Swollen wrists
definition
Swollen wrists can be attributed to fluid that remains in the tissues of the wrist or in the hand in general for various reasons. This can be, for example, blood, which can drain more poorly, or lymph fluid.
In addition, the wrist can be swollen from inflammation, from disease (either local or affecting the entire body) or from injuries and damage to the hand. It is important to distinguish whether only one wrist is swollen or several joints, possibly even (almost) all joints and regions. How quickly the swelling occurs, how long it lasts, and whether it occurs regularly depends on the problem that caused the swelling.

causes
The causes of a swollen hand are many. If it is not just the wrist that is swollen, edema (fluid retention) can be the result of poor drainage. This happens when the kidneys or heart, as the driving force of the circulatory system, no longer function properly.
Also a protein deficiency (Hypoalbuminemia) as well as a problem with the blood vessels such as a thrombosis (a vascular blockage) or a malfunction of the veins can lead to a visible swelling.
An underactive thyroid can also be the cause. This can be both chronic and acute. With these diseases of the entire organism, swellings can mostly (also) be found on the legs. If only one wrist is swollen, these reasons are unlikely. Then a local problem can be the cause of the swelling. One possible cause is trauma to the hand, i.e. wounds, sprains, broken bones or bruises. These can lead to swelling.
Inflammation, for example from an infection of the skin, muscles (Myositis), Tendons (Tendonitis) or bone (Osteomyelitis) can also cause wrist swelling.
It is also possible that you have an allergic reaction to a substance or something that you have previously touched. You should also check your wrist for puncture sites, an allergic reaction to a wasp sting or similar is possible.
A blood clot in a vessel can obstruct drainage and cause swelling. The drainage can also be disturbed by or as a result of burns or scalds.
Tendinitis
This disorder, too Tendovaginitis called, is an inflammatory reaction of the sheath of long tendons. This usually arises from repetitive, monotonous strain on the hand, such as desk work or screwing. The swelling is painful, especially when moving. Sometimes creaking noises can be made when the tendon rubs against nodular thickenings in the tendon sheath (Crepitations).
The best way to deal with tendinitis is to relieve and protect the affected hand. Besides, you can Glucocorticoids Inject (cortisone) into the tendon sheath. However, this should not be repeated. If the tendinitis persists for a long time, the tendon sheath can be surgically split longitudinally.
Read more about this under Therapy of tendovaginitis
After carpal tunnel surgery
Swollen wrists after surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome are not uncommon. Every surgical procedure is associated with injuries to the skin, soft tissue and the surrounding anatomical structures. This is an unavoidable side effect of surgical interventions. In order to keep the swelling, which is usually caused by a bruise, as small as possible, small blood vessels are electrically obliterated during the operation.
In addition, a drain can be inserted in the operating room, which sucks the blood out of the operating area in the first postoperative days. The bruise can also be minimized by immobilization, cooling and a compression bandage after the operation. Depending on the severity of the bruise, the swelling and the associated pain can be completely reduced within a few days to weeks. In rare cases where the swelling is particularly severe, another operation with hemostasis is unavoidable.
Read more about the topic: Carpal tunnel syndrome here
After a fall
A fall can also typically cause swelling of the hands and wrists. Even if there are no obvious injuries to bones, joints, muscles, and tendons, the fall may injure smaller soft tissues and cause wrist bleeding. As a result, these show up as swollen wrists.
Depending on the severity of the soft tissue injuries, the swelling can recede within a short time; a puncture is rarely necessary to drain the bruise. To reduce the risk of swelling after a harmless fall, it is advisable to immobilize the wrist in a pressure bandage and to cool it.
After an insect bite
An insect bite can typically cause local but also generalized swelling of the skin of the whole body. The wrists are a common place for insect bites because they are largely uncovered. The toxins and pathogens transferred during the sting cause local inflammatory reactions that lead to swelling.
If there is an allergy to the insect venom, the swelling can be particularly pronounced. In severe cases, insect bites trigger severe allergic reactions with wheals all over the body, enormous itching, and respiratory and circulatory problems. Cooling, anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory ointments can be used to treat all insect bites.
Concomitant symptoms
In addition to swelling, pain, itching, restricted mobility and stiffness of the wrist or a rash may occur. The hand can also be overheated. All of this allows conclusions to be drawn about the cause of the wrist swelling.
Accompanying itching makes an allergic reaction likely. Here you should watch out for other skin changes, such as a rash or reddening. In addition, skin problems such as Neurodermatitis, a possible cause.
If there is also stiffness of the wrist, a rheumatic disease should be clarified, especially if this occurs regularly in the morning.
An overheated, reddened wrist indicates an inflammatory process, e.g. as part of an infection.
Pain
If the wrist also hurts, traumatic causes or inflammation in this area are likely. The exact location of the pain must be recorded.
The back of the hand can suffer from joint wear (arthrosis), ganglia (overbones, bulges from a tendon sheath), infections or injuries such as broken bones.
Read about this too
- Wrist osteoarthritis
- ganglion
Carpal tunnel syndrome, where a nerve (Median nerve) is restricted by constant pressure. Above all, this leads to nocturnal pain and abnormal sensations in the thumb, index and middle fingers. However, swelling is rare here.
Read more about this under Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
An acute attack of gout in the wrist can also be very painful, but this is not a “classic” location for gout. Psoriasis (psoriasis) can lead to joint inflammation (arthritis) and thus to pain. Tendonitis can also be painful in the wrist area, especially when twisting.
Without pain
Swollen wrists do not have to be accompanied by pain symptoms. A common cause of hand and wrist swelling is water retention. They can be caused by weak veins, muscle strain, at the end of the day, by certain medications or seemingly without a cause for hours.
As a rule, there is no pain, only a feeling of tension in the skin can occur. In the case of significant swelling, unpleasant movement restrictions of the wrist can also occur. Often pain occurs only in the long term with edema. The soft tissue in the area of the swelling can be damaged after a while by the increased tissue pressure, which can lead to tingling, pain and numbness. A venous insufficiency with persistent congestion of the blood can also lead to painful skin ulcers and poorly healing wounds in the long term.
diagnosis
The doctor will first ask exactly what the symptoms are and how long they have existed. He or she will also want to know if there was a triggering event or activity and if it improves or worsens with movement. Additional complaints are also important, as well as previous illnesses and medication taken.
Depending on this, the wrist is examined: this can be done manually or by means of imaging diagnostics, such as x-rays, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRT).
In addition, a blood sample can be taken to get a rough overview of organ functions, especially with regard to uric acid and inflammation values as well as kidney function. If necessary, a puncture of the wrist and thus the removal of synovial fluid may be necessary. A joint reflection is also possible (Arthroscopy).
Treatment / therapy
Acutely, it is important to make the symptoms such as pain and inflammation bearable, for example with the help of pain medication such as ibuprofen or diclofenac. It may be necessary to immobilize the wrist, for example using a splint or a bandage.
Depending on the underlying disease, cooling or warming the affected wrist is advisable.
Glucocorticoids can be given for inflammation and antibiotics for wrist infections.
Physiotherapy to mobilize, stretch and strengthen the wrist can help, especially after the end of the acute phase.
If a disease affects the entire system, the swelling can also decrease with improvement in kidney or heart function, for example with medication. If the local complaints in the wrist do not improve, operations such as artificial joint stiffening, joint repositioning (Corrective Osteotomy) or a cartilage transplant should be useful if joint wear (arthrosis) be the cause of the discomfort.
Duration
The duration of wrist swelling depends on its cause. If, for example, there is insufficient heart function, the swelling can also be permanent and / or already chronic. If the swelling sets in acutely, for example as part of an infection or inflammation, the swelling can last for a few days. If the swelling persists or if no cause can be found, you should consult a doctor to clarify the symptoms.
Involving the fingers
Is there generalized fluid retention (edema), the fingers can also be affected.
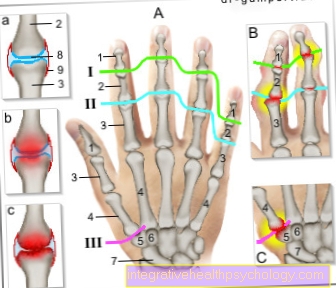
If the swelling affects the metacarpophalangeal and median joints in particular, rheumatoid arthritis is likely.
rheumatism
Rheumatoid arthritis (joint inflammation) is a common autoimmune disease. The little finger joints are particularly affected (metatarsophalangeal joints, wrist, middle finger joints), they are then symmetrically swollen and painful even at rest. The end joints of the fingers, on the other hand, are almost never affected.
A strong handshake can cause pain (Gaenslen sign). Also noticeable is a morning stiffness over 30 minutes and the occurrence of rheumatic nodules, e.g. near the elbow. Internal organs such as the lungs, heart, eyes and blood vessels can also be affected.
If rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, additional blood tests and x-rays will be done. If the suspicion is confirmed there, basic therapy with, among other things, methotrexate (MTX) and, in an acute episode, with glucocorticoids, pain medication, cold applications and exercise therapy is initiated. This is important for the further course of the disease.
Read more about this under
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Methotrexate
With the participation of the feet
Simultaneous swelling of the wrist and feet suggests a non-local cause. Particularly in old age, fluid retention due to poor blood vessels or insufficient cardiac output has to be taken into account. Impaired kidney function and thus less fluid excretion can also cause swelling of the feet and hands.
Here you can also test whether an indented area, for example on the ankle, regresses quickly or the dent is only slowly getting smaller. The latter suggests edema at this point.
A disturbed lymph drainage can also be the cause. Increased leakage of fluid from the vessels into the surrounding tissue is also possible, for example after injury, inflammation or an allergic reaction.
Along with rash
Diseases that cause rashes all over the body, such as the "teething troubles" measles, rubella, rubella or hand-foot-mouth disease (blisters on hands and feet, mouth ulcers) can also cause this rash on the wrist. In addition, wrist swelling is possible.
Other symptoms are also important here: Is there also a fever, nausea, sweating, difficulty breathing, sweating? If the rash is confined to the wrist, an allergic reaction must be considered. A rash can also develop as a reaction to a (new) drug. In general, this would not only be limited to the wrist. An extensive, sharply defined reddening with overheating can also be caused by an infection of the skin with bacteria, a so-called erysipelas or wound rose. If this is the reason, one often feels generally exhausted and has a fever.
During pregnancy
Many women experience swelling of their hands and feet during pregnancy or, in general, water retention throughout the body. This can also affect the wrist. If there are no other symptoms, this swelling should be rated as harmless. If pain occurs in the inside of the hand, especially at night, then one should think of carpal tunnel syndrome, which also occurs more frequently during pregnancy and usually disappears on its own at the end of pregnancy.
With children
They can have injuries such as a fall on the wrist, especially if the wrist is also painful. Neurodermatitis can be present in additional, severely itchy, inflammatory areas of the skin as well as generally dry skin. Infection of any kind can lead to swelling, as can congestion and subsequent inflammation, such as tendonitis. In principle, the same triggers can be behind it as in adults, but systemic diseases such as heart failure are much less likely. Joint wear can also be ruled out.












-mit-ten-(titanic-elastic-nail)-oder-sten.jpg)


.jpg)