Hip impingement
Synonyms
Femoro acetabular impingement (FAI)
Definition of hip impingement
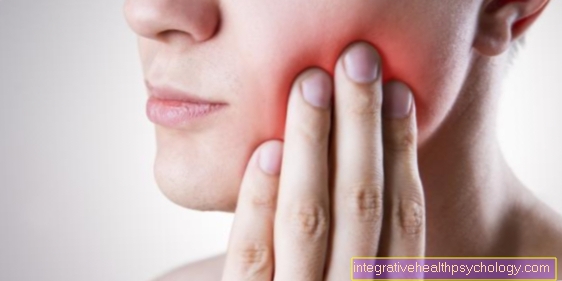
At a Hip impingement it is something that has been changed by anatomical or structural circumstances hip joint, with resulting painful restrictions on movement.

Symptoms
The main symptoms of a hip implantation are first movement-dependent pain. These occur especially with Turn outwards of the leg or when bending the leg. Also Jumping movements can cause severe pain in impingement syndrome. The onset of hip impingement syndrome is sometimes not or only weakly perceived by the patient. At the beginning of an illness, the symptoms only appear when there is strong physical exertion and disappear as soon as a quiet situation occurs. As a result, patients usually do not pursue the first symptoms. Only when the pain gets worse and sometimes occurs at rest do the patients seek medical advice. The pain is called stabbing and pulling described, they can be of strong to very strong intensity.
In advanced stages it can too Resting pain come. Movement restrictions also occur. Movements such as turning the leg outwards or lifting the leg are no longer possible or only possible to a limited extent, usually triggered by pain. This is a classic restriction in daily life Uphill- or Downhill as well as that Sit downwhich usually causes particularly severe pain.
Depending on how severe the damage has already progressed, the structures surrounding the hip joint are also impaired. To be mentioned Irritation and Impairments of the annoy and the Blood vessels. In extreme cases, an impingement syndrome can also cause it Sensory disturbances in the area of the hips and legs (nerves). Furthermore, it can too Undersupply especially of the femoral head, which is supplied by a small vessel that enters the bone at the tip of the head. If the blood supply to the femoral head is impaired over a long period of time, it can lead to a Femoral head necrosis come, in addition to very severe pain, the immediate replacement of the femoral head with a Endoprosthesis makes necessary.
causes
In the healthy, he sits Thigh over the femoral head in the Socketthat belongs to the hip bone. The ball enables normal movements in the leg. muscle and Tapes stabilize the hip joint and hold the head of the femur in the socket. The so-called Joint lip encloses the joint head and seals it. At anatomical to broad femoral neck or to deep socket, the thigh is in direct contact with the joint lip with every movement, beating against it with every movement. This can injure the joint lip and the cartilage surfaces. Sometimes parts of the cartilage and the joint lip can peel off.
If there is a bump in the leg movements for a long time, some kick irreversible damage on the bones. In addition to further tears on the structures near the joint, it can also degenerative changes that better come under the umbrella term arthrosis are known. The mechanical obstacle described, which causes pain with every movement, is called Impingement Syndrome designated.
Appointment with a hip expert?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The hip joint is one of the joints that are exposed to the greatest stress.
The treatment of the hip (e.g. hip arthrosis, hip impingement, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I treat all hip diseases with a focus on conservative methods.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
to form
There are numerous subtypes of hip impingement syndrome. The so-called Camshaft impingement (CAM) is the femoral head compared to the neck too wide. The head is therefore no longer an exact fit in the socket, with the result that the joint head is pushed a little further out of the socket when it is moved. If fast or stretching movements are carried out, the femoral head will eventually tear off or tear off the cartilage and the joint lip.
The further the femoral head rotates out of the socket, the more bone parts rub against the surrounding structures, which is too much severe pain can lead. If excessive pressure of the joint head on the socket leads to injuries to the joint socket, it can happen that the socket expands and that the joint lip or cartilage is torn. The joint lip is thinned and pushed aside. Take their place Bone ringthat is more stable and shapeless than the joint lip.
The disadvantage of this is that the probability that the femoral neck will hit is higher with every movement. In the case of an impingement that originally originated in the joint socket, one speaks of a Pliers impingement (Pincer impingement). If there is massive damage to the surrounding bone and cartilage material, one also develops arthrosis. In many cases, it is not an isolated form of impingement syndrome, but rather Mixed forms.
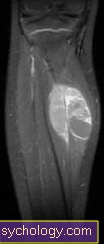
MRI of the hip
While the CT examination gives a good overview of the changes in the bone structure during hip impingement, the relevance of an MRI examination is the representation of the cartilage structure on the hip. With the MRI the abrasion and the degenerative changes on the cartilage of the joint surface and on the cartilage lip at the edge of the socket (Labrum) being represented. This is important for planning further treatment and provides information on how much damage has been caused by the impingement.
More on this topic at: MRI of the hip
Treatment / operation
The treatment of hip impingement is basically conservative and surgically possible. If the symptoms are not yet very advanced, an attempt can be made to achieve therapeutic success by avoiding an operation. With conservative treatment options however, only the Symptoms of hip impingement therapy. The basic problem, the form defect of the femoral head and socket, is not eliminated.
Conservative treatment methods
Conservative treatment methods include drug therapy with NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as aspirin, diclofenac or ibuprofen. These substances work anti-inflammatory and pain reliever and thus improve the symptoms of hip impingement patients. Furthermore you can intra-articular injections (into the joint), which place the active ingredient directly on the affected area. Physiotherapy can strengthen the muscles and thus improve mobility. Since hip impingement is often associated with certain sports, one is Pausing these sports sensible to avoid the pain-causing movements. In any case, sports leave should be discussed in detail with the attending physician. Since all conservative treatment methods cannot eliminate the cause of hip impingement, long-term therapeutic success is not guaranteed.
Operative therapy
If conservative treatment fails, surgical therapy is indicated. The aim of the operation is, on the one hand, to treat acute pain by eliminating the cause of the pain and, on the other, to repair the damage that has already occurred. Hip arthroscopy is a low-risk alternative.
Hip arthroscopy (hip arthroscopy) is a minimally invasive procedure for diagnosing and treating changes in the hip. An endoscope and the necessary surgical tools are inserted into the joint through small incisions (cuts).
Especially with CAM impingement, hip arthroscopy is an alternative to larger open surgery. A camera at the end of the inserted probe makes damage such as a crack on the cup lip visible to the surgeon on a screen. With this minimally invasive procedure, the surgeon can then stabilize the lip again. Furthermore, growths of the cartilage or small deformations of the bone in the pelvis or on the thigh can be removed. Special tools for this technique make it possible to restore the femoral neck to its original waisted shape and thus restore pain-free joint function.
With pincer impingement, hip arthroscopy is a little more complicated to perform, but it is also possible. The aim here is to move the edge of the pan further inwards. In place of the original joint lip, there is now a ring of bone, which is removed by the surgeon.
An older procedure is surgical hip dislocation as part of an open operation. To do this, the hip joint is opened in order to dislocate (luxate) the hip ball from the socket. The hip dislocation offers an optimal view of both parts of the joint so that the damage can be shown and repaired.
Today's surgical procedures offer an effective therapy to relieve acute pain and limitations. While hip arthroscopy, as a minimally invasive procedure, speaks for faster recovery and mobilization of the patient and less pain, open hip dislocation is technically less demanding and time-consuming and in some cases cannot be avoided due to the special anatomical conditions in the hip.
Read a lot more information at: Hip arthroscopy and Pain after hip surgery
physical therapy
Physiotherapy can be used with purely conservative treatment to change the gait pattern and strengthen the muscles. However, since in most cases an operation is carried out, physiotherapeutic therapy usually takes place in the follow-up treatment. In the first 2-4 weeks or up to 6 weeks, if parts of the cartilage had to be fixed (labrum refixation), you may only walk with forearm crutches and only partially put weight on the leg. The use of a bicycle ergometer and the movement of the leg by the physiotherapist are also possible. Up to 10 weeks you can train in a closed chain (e.g. leg press or squat) and also work with cross trainers and aqua aerobics. It is important that there is no overload and that you only train in a pain-free area. From the 10th week up to 70% load can be exerted on the leg. Increased strength, coordination and endurance training should also be part of the therapy plan. From the 4th month onwards, full weight-bearing stress can be resumed in most cases without pain.
Which exercises are useful?
At the beginning of an operation on the hip impingement, it is important that the hip joint is not overloaded. Therefore, it is advisable to exercise carefully on the bicycle ergometer or cross trainer at the beginning. Later you can also train on the treadmill or in the swimming pool. Full loads on the leg should be avoided as a matter of urgency. If no surgery is performed (for the time being), then stretching exercises are a key component.
The gluteus muscles (Gluteus maximus) need to be stretched. To do this, stand up straight and pull one leg up as if you were marching. Both hands grasp the knee and pull it to the stomach. It should pull in the corresponding buttocks.
The second exercise is also done while standing. While standing, one leg and the upper body are brought into a horizontal position and the arms stretched out to the side. You try to hold that for about 30 seconds. In addition to stretching muscles, this exercise is helpful for coordination and strength development.
The third exercise is done in the supine position. While lying on your back, one leg is bent on the floor and the other is held by the knee with both hands and pulled towards the stomach. You push yourself off the ground with the other leg, so that you are practically building a bridge. Do this alternately with both legs and repeat this a few times. On the one hand, the deep muscles are stretched here, and on the other hand, they are also strengthened.
The fourth exercise takes place on your side. Both knees are on top of each other. A mini-band is stretched between them - this is a teraband that is continuous, like a large, strong rubber band. Now the upper leg is slowly and calmly lifted off the lower leg against the pull of the tape and then lowered again. This is repeated 8-12 times and then the leg is changed. Other stretching exercises to stretch the front hip muscles and adductors can also be used. Squats can also be useful, but should be done in a controlled manner, as improper execution can increase the hip impingement.
CAM - impingement
In one joint (Articulatio) always articulates a joint head with a joint socket. in the hip joint (Articulatio coxae) are the components involved in the Femoral head (Head femoris) and the Acetabulum (Acetabulum). If these two anatomical structures do not harmonize exactly, it can become one Impingement (Collision) come.
At the Hip impingement (femoroacatabular impingement) one differentiates CAM impingement (Camshaft impingement) from the so-called Pincer impingement (Pincers impingement). In both cases there is a deviation from the normal structural relationship between the acetabulum and the head. Such anatomical constellation can cause the femoral head to hit the acetabulum with certain movements.
Through the entrapment caused by this injuries to the joint lip occur Acetabulum (Labrum) and des Articular cartilage. If left untreated, this can result in a Hip arthrosis (Coxarthrosis) end up.
At the CAM or camshaft impingement the femoral head is enlarged so that it is direct without adequate sidecut merges into the femoral neck. As a result, the originally usual spherical shape is lost and the head hits powerful movement on the acetabulum. In the long term, the cartilage can start from the edge of the socket worn inwards and also the so-called Joint lip the anterior upper edge of the acetabulum can be damaged (labrum lesion).
Through the high force becomes the cartilage during CAM impingement usually damaged more quickly than with pincer impingement. Most commonly it affects the CAM impingement athletic young menwho do intense sport. CAM impingement is particularly suitable for a arthroscopic treatment. In this way, the surgeon can reattach a loosened cup lip or restore the femoral neck to its original waisted shape and thus a painless joint function restore.

Red shows the typical CAM impingement change on the femoral neck.
Pincer
At the Pincer or nipper impingement the acetabulum is usually significantly deepened, but the shape of the femoral head is normal. It arises in cross section that Image of a pair of pliers, with the acetabulum den Thigh bone how the lever arms hold the tool. As a result, the femoral neck hits the edge of the socket when it moves and thus displaces the Joint lip. The femoral head-femoral neck transition is also heavily used and affected drawn. Pincer impingement occurs frequently in women between 30 and 40 years of age on. Disturbances of the pan region arise while the pool trains, that is, as early as infancy or childhood.
However, most patients do not suffer from one isolated CAM or an isolated Pincer impingement, but in a variety of variable intermediate forms.
The diagnosis of hip implantation is made with the help of an X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In the context of this imaging, it is then also possible for the doctor to differentiate between a CAM impingement and a Pincer impingement.