Inflammation of the root of the tooth
introduction
The tooth root is the part of the tooth that secures the tooth in the tooth socket. It is not visible from the outside because it lies below the tooth crown.
At the top of the root there is a small opening called the Foramen apicale dentis. This is the gateway for nerves and blood vessels into the pulp cavity (tooth pulp). In the pulp cavity there are blood vessels, nerve fibers and connective tissue. If the pulp is inflamed, one speaks colloquially of tooth root inflammation or pulpitis. It usually takes place at the tip of the root and can cause severe pain,

Symptoms
Is there a Root inflammation, the patient suffers from pain in the affected area. This occurs especially when the tooth is under pressure, e.g. while chewing. It's a so-called Sensitivity to knocking available. Also warmth and cold can lead to pain symptoms. The pain can spread to the eyes and neck area.
After a certain time, the tooth can also loosen. Other signs are Gingival pockets, a strong reddened gums and possibly pus as well. A thick jaw is also a symptom of such inflammation.
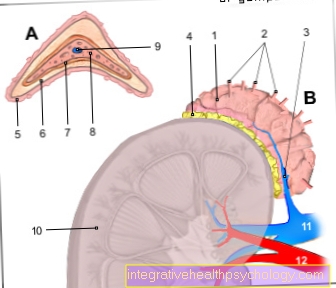
Figure root inflammation

- Tooth enamel -
Enamelum - Dentin (= dentine) -
Dentinum - Tooth pulp in the tooth cavity -
Pulp dentis in Cavitas dentis - Gums -
Gingiva - Cement -
Cementum - Root skin -
Periodontium - Alveolar bone (tooth-bearing
Part of the jawbone) -
Pars alveolaris - Opening of the tooth root tip -
Foramen apicale dentis - Blood vessels
- Nerve fibers
Root inflammation -
Pulpitis
a - dental caries -
Caries dentium
b - gingivitis -
Gingivitis
c - Entz. of the tooth support system -
Periodontal disease
d - Entz. at the root tip -
Apical ostitis
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
causes
There are many different causes that can lead to an inflamed root.
The most common cause is one untreated tooth decay. At first, the caries is only found in the enamel area, but over time it works its way further and further and comes close to the tooth pulp. Once there, it attacks the surrounding nerve fibers and blood vessels. Of the Tooth becomes infected, causes severe pain and begins to die. Abruptly stopping the toothache is usually not a positive sign because the inflammation has not disappeared into thin air, but rather that the tooth has died.
However, bacteria not only get close to the root in the form of tooth decay, they also get through existing gingival pocketsin which they accumulate. These are usually caused by an untreated one Inflammation of the gums. The deeper the gum pockets, the more dangerous it becomes for the tooth.
A slightly less common cause is one previous traumatic tooth damage. These include blows to the tooth, unfortunate falls or very strong grinding. Particularly when grinding, the patient does not notice the existing damage until the pain symptoms set in. Crooked ones Wisdom teeth can also promote inflammation of the roots.
The inflammation
When it comes to inflammation, a distinction has to be made between tooth root inflammation, the Pulpitis, and one Tooth root tip inflammation (Apical periodontitis). In tooth root inflammation, it is not the root itself that is affected, but the tissue surrounding the root. This is called Periodontium. The periodontium includes the gums (Gingiva), the Dental cement (Cementum), the Tooth socket (alveolus) and the Root skin (Periodontium / Periodontium). In the case of tooth root tip inflammation, the tooth root tip and the surrounding tissue are affected. Starting with a caries, for example, the bacteria spread further and further into the tooth. At first the enamel is only affected selectively, then several parts of the tooth until they attack the dentin and finally into the Tooth cavity penetration. There they attack the supplying vessels and fight their way further and further towards the tooth root, nerve and tooth root canal. They can also spread to the surrounding bone tissue, creating a Jaw osteitis cause. If the inflammation spreads further, an abscess and / or a fistula arise. Great caution is required here, because if an abscess bursts, the bacteria can spread throughout the body. If the vessels are damaged, it begins Tooth die off, since his supply is no longer guaranteed. As mentioned above, this phase can lead to a sudden decrease in pain. You can recognize a dead tooth by its dark discoloration and the fact that parts of it can easily break off. A dead tooth must also be treated quickly, otherwise it can be lost. The inflammation of the tooth root tip is usually a consequence of the previously inflamed tooth pulp, from which the bacteria have spread further and further towards the tooth root.
treatment
In the case of the symptoms mentioned, a Go to the dentistbecause the sooner you intervene, the more tooth tissue you can save. The dentist will take a close look at the sore tooth and find out about that Duration, intensity and Type of pain to inform. A Cold test can show whether the pulp is still alive or whether it has already died. An x-ray gives more information about the origin of the inflammation or how far it has progressed.
The first step is usually that Root canal treatment. With this, the tooth is drilled open and that neatly removed inflamed tissue. The root canals are cleaned and rinsed with an antibacterial solution. These steps should be followed very carefully so that all bacteria are caught and none are left behind that could cause inflammation again later. If the ducts are infected with bacteria, they are treated with various inserts that inhibit the inflammation and kill the bacteria. After this step, or if the channels are not infected, they are filled with a paste.
This filling can only be checked x-ray whether it is completely leak-proof. After this procedure, only one follows temporary filling, which is replaced by a definitive one if there are no symptoms. In most cases the inflammation is eliminated and the tooth can be preserved. Root canals can also be very branched, so that a complete removal of the bacteria is often very difficult. It can also persist in the area of the root tip. If this happens, you can either renew the root filling, but if this is not helpful, a so-called Apex section carry out. During this procedure, the gums as well as the bone around them will be removed Surgically opened root tips. Part of the tip of the root and inflamed tissue is removed to remove the inflammation. This is the last tooth-preserving measure. If this is not successful, the tooth must be extracted.
prophylaxis

The daily cleaning of the oral cavity is the most important prophylactic measure. By sticking longer Plaque (Biofilm) the bacteria emerge, which then attack the tooth and begin to destroy it. So that it doesn't get that far, you should Brush your teeth at least twice a dayto remove this plaque caused by leftover food. Mouthwashes, Tongue scraper and Floss are to be used in addition. Regular checks by a specialist should also be observed. By a healthy eating can complement that Lower the risk of tooth decay.
Summary
The Inflammation of the root of the tooth is a very painful affairwhich in most cases relate to a inadequate oral hygiene can lead back. After the initial slight pain, it increases more and more until it suddenly subsides. If you experience symptoms, see a dentist as soon as possible. If the inflammation is not so advanced, the therapy usually works well and the tooth can be preserved. Extracting the tooth is the last option.















.jpg)