Straight abdominal muscle
Synonyms
Latin: M.. rectus abdominis
- to overview abdominal muscles
- to the musculature overview
introduction

The straight abdominal muscle (rectus abdominis muscle) runs on both sides of the medial line of the abdomen. It is up to 40 cm long, 7 cm wide and can be up to an inch thick. The muscle has 3-4 sinewy transverse ridges that divide the straight abdominal muscle into 4-5 individual sections.
These sections can be shortened in isolation, which must be taken into account when doing targeted abdominal muscle training.
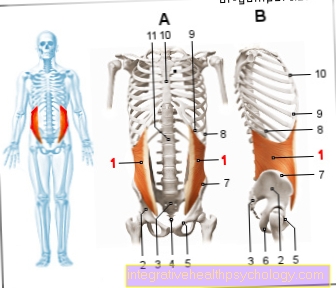
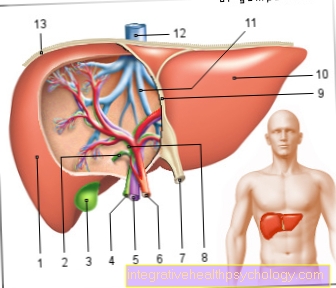
Figure straight abdominal muscle

Straight abdominal muscle
- Straight Abdominal Muscle -
Rectus abdominis muscle - Ischium -
Os ischii - Pubic symphysis -
Pubic symphysis - Pubic bone -
Pubis - White line -
Linea alba - Intermediate string -
Intersectio tendinea - Rectus sheath -
Vagina recti abdominis muscles - Costal cartilage -
Cartilago costalis - Sword extension -
Xiphoid process - 7th rib - Costa VII
- 5th rib - Costa V
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Approach, origin, innervation
Approach: Pubic bone next to the pubic symphysis (Pubic tuberosity)
Origin: 5. - 7. Costal cartilage, sword process of the sternum (processus xiphoideus sterni)
Innervation: Nn. intercostales 5-12
How is the straight abdominal muscle trained / contracted?
The straight abdominal muscles are usually trained by straightening the upper body while lying down. The athlete lies flat on his stomach and slowly straightens up.
Further information on this topic is available at:
- Abdominal crunch
- Reverse crunch
You can find an overview of all relevant topics in the area of strength training in the overview of strength training
How is the straight abdominal muscle stretched?
The abdominal muscles (rectus abdominis muscle) are rarely stretched in sports practice. In order to set an effective stretch stimulus for the straight abdominal muscles, the upper body must be brought into a hollow back position.
The athlete kneels on the floor and extends his arms far in front of the body. To optimize the stretching of the abdominal muscles, we recommend using a Pezzi ball. The athlete ligates on the ball in a supine position and tries to maintain contact with the ball over the entire spine. It is important that your feet stay in contact with the ground.
Further information:
- Stretching
- Overview of stretching exercises
function
The straight abdominal muscle is the main antagonist of the deep, straight and short back muscles. It fixes the trunk when carrying objects.
If the pelvis is not fixed (In the free slope), the straight abdominal muscles are responsible for lifting and holding the pelvis. When the pelvis is fixed, the rectus abdominis is used for bending the trunk (Straighten up of the upper body from lying down) responsible.













.jpg)

.jpg)