic candidiasis) the examination of chair or urine, Blood, tissue biopsies or Liquor help with a diagnosis.
A detection of antibodies against the pathogen is possible in principle with immunocompromised patients but often false negative. At a invasive candidiasis can also imaging procedures (Ultrasonic, roentgen or CT) can be used to create a To recognize organ involvement.
As part of a diagnosis (especially of generalized candidiasis), the search for predisposing (favoring) factors are of great importance. Sufferers should regularly check for underlying diseases such as Diabetes mellitus, Immunodeficiencies, AIDS or a HIV infection (candidiasis is often the first clue here), leukemia or Tumors to be examined.
Therapy / treatment for candidiasis
The therapy / treatment of candidiasis is carried out with a Antifungal agent, a drug that helps against fungal infections. Come with a candida infection Nystatin, Amphotericin B, Triazole antifungal drugs or more rarely Caspofungin for use.
In principle, you can remember that local infections also treated locally be while a systemic infestation also one systemic therapy requirement.
- 1. In mucocutaneous candidiasis, ointments or pastes can be applied or mouth rinses performed; if deeper-lying mucous membranes are affected, juice or tablets can also help.
Vaginal suppositories are also available for treating vaginal thrush. - 2. In the case of systemic candidiasis, the drugs (in this case usually Fluconazole) administered intravenously or taken in tablet form. In addition, it is of course extremely important to adequately treat any underlying disease and to minimize risk factors in order to get rid of candidiasis.
There are several guidelines for an appropriate therapy / treatment of candidiasis, the guideline for the procedure in hemato-oncological patients from the "Working Group on Infections in Hematology and Oncology" is widespread. The Prophylaxis in high-risk patients (for example HIV-infected people) usually takes place with fluconazole.
Treatment of candidiasis, especially if it is superficial, is usually relatively easy to carry out and leads to one Cure the disease. However, it often happens even after a successful treatment recurrence of infection, so a so-called relapse.
This is precisely why it is important to train patients to do this with themselves to notice renewed candidiasis as soon as possible and in case of uncertainty one To see a doctor. In order to reduce the risk of this, it is important to carry out the therapy correctly and consistently and also favoring diseases treat well.
Candidiasis in the place of occurrence
Candidiasis of the mouth / oral mucosa
Candidiasis or also thrush describes an infection with the Candida albicans fungus or other forms of Candida. Candida fungi occur in healthy people in small forms and without any disease value.
For people with an existing one Defensive weakness (For example, in AIDS or leukemia, malignant lymphoma or under prolonged therapy with Corticosteroids, Cytostatics or Immunosuppressants) however, a clear infection with disease value can occur. Such an infection can affect the lining of the mouth.
This results in a whitish to yellow coating in the mouth. This coating can be wiped off, but the oral mucosa can bleed easily afterwards. The infestation can last the entire Oral cavity and throat affect. However, it is always limited to the oral mucosa. Symptoms can include pain while eating or so-called dysphagia, which means difficulties and Pain when swallowing.
For a reliable diagnosis, a swab must be taken from the affected oral mucosa. The Candida fungi can be detected in this material.
As a form of therapy for candidiasis of the oral mucosa, so-called antimycotics, i.e. antifungal agents, come into question. Such agents can Nystatin, Natamycin, Amphotericin B, Ketoconazole, Fluconazole or Flucytosine be. Such active ingredients are best used in the mouth as a mouthwash.
The course of such candidiasis is usually very good, as the mouthwashes work well as long as they are used appropriately and for a long enough time. However, fungal infections generally tend to recur, which means that the risk of the symptoms recurring is very likely. In order to avoid such recurrences, underlying diseases that encourage renewed infection should be treated as well as possible.
As a preventive measure, especially in the case of risk factors, it should be ensured that symptoms are recognized at an early stage. Regular checks of the oral mucosa in cases of AIDS or similar diseases that weaken the immune system are therefore necessary.
Candidiasis in the intestine
If there is a local infestation of fungi the Genus Candida, what is known as candidiasis or thrush occurs. The most common triggering fungus is the so-called Candida albicans. However, the disease can also be caused by other fungi of the Cancida genus.
Cause one Intestinal candidiasis are often antibiotic treatments. These damage the intestinal flora. This means that there are no opponents for a fungal attack. Due to the lack of natural intestinal flora, fungi, which can also occur naturally in the intestine, can trigger symptoms. Because the fungi metabolize carbohydrates in the intestine, gas is formed in the intestine, which can lead to flatulence and pain.
Such an infestation can affect the esophagus (Esophagus) or affect the entire subsequent gastrointestinal tract. Candidiasis of the esophagus is often involved Pain when swallowing noticeable. Intestinal candidiasis mainly leads to diarrhea, Flatulence and one Bloating. However, these symptoms are very unspecific and do not directly indicate a fungal attack. In addition, other unspecific and secondary symptoms such as migraines, skin changes or joint pain can also occur. But the direct symptoms of the intestinal involvement are superficial.
The diagnosis of intestinal candidiasis can be a little difficult. On the one hand, the Stool on candida getting tested. However, the fungus is not always detectable here. Attempts can also be made to determine antigens in the blood that would indicate an infestation. Traces of the fungus can also be found in saliva and may be detected. Reliable evidence is when the fungus has been definitively identified by means of a culture and microscopic examinations.
Come as therapy antifungal drugs in question. These have an effect against fungi. In the case of intestinal candidiasis, this would be the active ingredient, for example Nystatin. When ingested orally, this does not go directly into the blood, but acts locally in the affected intestine. It is recommended to follow the treatment with an immune system-strengthening therapy and to follow an anti-fungal diet for a few weeks. Nevertheless, the risk of re-infestation is increased.
In this context, of course, the fungal attack should be totally reduced. Since the oral cavity is often affected, proper oral hygiene should be carried out. A strong immune system is also important and secondary diseases that could be the cause of intestinal candidiasis are treated.
Candidiasis of the vulva
The vulva and vagina can also be affected by candidiasis. With a frequency of 20%, this is one of the most common genital infections, especially in women of childbearing age. Women with existing diabetes mellitus or during pregnancy are particularly affected.
This is noticeable through various symptoms of vulvitis or vaginitis (also colpitis or vaginal inflammation), i.e. inflammation of the outer vagina or the inner vagina. This results in a reddened and swollen vaginal lining.
The mucous membrane of the vagina is also covered by a white coating that can be removed and which can also crumble a bit. The inflamed mucous membrane is hidden underneath. Often burns or itches (so-called pruritus vulvitis) the mucous membrane and thus the outer vagina or the inside of the vagina.
There is also increased discharge (Genital fluorine), which is also whitish and crumbly. In addition, swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin area may be possible. Also pain during intercourse (Dyspareunia) or painful urination (Dysuria) can occur. These can be so strong that sexual intercourse is no longer possible during an infection.
The diagnosis is made through several examinations. On the one hand there is an anamnesis (a detailed conversation with the patient) necessary. Important symptoms are queried, possible risks of infection are clarified and, best of all, differential diagnoses of candidiasis are excluded based on certain criteria of the disease.
The next step should be a gynecological examination, paying particular attention to redness of the vulva, pain and the whitish coating. In the differential diagnosis, ulceration or bleeding, as can occur in other inflammatory diseases of the vagina, should be excluded.
Furthermore, a speculum examination is carried out, during which the inside of the vagina can also be assessed. Here you can observe how far the infection has spread to the vagina or whether it is only limited to the vulva. If necessary, a smear is then obtained for a native preparation. This is examined directly for Candida fungi under the microscope.
If the diagnosis of thrush vulvitis, i.e. candidiasis of the vulva, has been made, treatment with local antimycotics can be considered. This means that the anti-fungal agents must be applied directly to the vulva. Clotrimazole comes into consideration here. This can be used in the form of vaginal suppositories or ointments.
Is this form of therapy ineffective (Therapy resistance) fluconazole can also be taken orally and thus be effective. It is important that if the vagina is infected by Candida fungi, the partner is also treated, even if he does not show any symptoms, as otherwise the infection can recur.
Also read our article: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Candidiasis in the throat
Just like the mouth, candidiasis can affect the entire throat. Symptoms are similar to difficulties swallowing and Pain when swallowing which are also typical for candidiasis of the mouth. The whitish coating of the mucous membrane also occurs. This coating can be wiped off, but the mucous membrane of the throat can bleed easily afterwards.
The diagnosis is also best made here by swabbing the affected oral mucosa. The Candida fungi can be detected in this material and a reliable diagnosis can thus be made.
As with candidiasis of the mouth, so-called forms of therapy are available Antifungal drugs so Antifungal agents in question. Such agents can Nystatin, Natamycin, Amphotericin B, Ketoconazole, Fluconazole or Flucytosine be. Such active ingredients are best used in the throat as well as the mouth as a mouthwash. The prognosis here is also quite good, although recurrences can still occur.
Candidiasis of the lungs
Candida fungi can cause pneumonia in the case of systemic candidiasis in the lungs. There are different ways of infection. On the one hand, the infection of "Inside" come.'
This means that the fungus is usually already on the skin Mucous membranes or in the body is present and can only lead to illness, in this case pneumonia, if the body's immune system is weakened.
The infection can also be caused by "Outside“Come, that means that the fungus has first penetrated the body or the lungs and then causes pneumonia. However, in this case too, a disturbed or weakened immune response of the body promotes an outbreak of the disease.
The symptoms of pneumonia through Candida fungi are very unspecific. The lung function can be restricted, i.e. shortness of breath and coughing. Accompanying this, a fever can occur and the breathing rate increases.
However, pneumonia caused by Candida fungi is considered one atypical pneumonia and does not always show all symptoms or severe symptoms. You can also (as usual) Rattling noises when listening or a muffled knocking sound when tapping are less likely to perceive.
Two different antimycotics (anti-fungal drugs) are available as therapy. If there has not yet been a previous exposure to azoles or if the pathogens are sensitive to fluconazole, fluconazole can be used for therapy. If the patient is unstable, there is a previous exposure to azole or if the pathogen is resistant to fluconazoles, echinocandins can be used instead.