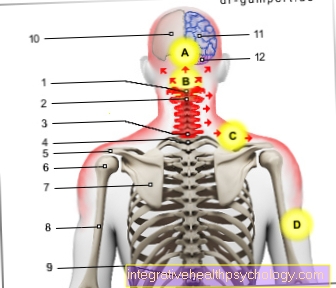
Boils on the neck
definition
A boil on the neck is a form of abscess (encapsulated collection of pus) that causes a purulent inflammation of a hair follicle. Typically, boils appear on the neck in the side or neck area and are extremely painful.
Read more on this topic: Boils - Causes, Treatment, Prevention & More

Causes of a boil on the neck
The hair follicles (root sheaths) lie around the hair roots and anchor the hair in the skin. Penetration of bacteria can cause deep inflammation of the tissue around the follicle and its sebum, creating a boil.
The most common germs that lead to the formation of boils are staphylococci and streptococci. These bacteria naturally colonize the skin and mucous membranes of humans and are mostly harmless, but can also lead to infections. The most well-known causative agent of skin infections is Staphylococcus aureus, a rod-shaped bacterium that is part of the normal skin flora.
Usually it comes to a self-infection, that is, the bacteria come from the own body. If the skin on the neck is irritated, for example by wearing tight collars, ties or chains, a hair follicle becomes infected and a boil on the neck can develop. Men who shave in particular are at risk of developing a boil on their necks if the skin is not adequately disinfected after shaving.
You might also be interested in: Skin itches after shaving, boils after shaving
Other reasons for the development of boils on the neck can be heavy beard growth or poor personal hygiene. Often people with suppressed or impaired immune systems suffer from boils. A lack of defense mechanisms makes it easier for bacteria to penetrate the hair follicles and cause inflammation there. In addition, unrecognized or poorly controlled diabetes mellitus can be the cause of boils.
Read more on this topic: Causes of a boil
diagnosis
The family doctor or dermatologist usually makes the diagnosis by inspecting the affected area and based on the typical appearance. A smear can also be taken if necessary. The smear is obtained from the purulent contents of the punctured boil and examined microscopically. For the detection and clear identification of the bacterial pathogens, the sample is sent to a laboratory and a bacteriological culture is created.
Symptoms of a boil on the neck
With a boil on the neck, a deep inflammation forms around the affected hair follicle within hours to days, which can lead to swelling of the neck. The boil can be seen as a reddened nodule with a yellow pustule in the middle. A boil is characterized by a central accumulation of pus, which is caused by the destruction of tissue (necrosis) as part of the immune reaction. The reddened inflammatory focus lies around the yellowish pus plug in the middle. A boil on the neck can grow up to two centimeters.
The pus that forms puts pressure on the surrounding tissue of the neck, causing those affected to experience pain in the neck. The entire area is red and very sensitive to pressure.
The boil leads to the typical signs of inflammation: in addition to the swelling, there is reddening, heat build-up and pain. In addition, the function of the neck is impaired and you can no longer move your head without pain.
Read more on this topic: The inflammation
The boil can either empty spontaneously to the outside or in rarer cases it can be resorbed. Resorption means that the pus is absorbed and broken down by the body. The healing of the boil usually leaves small scars.
Sore throat from a boil on the neck
The boil on the neck causes pain in the area of inflammation and the surrounding skin is very sensitive to pressure. The formation of pus creates a plug that presses on the surrounding tissue and causes pain. The skin over the boil is tight and the throat can swell a lot.
Treatment of a boil on the neck
In most cases, no treatment is necessary for a boil on the neck, as the abscesses burst and empty on their own after a few days. Small boils can also be treated with a so-called pull cream (or pull ointment). These are over-the-counter preparations that contain anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents and accelerate the healing of the boil.
Read more on this topic: Ointment for a boil
In the case of larger abscesses on the neck, it is better to see a doctor, otherwise there is a risk of blood poisoning. The doctor cuts open the boil and drains the pus. Then an antibiotic ointment (e.g. penicillin against staphylococci and streptococci) is applied to prevent the bacteria from multiplying.
The most important thing to do with a boil on your neck is not to push or squeeze it. Otherwise the germs may be pressed into the tissue and blood, which leads to serious complications.
In the case of frequently recurring boils, the pathogen must be identified and the causes of a disturbed immune defense or a metabolic disease (e.g. diabetes mellitus) must be looked for.
You might also be interested in: Proper treatment of a boil
Duration
Most boils on the neck are harmless and burst on their own after a few days, whereby the pus drains outwards. The wound then heals and a small scar remains. In some cases, it comes back to relapse and recurrent boils. This is also known as furunculosis. Then the pathogens have to be identified and appropriate antibiotic therapy initiated.
Also read the article: The duration of a boil.
When does a boil on the neck become dangerous?
A boil on the neck is harmless in most cases, but if bacteria infect the surrounding lymph vessels or blood vessels it can even be life-threatening.
The accumulation of pus lies in a cavity (abscess cavity), which is separated from the surrounding tissue by a capsule, thus preventing the bacteria from spreading. The entry of germs into the lymph vessels leads to regional inflammation of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis) and the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis). Patients feel exhausted and have a fever.
Read more about these topics:
- How dangerous is lymphangitis?
- Inflammation of the Lymph Nodes - How Dangerous Is It?
It becomes dangerous when bacteria from the boil find connection to a blood vessel. Blood poisoning (sepsis) then occurs and the pathogen can spread throughout the body. Sepsis is one of the most common causes of death in Germany and must be treated quickly, as septic shock can lead to organ failure and death.
You might also be interested in: Symptoms of blood poisoning


-cola.jpg)