Vomiting during pregnancy
introduction
When the subject of pregnancy comes up, the same problems are often mentioned over and over again. The pregnant woman feels bloated, has problems with skin changes and her breasts are sore. Another complication is very often at the center of pregnancy and affects a large proportion of expectant mothers - that Vomiting or Emesis gravidarum. Depending on the clinical study, 25 to 90% of pregnant women suffer from nausea and vomiting, at least in the first trimester of pregnancy. This is a natural reaction of the body to the changes that pregnancy means for the female body and usually only needs to be treated conservatively.

A serious illness can result from this Hyperemesis gravidarum develop, whereby the transition cannot be precisely delimited and happens smoothly. Due to its occurrence during pregnancy, the disease is one of the gestoses, a group of diseases that only occur during pregnancy and are therefore time-limited. A Hyperemesis gravidarum On average, only 1-2% of pregnant women develop.
Symptoms and complications
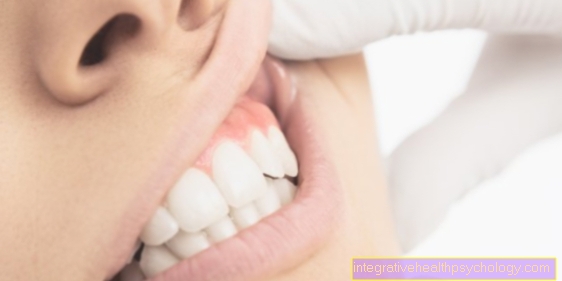
How a Emesis gravidarum shows should be clear. Everyone has already consciously experienced the process of vomiting in his or her life and knows the constricting and extremely uncomfortable feeling. The Vomiting usually already happens In the morningwithout causing any nausea. It will vomited soberly ('Vomitus matutinus"), which puts additional strain on the stomach, esophagus and throat, since only stomach acid can be choked out. This can heartburn trigger and the Damage teeth. That piles up over the day Vomit up in the cut to 10 times on. A minor one Weight loss can be the result of a normal Emesis gravidarum be and contribute at first normal weight (or overweight) no danger represent.
The complications get worse when it comes to the more aggressive form Hyperemesis gravidarum comes. The longer-term and stronger or more frequent vomiting can lead to various deficiency symptoms come. The Weight the patient sinks clearly, which can be particularly dangerous for women with low body mass or underweight. A state of Dehydration sets in: the constant feeling of thirst cannot be satisfactorily quenched, since vomiting occurs again with greater fluid intake Mucous membranes are reddened and the tongue is dry, the Body temperature rises on and the Urinary excretion minimizes.
Also the Electrolyte balance gets out of hand, as these cannot be supplied to the body according to consumption. Since not enough food can be ingested through vomiting, sinks of the Blood sugar level (Hypoglycemia) and there are so-called Ketone bodies formed for the necessary supply of the cells. These can be detected in the blood and urine and can be used to diagnose the severity.
The patient is clearly ill. In addition, the liver in their function limited becomes. This is impressively evident in one thing Jaundicewhich the patient then has. With jaundice, popularly too Jaundice called, that changes Inside of the eye (Sclera) from white to yellowish and also the skin gets a clear one Yellowish tinge. These changes are reversible after treatment.
Disease mechanism

The mechanism by which vomiting occurs is not yet fully understood. However, there are theories that can provide an explanation, at least in part. The hormonal change probably plays a major role in the clinical picture of Emesis gravidarumas many of the complications in pregnancy hormone based problems are.
That seems particularly important Hormone hCG to be that human chorionic gonadotropin. Its task is to Preservation of pregnancyafter the egg has been fertilized. It will be in the placenta formed and ensures various changes in the maternal body, as well as for the Formation of pregnancy-maintaining hormones, how progesterone. About 24 hours after the egg cell is fertilized, the level begins to rise. In the 8th to 12th week of pregnancy the value reaches hCG be maximum. After that is the Placenta mature and even forms those hormones to maintain pregnancy. Of the hCG levels sinks again. During this period, the symptoms relieve relatively quickly, which suggests the connection. Furthermore could progesterone and estrogen, so other female hormones, as well as those thyroid (Hyperthyroidism) play a role.
Another approach to clarifying the fundamentals of disease development deals with the psychosomatic aspectswhich have an important position in medicine as well as in pregnancy. It is assumed that the majority of all cases of Hyperemesis gravidarum has a psychological origin, which is then reflected in the physical. Problems can arise when a woman is confronted with the fact that she is about to become a mother. Due to the restrictions and the increased responsibility, the fetus may appear as a so-called "Blackheads“What is felt which hinders the formation of a maternal-child symbiosis (bond). This can be done in massive pregnancy-related vomiting flow out. The therapeutic procedure for such psychosomatic problems is usually very simple. The mother will stationary admitted because of vomiting. With the presence and care of the attending doctors and nursing staff, the mother is relieved of part of the responsibility and is looked after by the staff. These simple circumstances dampen the pressure on the expectant mother and usually lead to within a very short time The hyperemesis gravidarum subsides.
Causes of Vomiting During Pregnancy
The so-called vomiting of pregnancy occurs especially in the Early pregnancy on (1st-3rd month), preferably in the morning hours. To be distinguished from the usual pregnancy sickness, which can be accompanied by malaise and vomiting, is the clinical picture "Hyperemesis gravidarum"(Which translates as" very severe vomiting during pregnancy ", see section" When do I have to see a doctor? "). The causes of vomiting have not yet been adequately clarified. There are various theories that can be used to draw connections between nausea and the natural processes involved in pregnancy.
The most common guess is related to that hormonal changes in early pregnancy. The focus is on the hormone hCG (= human chorionic gonadotropin), which has a pregnancy-sustaining function. HCG is already formed 24 hours after fertilization and reaches its highest concentration around the 8th and 12th week. After that, the pregnancy-maintaining hormones are released from the placenta (the placenta) and at the same time the nausea is less in most of the pregnant women. Most women feel nauseated after the third month. With multiple pregnancies, the nausea can be more pronounced.
Vomiting in the 1st third
The Emesis gravidarum, the common vomiting from pregnancy, from which the majority of all expectant mothers suffer, is often limited on the first third pregnancy. Because at the end of the first trimester (Third) the concentration of the Pregnancy hormone hCG starts again in the blood to descend, at this point the symptoms also alleviate - at least according to the theory being evaluated, there hCG has been directly linked to vomiting. The transition from normal form to Hyperemesis gravidarum happens fluently and is difficult to differentiate at first.
Vomiting in the 2nd third
If vomiting does not occur until the second trimester, it is almost certainly one Hyperemesis gravidarum. According to researchers, this is probably caused by a too high level of hCG and Thyroxine, a thyroid hormone. The high levels of these hormones in the blood are likely to cause severe nausea and impair the function of the placenta. As a result, a Pre-eclampsia develop - a syndrome in which blood pressure increases (hypertension) and more proteins are excreted in the urine (Proteinuria). As the syndrome becomes a Eclampsia that is associated with seizures and coma should be treated immediately. Severe vomiting during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy can, in the worst case, lead to premature placenta detachment, which endangers the life of the unborn child and the mother.
Also read on this topic: second trimester
Vomiting in the third third
For nausea and Vomit In late pregnancy, the causes can often not be found. Probably the burden on the mother, which has increased to its maximum in the last three months, plays an important role. It also happens again at the end of pregnancy hormonal changeswhich can cause reactions in different body systems.
therapy

Simple Vomiting Although it is a great burden for expectant mothers, the treatment is usually relatively simple. As a rule, the vomiting phase is waited for and nausea is prevented as much as possible. This is through different Nutrition and diet plans possible at which one on gentle diet and small meals that you spread over the whole day. Also, the pregnant woman should drink dispensethat put additional strain on the stomach, such as coffee or Carbonated liquids.
ginger tea however, it is recommended by many women who suffer from vomiting. An alternative medical treatment has also become established over the years - the acupuncture or acupressure. Needles and Massages used to influence various systems in the body. The scientific background could not yet be clarified, but the results speak of an alleviation of the symptoms in 50% of the cases for themselves. Only very seldom, preferably with very strong nausea, come here Anti-vomiting medication used because the side effects and contraindications must always be observed.
With a serious one Hyperemesis gravidarum cannot wait for the disease to subside. The patient can quickly become critical the undersupply slide in which also that unborn child harmed becomes. That is why the gift of fluids and Electrolyte solutions in combination the means of choice. This cannot be done on an outpatient basis, i.e. not at home, which means that inpatient admission to the hospital is necessary. There you can also improve your diet with the help of a Nasogastric tube performed, which reduces the risk of vomiting. In the case of an inpatient stay, one should always Fluid balance can be made: it records what fluid the patient has ingested (through drinking or through a infusion) and submitted (urine) Has.
Anti-vomiting medication during pregnancy

Most drugs can cross the placental barrier (a type of cell barrier that separates the child's and maternal blood) and thus also act on the fetus.
Since this is mostly unnecessary, as the treatment of the mother is the primary focus, any pharmaceuticals should be avoided due to the effect and possible side effects.
Exceptions are various medications which, if not used, pose a risk to the mother's well-being.
Especially in the first trimester, that is, in the first trimester of pregnancy, that is unborn child particularly sensitive and reacts sensitively to a wide variety of foreign substances.
Medication should be avoided, especially during this time, when pregnancy sickness unfortunately occurs.
Only if the suffering and stress on the mother can no longer be justified and a change in diet was unsuccessful, so-called means of relief can be used Antiemetics.
Antihistamines are used as anti-emetics, such as Diphenhydramine or doxylamine.
These are H1 receptor antagonists, so block the binding site on a histamine receptor, which when activated nausea and Vomit can convey.
The antihistamines are very popular with motion sickness or vomiting and are considered harmless for the fetus.
Another drug that is often used for vomiting of any kind, including during pregnancy, is Dimenhydrinate (better known as Vomex®). It is made up Diphenhydramine and another active ingredient together.
In severe cases of Hyperemesis can also be used on stronger drugs such as ondansetron. Ondansetron is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist and thus blocks the receptor for Serotoninwhich, when activated, has a similar effect to the histamine receptor. Metoclopramide, as Dopamine antagonist, relieves nausea and increases the Gastrointestinal motilitywhich can also be beneficial.
In addition to the means mentioned, various Anticholinergics, Inhibiting substances of the cholinergic system. Most of the drugs that are useful for treating vomiting or hyperemesis have side effects. However, these are mostly easy, such as tiredness.
The gift of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) in the form of vitamin preparations, as well as the independent intake through various foods, can reduce the symptoms significantly alleviate.
A consistently increasing dose should be used up to between 10 and 25 mg a day be sought. Since the intake of vitamins through food should be preferred in principle, this can be additionally supported by preparations if insufficient nutrients can be absorbed orally due to nausea.
The Benzodiazepine Diazepam also has a positive effect in experience Hyperemesis gravidarum out. Diazepam is a psychotropic drug which is a anxiety-relieving, muscle-relaxing, but also has a sedative effect. According to experts, the latter component is responsible for the relieving properties related to vomiting.
Because diazepam is permanent makes you dependent and the teratogenic (harmful to the unborn) effect has often been discussed, the drug should only be used when absolutely necessary, under the greatest care and under medical supervision.
Hydrocortisone and other Corticoids can be used in cases of severe vomiting that have previously shown themselves to be resistant to therapy. A harmful effect on the child is also discussed here.
There are also drugs that have an antiemetic effect, but must not be administered during pregnancy, i.e. are contraindicated. NK1 receptor antagonists for example, act on that directly in the brain Vomiting center and thus prevent the development of nausea, but are allowed to not by pregnant women be taken. '
Avoid preparations such as Aprepitant or Fosaprepitant. The teratogenicity of Domperidone, one Dopamine antagonists like metoclopramide, has not been proven. Nevertheless, many doctors recommend that drugs that contain the active ingredient not to be taken.
Harm to the child from vomiting
Uncomplicated vomiting during pregnancy, which disappears without or with light treatment, does not endanger the mother or the child. The fetal prognosis arises almost always promising dar - neither the rate Miscarriages, nor growth or the time of birth are affected.
The Hyperemesis gravidarum poses a greater threat to the child's well-being, but also to the mother's health.
Due to the undersupply of the fetus in important development phases it can Stunted growth come, which can no longer be caught up within the womb. In addition, the Hormone fluctuations to disturbances in the function of the placenta to lead.
Since this connects the fetal with the maternal organism, a restriction has a direct effect on it unborn child.
In addition to the hormonal causes, other underlying diseases can also cause nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
Inflammation of various organs of the Digestive tract, such as a Inflammation of the stomach lining, one Inflammation of the pancreas) or one Appendicitis can also trigger the symptoms.
Since these diseases are usually infested with Pathogens are associated, there is also a direct danger to the fetusthat can become infected and is an easy target for most pathogens.
A detailed one Differential diagnostics should be aimed for when vomiting caused by pregnancy is unlikely or can be ruled out.
When do I have to go to the doctor?
In addition to morning sickness, most women complain of malaise due to certain triggers. During pregnancy it can happen that certain smells and flavors that were previously not perceived as unpleasant suddenly cause nausea. This can also be the partner's body odor or perfume, or smells from a pet. Under certain circumstances, this can be very stressful for those affected, but it is completely natural process. Attempts should be made to avoid or change these triggering factors.
Pregnant women with nausea are often well advised to go out into the fresh air, to surround themselves with pleasant smells, to evade stress factors and to strengthen an overall positive attitude towards their own body changes during pregnancy. Before going to the doctor, you should naturopathic and holistic means can be used. The most successful here is the ginger tea made from freshly brewed ginger; a pregnancy guide provides further tips.
If these aids are exhausted or a pregnant woman is vomiting repeatedly and repeatedly (Hyperemesis gravidarum), she should see her gynecologist to talk to him about drug therapies. The standard therapy here is the drug Dimenhydrinatewhich is also used against travel sickness.
Further information can be found here: Homeopathy against vomiting
When does it get dangerous?
Pregnancy sickness only becomes dangerous when it becomes part of the clinical picture "Hyperemesis gravidarum" transforms. However, the transitions to this are fluid and cannot be clearly identified. Alarming should however daily, repeated and severe vomiting in which the pregnant woman is unable to take in enough fluids (about 2-3 liters of water or tea) or her usual amount of food. This can also occur at night and on an empty stomach. Loss of fluid and Electrolytes (the blood salts), as in non-pregnant people, can lead to serious clinical pictures. The most dangerous are dehydration ("Desiccosis"), A shift between acids and bases in the body ("Acidosis or Alkalosis") Or cardiac arrhythmias ("Arrhythmias“).
In principle one is Dehydration a danger for all organs in the body as well as for the pregnant woman and for those of the growing child. It becomes dangerous for the pregnant woman and her child when symptoms such as dizziness or Fainting spells (Beware of falling!), Severe weakness, persistent constipation, little and dark yellow urine, seizures or confusion, and sudden severe pain in the legs (see thrombosis) or flank pain in the kidney area (lateral lower back).
Whether a person is threatened with dehydration can easily be determined with the test of the standing skin folds determine: the skin on the back of the hand is pulled up with two fingers to form a skin fold. If this skin fold remains and only sinks very slowly down to the back of the hand, the pregnant woman should urgently go to an emergency room to get an infusion and further care. Should a pregnant woman notice the above-mentioned complaints, it is important to inform bystanders in case she faints and to be able to alert an ambulance as soon as possible.
The clinical picture of hyperemesis gravidarum described here only occurs in around 0.5% of all pregnant women.

.jpg)