Factor 5 suffering
Alternative spelling
Factor V Leiden
Introduction / definition
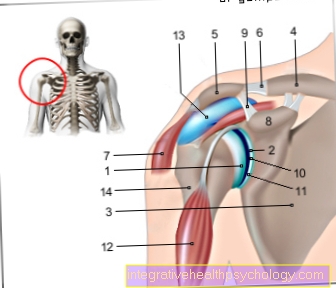
As Factor 5 suffering, also APC resistance called, a disease is called the so-called Coagulation system affects the body. The coagulation system ensures that the blood quickly flows in the event of an injury coagulates, the bleeding stops and the wound can heal.
In addition to the platelets (Platelets) there is another system that ensures that the blood clots. The so-called factor 5 is a specific protein that is largely responsible for blood clotting. In the clinical picture of Factor 5 suffering there is a mutation in a gene that is responsible for the expression of this factor. Due to this mutation, the factor is still present, but can no longer be identified by the so-called "activated protein C" columns. The activated protein C, or APC for short, normally ensures that the blood clots not too fast and runs strongly by splitting the factor 5 and thus making it ineffective.
Read more about the topic here: Blood clotting

Due to the mutation, however, factor 5 is resistant to protein C, which is a increased coagulation entails. Increased blood clotting caused by this mutation is a very common reason why a so-called thrombosis, So a Blood clots, arises. Normally, blood should only clot when a vessel is damaged and needs to be closed. However, the disease can lead to the blood clotting without a damaged vessel wall and thus forming a blood clot. For this reason, an existing factor 5 condition is considered to be a significant risk factor for the development of such a blood clot.
frequency
Factor 5 disease is the most common genetic cause that increases the likelihood of developing a blood clot. Overall are about 2-15% of the European population affected by the disease.
About 10% of the peoplewho are affected by a factor 5 disease homozygous ill. This means that both genes that contain the information for the expression of the protein are affected by the mutation. The remaining 90% are heterozygous become ill and thus only have one affected mutated gene.
Symptoms
The factor 5 disease itself does not cause any symptoms without bleeding. However, the disease affects the body's coagulation system and causes a blood clotting disorder. This bleeding disorder is the reason why the chances of developing a blood clot increase significantly. How much the probability of such an event occurring depends largely on whether the mutation is present on both genes responsible or only on one of the two genes. If only one gene is affected, which doctors call "heterozygous", the tendency to coagulate is increased by 5 to 10 times compared to people who are not infected.
If both genes are affected ("homozygous"), i.e. the gene was mutated from father and mother, the tendency to coagulate increases many times over. If this so-called homozygous gene situation is present, the probability of a blood clot increases by about 50 to 100 times. People who have both genes mutated are more likely to develop thrombosis at some point in their life.
Symptoms can arise when such a blood clot has formed and blocks a vein in the body. Usually it affects the so-called deep leg veins or the veins in the pelvis. If a blood clot clogs these vessels, severe pain is a key symptom for the presence of a blood clot. The affected leg may also swell and the skin may be darkly discolored. If the blood clot stays in the vein for a long time, the lack of blood circulation can cause an open area to form on the affected leg.
As a consequence of a blood clot, different clinical pictures and associated symptoms can arise. When a blood clot separates from the vessel wall on which it was formed, what is known as an embolus occurs. An embolus is nothing more than a thrombus that “migrates” in the vascular system. An anatomical structure that is connected to the deep leg veins or the pelvic veins, in which the supplying vessels become smaller, is the lungs.
Such an embolus therefore often leads to a so-called pulmonary embolism, which is usually associated with shortness of breath as well as pain and pressure on the chest. A stroke or a heart attack can also occur as a result of an embolus and due to the increased tendency to clot with a factor of 5 disease.
Read more on the topic: What are the causes of a cerebral hemorrhage
root cause
The cause of a factor 5 condition is genetic. A mutation in the gene, which is responsible for the formation of the protein "factor 5", ensures a resistance of this factor to the activated protein Cwhich in turn leads to increased coagulation. Factor 5 disease is the best known congenital form of APC resistance. In most cases, such a mutation of the gene is passed on from parents to children, although it can also happen that the mutation occurs spontaneously in the child without it the parents suffer from a factor 5 condition. Depending on whether only a parent transferred the mutated gene to the child or both parents have transferred a mutated gene, the severity of the disease varies.
In some rare cases it can happen that factor 5 is resistant to activated protein C despite normal, non-mutated genes, and so there is increased coagulation. This is for example during pregnancy and when taking the "pill“Possible. Also overweight or excessive cholesterol in the blood can be the trigger for such acquired APC resistance. However, this must be differentiated from the genetic mutation in that once the causes have been removed (for example, after stopping the pill), blood clotting occurs normally.
therapy
Usually after a diagnosis of a factor 5 is diagnosed no therapy necessary. Only with one present thrombosis Care must be taken to prevent the thrombus by giving the correct medication dissolved can be. However, if the person concerned is temporarily at increased risk of developing blood clots, certain anticoagulant drugs be indexed. This can be the case, for example, after a major operation with limited mobility.
For the right therapy, it is important whether the mutated gene is homozygous, i.e. twice, or heterozygous, i.e. only once. It is important for women with a factor 5 condition that, in the event of pregnancy, the attending gynecologist is informed about the disturbed blood clotting so that he can weigh up the necessary therapy. In addition to medication, it can also be increased Move as prophylaxis to protect against the formation of a blood clot. This should especially be taken into account by people at increased risk. In any case, every attending physician and family doctor should be informed of the mutation in the gene concerned.
diagnosis

Since the cause of the presence of a factor 5 condition is one genetic background genetic diagnostic methods come to bear for a reliable diagnosis of the disease.
There are two methods that can be used for the specific diagnosis of the disease. On the one hand, the exact base sequence of the DNA can be determined by DNA sequencing. If there has been an exchange of a base in the affected gene, the factor 5 disease is definitely diagnosed. However, the disadvantage of this method is a significant one Expense, which is why another diagnostic test is usually done:
This test uses certain DNA-cutting enzymes to examine the person's DNA and can use the length of the resulting DNA fragments determine whether there is a mutation in the gene and thus reliably diagnose the disease. Both tests are extremely safe and have almost no false positive results.
People are examined if there are frequent blood clots in close relatives or in the person himself and there is therefore a suspicion of an inherited factor 5 condition. Such genetic diagnostics are recommended, especially if the events cannot be traced back to specific risk factors for the development of a blood clot.
forecast
The individual prognosis with existing factor 5 disease depends on whether the mutated gene is heterozygous, i.e. only once, or homozygous, i.e. twice. Should the mutated gene have been passed on to the child from the mother and father, i.e. the person concerned homozygous If you are ill, the likelihood of a blood clot will decrease 50 to 100 times elevated. In this case, the likelihood of developing a blood clot in the course of life is very high.
The probability for people who only heterozygous are sick, i.e. the gene has only mutated once, is just about 5 to 10 times increased compared to non-sick people. The disease is dangerous if a thrombus is very large and disrupts the blood circulation in the leg, or if the blood clot loosens and an embolus develops, which can then trigger a pulmonary embolism or a stroke.
Recent studies suggest that people who have a factor 5 condition are more likely to have a coronary heart disease to get sick, possibly increased.
Pregnancy with factor 5 ailments
Pregnant women with a factor of 5 ailments should inform their gynecologist and family doctor. During pregnancy, the hormonal and so-called change hemostatic Conditions. That is, due to the influence of hormones, factors that increase blood coagulation are more active and at the same time factors that inhibit blood coagulation are reduced. It is believed that especially the estrogen, which is present in higher concentrations during pregnancy, contributes to this. The tendency for blood to clot, the so-called Thrombophilia, is therefore greatly increased. This mechanism could be evolutionary in order to possibly reduce blood loss during pregnancy, especially shortly before birth, in order to protect the mother and fetus. However, this increases the risk of thrombosis for pregnant women.
Studies have shown that the risk of thrombosis increases 5-6 times during pregnancy. In addition, other risk factors can increase the risk of thrombosis during pregnancy. In pregnant women with factor 5 disease, the risk of thrombosis increases accordingly to 7-16 times. Therefore, heparin treatment is usually recommended. The heparin strengthens the body's so-called Antithrombin and thus reduces the risk of blood clotting. Since the heparin does not cross the placenta membrane, it cannot harm the fetus.
Those affected should be given detailed information about the heparin treatment and individually instructed by their doctor. When this was done, most of the pregnant women affected reported that self-treatment with heparin injections was problem-free.
Also read:
- Pulmonary Embolism in Pregnancy
Does the factor 5 condition affect my desire to have children?
There are many women who have the factor 5 genetic modification and have no problem with theirs Desire for children could meet. Many women do not know and often do not even notice that they are affected by it. However, according to some studies, one also suspects a increased risk of miscarriage in women with factor 5 disease. This genetic change is often only discovered when the woman concerned does not wish to have children due to repeated miscarriages.
But with suitable thrombosis prophylaxis Heparin a factor 5 disease does not generally hinder the desire to have children. Therefore, if you wish to have children, adequate drug treatment is recommended, at best 3 months before the start of pregnancy. Since the genetic modification of factor 5 Leiden is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, it will continue to be inherited. If both parents are affected, the child develops the homozygous form. If only one parent is affected, the child inherits the heterozygous form.
This article might also interest you: Unfulfilled desire to have children
Miscarriage with factor 5 ailments
The increased miscarriage rate in women with factor 5 disease is controversial. Different studies show different results. This has been found in some studies no significant accumulation of miscarriages in women suffering from factor 5. However, in other studies, women with factor 5 showed suffering increased recurring miscarriages.
The pill and factor 5 suffering
The colloquially known “pill” includes the group of so-called Contraceptives. These are not only used to prevent pregnancy, but can also be used for other gynecological diseases such as the so-called Iron deficiency anemia can be used. However, various undesirable side effects can occur. In particular that estrogenThe pill that contains the pill increases the tendency for blood to clot, similar to pregnancy. So that is also Risk of thrombosis elevated. The preparations have different levels of estrogen and their influence on blood clotting varies accordingly.
The minipill only contains so-called Progestins, but is considered to be the least safe oral contraceptive method and can cause some other undesirable side effects as well. As a general rule When taking the pill, the basic risk of getting a thrombosis increases by 3-5 times. In a woman who is a heterozygous carrier of the factor 5 disease, the risk of thrombosis increases by 20-30 times. With the homozygous expression of the factor 5 suffering, the risk even increases by a factor of 200. According to statistics, that's 150 to 300 thromboses per 100,000 women. In other words, this means that 1.5 to 3 women in 1000 women with the pill and factor 5 disease are affected. This risk increases accordingly when other risk factors add up. For example, if the person concerned smokes or is overweight, the risk of thrombosis increases further. Hence, women usually suffer with a factor of 5 hormonal contraception is not recommended.
You can find more articles about the "pill" on our site here: pill
Morning after pill - what is the risk
The Morning-after pill, also known as the "Morning After Pill", is a normal, so-called contraceptive, made from the hormones estrogen and progestin. However, it is dosed twice as high. Accordingly, the risk of side effects, including the risk of thrombosis, can increase enormously.
How should I prevent suffering with factor 5?
All methods that are not hormonal contraceptives can in principle be used. Every contraceptive has its advantages and disadvantages. Before using it, it is advisable to do extensive research. If necessary, a consultation with a gynecologist is useful. For example, it is possible for a woman with factor 5 ailments to have an IUD inserted without hormones. There are coils that release copper ions instead of hormones. Accordingly, they are called copper spirals or copper chains. The classic spiral has developed further, especially in its shape.
Please also read the article: GyneFix® copper chain
There are now different models so that an individual shape and adjustment can reduce discomfort and pain. The use of a condom does not pose an increased risk of thrombosis. Other contraceptives and methods should only be considered if pregnancy would be acceptable if appropriate.
You can find more information on our page on the subject of "contraception" here: prevention
Blood donation with factor 5 ailments - what should be considered?
Since the factor 5 disease is not a contagious disease, but mostly an innate genetic change, is one Blood donation possible in principle. However, since it is a blood clotting disorder, many blood donation services exclude people with the factor 5 from donating blood. When donating blood, the puncture site is a kind of injury that can lead to a blood clot, for example. People with factor 5 conditions are at greater risk of having a blood clot called a thrombus, to develop. Such a blood clot can lead to a blood vessel blockage. This closure is known as thrombosis. The blood donation service naturally wants to keep the risk of thrombosis low. In particular, if the willing blood donor has already suffered a thrombosis, the blood donation service usually does not want to take this risk.
The risk of thrombosis in people with factor 5 disease depends on the form of this genetic change. Is the so-called heterozygous form before, the risk of thrombosis is 5-10 times higher. However, if the so-called homozygous form before, the risk increases by 50-100 times. In any case, the coagulation disorder must be reported to the doctor of the blood donation service. There the decision is made according to the relevant guidelines. If a blood donation service allows blood donation, it is important to contact one directly in the event of any complications and a suspected thrombosis after the blood donation doctor to seek out.