Hand eczema
introduction

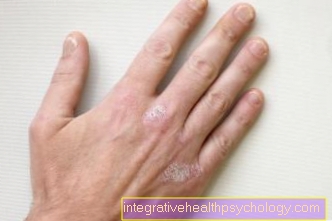
Hand eczema is a non-contagious, inflammatory change in the skin on the hands. Hand eczema is very common, around 10 percent of the western population suffer from hand eczema. It occurs equally in men and women and can occur at any age. There are different forms of hand eczema. Allergic hand eczema is caused by contact with certain substances. Cumulative subtoxic hand eczema is the most common form and is also called wear and tear eczema, and atopic hand eczema occurs mainly in people with neurodermatitis.
The disease can lead to severe psychological distress, as the painful cracks, itching, redness and the thick cornea of hand eczema can lead to restrictions in everyday life. People who put a lot of stress on the skin of their hands through external influences are particularly affected. In people with sensitive skin on their hands, for example, frequent hand washing, cleaning, rinsing or working with chemicals in certain professions can trigger hand eczema. Hand eczema can also be caused by special skin diseases such as neurodermatitis (atopic eczema), skin fungus, psoriasis or allergies.
Causes of the development of hand eczema
Hand eczema occurs due to inflammation of the top two layers of the skin, the dermis and the epidermis. There are various causes for such an inflammatory skin reaction. Since the skin on the hands comes into contact with a wide variety of substances and pollutants, it is not surprising that such eczema forms especially on the hands. Contact with harmful substances such as cleaning agents, acids, solvents or other chemicals attacks the skin, which triggers an inflammatory reaction in the body. Frequent contact with water damages the natural protective barrier of the skin on the hands, which can lead to inflammatory reactions and develop hand eczema. But allergies are also a common cause of hand eczema. Typical triggers for such a contact allergy are substances such as nickel, fragrances or cobalt.
Atopic hand eczema is characterized by particularly sensitive skin that is overly sensitive to environmental influences. It is a congenital predisposition (atopy) that is often associated with neurodermatitis. People with atopic hand dermatitis experience hypersensitivity reactions of the skin to substances that do not trigger a skin reaction in people without this predisposition.
Smoking as a risk factor
Smoke Has long been suspected of worsening or even triggering the symptoms of hand eczema. There is obviously a connection, since smokers suffer from hand eczema disproportionately often. When smoking is done through the skin nicotine absorbed and damages the skin. The skin's natural barrier function is mostly on the hands of smokers degraded, which is why the development of hand eczema is promoted. The previous damage to the skin by nicotine plays a role above all if the hands are washed after the damage caused by smoking or come into contact with allergenic substances. In addition, cigarettes contain a large number of substances that cause allergies (e.g. nickel), which is why smokers are more often sensitized to these substances and, when they come into contact with the skin, with a Inflammatory response and hand eczema. Basically, smoking is not healthy and promotes a wide variety of diseases. In particular, if there are diseases such as hand eczema, smoking should be avoided in the long term in order to enable the disease to cure.
Hand eczema and diet
A balanced and healthy diet is important for healthy skin. On the one hand, a healthy diet promotes general health; on the other hand, certain ingredients that are ingested with food can trigger or worsen allergies or diseases such as hand eczema. The diet should be as high-quality as possible, little processed, varied, regular and balanced. When consuming finished products and fast food, a particularly large number of ingredients and preservatives are absorbed that are not healthy for the body or the skin. The concentrated and "hidden" sugars found in many beverages and finished products should also be avoided. The extent to which the body reacts to certain environmental influences with an inflammatory reaction of the skin also determines, among other things, the general state of health of the person concerned. In many cases, the inflammatory reaction in hand eczema is not only controlled by contact with allergenic or harmful substances from the outside, but also from the inside (so-called endogenous hand eczema). The fewer harmful substances there are in the diet, the less the body reacts with inflammation and the protective function of the skin is strengthened.
Symptoms of hand eczema
Hand eczema can express itself very differently and cause different symptoms. As a rule, hand eczema causes severe itching and particularly dry hands, which is accompanied by reddening or flaking of the skin. The skin on the hands is tight, burning and painful. In addition, fluid-filled blisters can form or the skin tears, thickens or discolors.
Read more about the topic here: Blisters on the hand
In many cases, hand eczema is triggered or worsened when the hands come into contact with certain substances. The hand eczema and the accompanying symptoms appear quickly after contact with the substance. Within a short time, only a few areas are affected and both hands are quickly affected.
In the case of wear and tear eczema, on the other hand, symptoms occur more frequently in the area of the fingertips and on the nails. Wear and tear eczema often begins with a slight inflammation, dry flaking of the skin and broken bits of skin, which can then spread further to the fingers and hands. Atopic hand eczema is often associated with other allergic diseases such as hay fever or neurodermatitis and the associated symptoms.
Guidelines for the therapy of hand eczema
A guideline is a therapy recommendation for a disease that includes the current state of knowledge about the disease and its treatment. Due to the constant revision of guidelines, the best possible therapy for a disease remains up to date. Regardless of the extent of the hand eczema, the guideline currently recommends in principle one Basic therapy perform. This exists made of moisturizing care products, Compliance with protective measures (e.g. wearing gloves) and the Avoidance of allergenic or harmful substances. For mild hand eczema, topical therapy should be used to relieve the inflammation and itching. Also light therapy or Corticoids are recommended in the guideline. In the case of severe hand eczema, UV therapy and high-dose corticoids can also be used. Also the active ingredient Alitretinoin, a substance similar to vitamin A acid, is recommended when corticosteroids have little effect.
Treatment of hand eczema
The treatment of hand eczema varies from person to person and depends on the type and cause of the disease. The treatment usually has two goals, on the one hand to relieve symptoms such as itching and on the other hand to treat the cause of the hand eczema. Severe itching can be relieved with antihistamines or polidocanol, for example. If hand eczema has been around for a long time, the calluses on the hands often thicken. This can be reduced with high-percentage urea creams or ointments that contain salicylic acid so that the actual medication can penetrate the skin better and work better.
Ointment or cream for hand eczema
The skin on the hands should be cared for regularly. A skin care cream should be applied especially after handling harmful substances such as chemicals or cleaning agents. If you have hand eczema, you should also have a Hand cream with a high fat content used to regenerate the protective function of the skin. Protection by nourishing hand creams is still necessary a few months after the hand eczema has healed, which is why skin care creams should continue to be applied regularly. However, care must be taken to ensure that the cream or ointment is well tolerated, as certain ingredients in a cream can also trigger hand eczema if sensitized accordingly.
In addition to caring for the skin, creams or ointments containing cortisone can also be used to treat hand eczema. Ointments containing cortisone should only be used for a certain period of time, as typical side effects of the preparation can occur with long-term use (e.g. skin thinning or reddening).
Home remedies for hand eczema

If you have hand eczema, there are some simple home remedies to relieve the symptoms. For example, if you have sensitive skin on your hands, you should not use soaps with perfume or disinfectants; you should either wash your hands carefully with water or use skin-friendly soaps.
Contact with harmful substances should be avoided, including some foods that are particularly acidic. For example, gloves should be worn when handling citrus fruits, raw tomatoes or potatoes.
In addition, the hands should be protected against strong cold and heat, which is why thin cotton or silk gloves and gloves against the cold should be worn in winter.
Jewelry on the hands (e.g. rings) can also make hand eczema worse. No costume jewelry should be worn, only gold or stainless steel.
A popular home remedy for hand eczema is pansy herb, which can be used as a hand bath. To do this, the pansy herb is boiled in water and the hands are bathed in the cooled brew. Tannins can also support the healing of the skin. These occur, for example, in black tea, in which you can bathe your inflamed hands.
diagnosis
In order to diagnose "hand eczema", a detailed survey must first be carried out Medical history (Anamnesis). Among other things, it depends on which symptoms occur and how often they occur. It is also important which substances come into contact with the hands in everyday life or whether a substance is already suspected that may cause hand eczema. Other illnesses or skin conditions that run in the family are also important for the diagnosis. In a further step, the skin is usually examined using a so-called Patch tests. For this, small amounts of allergenic substances are applied to the back with a plaster. After a few days you can see whether the skin has reacted to certain substances with an inflammatory reaction such as reddening or blistering. However, an allergy is not always the cause of hand eczema, which is why other examinations such as Blood tests and the like can connect.
Prognosis and prophylaxis
Basically, hand eczema has a good prognosis as it usually does curable is. In many cases, however, the healing process is very tedious, as initially the Cause of the disease must be found. Professional and private handling of harmful substances should be avoided as far as possible in order to prevent the hand eczema from worsening again. Since hand eczema is an often job-related skin disease, it is not uncommon for a sick leave to be taken so that a cure and adequate treatment are possible at all.
An allergy test can also be useful in some cases. If you are known to be allergic to certain contact substances contained in items such as costume jewelry, cosmetics or ointments, these substances should be avoided.