Feel the lowering of the uterus
introduction
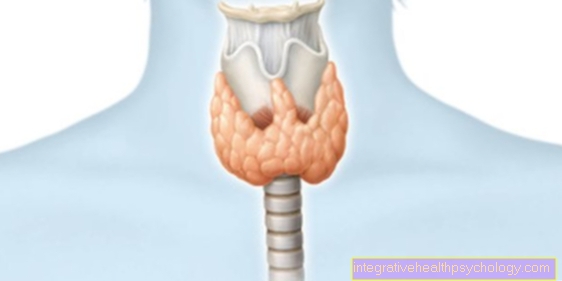
A lowering of the uterus describes a clinical picture in which the uterus sinks into the vagina. The reason for this are weaknesses in the supporting tissue in the pelvis and the pelvic floor muscles. The affected women feel a foreign body sensation in the vagina. Often the urinary bladder or rectum are also affected by subsidence due to direct neighborhood relationships.
The diagnosis of uterine subsidence can be made through a pelvic exam. On the one hand, a speculum is used to observe how the uterus behaves when coughing or pressing. On the other hand, a lowering of the uterus and the surrounding pelvic floor muscles can also be felt directly.
For general information on this topic, we recommend our website: Uterus subsidence

What does the gynecologist do?
If the uterus is suspected, the gynecologist first conducts an examination with a speculum. With the speculum, the vagina and cervix can be seen better. This exam is also part of any normal cancer screening exam. The vagina and cervix are only viewed in a relaxed state and then when the patient presses and coughs. The increase in pressure in the abdomen caused by these maneuvers can have a direct impact on the position of the uterus.
This is followed by a palpation examination of the internal genitalia. This determines how far the lowering has progressed. In addition, the firmness of the pelvic floor muscles can at least be assessed as a guide. The palpation exam also includes a digital rectal exam. During this examination, the gynecologist inserts a finger into the anus. The purpose of the examination is to determine the tension (tone) of the external sphincter muscle. If this muscle can no longer contract sufficiently, fecal incontinence can result.
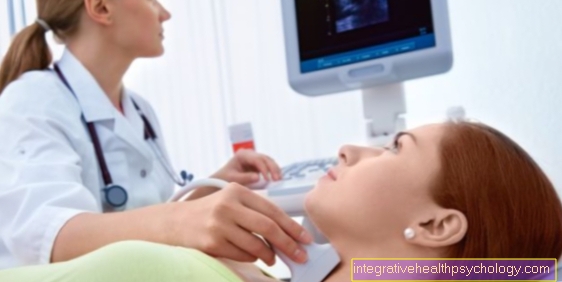
A reliable diagnosis of uterine subsidence is made with ultrasound (sonography). During this examination, the ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina. In this way, the uterus and the surrounding pelvic organs can be examined in detail. If the uterus has subsided, an ultrasound of the urinary bladder with various measurements must also be made during the course to ensure that there is no urine congestion in the urinary bladder and that the bladder can be emptied normally.
Are you interested in this topic? Read more about this under: Gynecological check
Palpation examination for a uterine subsidence
The uterine lowering can be determined by the gynecologist with a palpation examination. The higher the severity, the easier it is to feel the lowering of the uterus. The palpation examination tries to palpate the cervix. The cervix is the lowest part of the uterus. This makes it possible to determine how far the reduction has progressed and what degree of severity is present. During the palpation examination, the patient is asked to press or cough. This increases the pressure in the abdomen and can increase the uterine subsidence and only make it visible in the initial stages.
Even with a grade 1 uterine subsidence, the cervix extends deep into the vagina and can therefore be easily felt by the gynecologist. In the case of advanced subsidence, this can also be felt by the patient. If the uterus already protrudes above the level of the vaginal outlet, parts of the uterus located further up can also be felt in addition to the cervix.
What are the degrees of severity of uterine subsidence?
There are four degrees of severity in the case of a uterine subsidence. Grade 1 includes all subsidence that has progressed to the lower third of the vagina and there is still at least one centimeter between the cervix and the vaginal opening. This means that the cervix, which is the lowest part of the uterus, does not protrude above the vaginal level.
Uterine subsidence in which the cervix has sunk to the level of the vaginal opening are classified as grade 2. A grade 2 uterine lowering means that you can see the cervix just by looking at the vaginal outlet.
Grade 3 represents the highest degree of severity of the uterine subsidence. The cervix must extend at least two centimeters above the vaginal outlet in order to be able to classify this degree of severity.
Strictly speaking, grade 4 no longer belongs to uterine subsidence, since grade 4 is by definition a prolapse of the uterus. Nevertheless, it is given with the staging of the uterine subsidence, since the uterine prolapse represents the most extreme form of subsidence. One differentiates between a so-called subtotal and a total prolapse of the uterus. In a subtotal prolapse of the uterus, only part of the uterus extends over the level of the labia. In the case of a total, i.e. complete, uterine prolapse, the entire uterus has stepped outwards, which inevitably means that the vagina has also stepped outwards and is visible in an inverted form.
A uterine subsidence is always treated conservatively at first. In the case of a pronounced severity and thus a decrease, however, an operation can also be performed. Learn more at. Operation of a lowering of the uterus
I can tell that the uterus has subsided by these accompanying symptoms
Women with a uterine sagging describe a foreign body sensation in the vagina, which can be explained by the pressure of the uterus on the surrounding structures. It would also make it feel like something is falling out of the vagina. In addition to these abnormal sensations, pulling pains are perceived, which are mainly localized in the area of the lower abdomen and back.
Because the uterus is in direct proximity to the urinary bladder and rectum, increased pressure on these organs can also trigger accompanying symptoms. This can lead to problems urinating or stress urinary incontinence. With stress incontinence, as the name suggests, the urine cannot be held adequately during physical exertion. Similar to the urinary bladder, it can lead to difficult bowel movements, but also incontinence, which can be explained by a weakness of the muscles in the anal area. Increased urinary tract infections are also typical when the uterus has subsided. With more advanced uterine subsidence, parts of the sensitive vaginal mucous membrane protrude outwards.The mucous membrane dries out and inflammations or infections can develop.
For more information, we recommend our website to: What are the symptoms of uterine subsidence?