Broken wrist
Synonyms
Radius fracture, (distal) radius fracture, base radius fracture, Colles fracture, Smith fracture
English: fracture of the wrist
Definition of a broken wrist
The wrist fracture is the most common fracture to occur in humans.
The reason for this is that, as a rule, many people try to use their hands to catch falls, which affects the joint.
A wrist fracture is colloquially the fracture of the end of the spoke distant from the body and thus near the wrist (one of the forearm bones).

Epidemiology
With about 20 to 25% of all fractures The wrist fracture tops the list of common fracture injuries in humans.
In principle, it can occur at any age, but occurs more frequently in young people between 14 and 18 (here mainly due to risky behavior with a fall result) and older people over 60 before (here especially as a result of a Osteoporosis).
causes
Usually the cause of a radius fracture (broken wrist) is a fall. When you fall, you try to brace yourself and thereby exert a massive force on that wrist from which of these is often not able to cope - so it breaks.
Usually this happens with the wrist extended, the radius fracture in this case is called Colles fracture designated. In the rarer case of a flexed wrist in an accident, one speaks of one Smith fracture. The reasons for the fall can be very diverse.
In younger people, it is often sports injuries, for example in soccer, handball, skateboarding or snowboarding, that lead to unfortunate falls.
In the elderly, however, falls are often caused by unsteadiness and stumbling bone, by osteoporosis are usually already damaged, have an increased risk of significant damage even with minor injuries.

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me at:
- - orthopedics
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, appointments can only be made with private health insurers. I ask for understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at -
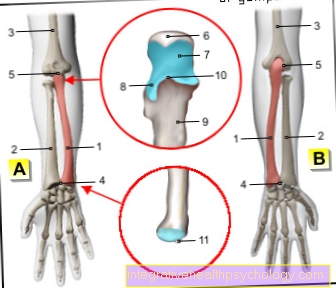
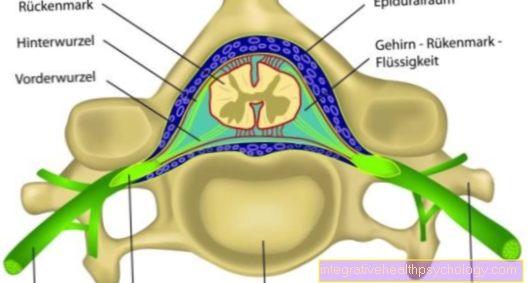
Illustration shapes of the wrist fracture

Broken wrist
- Pea bone -
Os pisiform - Triangular leg -
Os triquetrum - Moonbone -
Lunate bone - Ellenbruch
(Ulnar fracture) - Broken spoke
(Radius fracture) - Scaphoid fracture of the hand
A - Colles' fracture
(Distal radius fracture kink
to the stretching side)
B - Smith fracture
(Distal radius fracture kink
to the flexor side)
C - Closed reduction
(inserting wires)
D - Set up (reduction) -
Bones are in the correct
Brought location
E - implantation of a metal plate
(Osteosynthesis plate made of titanium)
Joints of the hand:
I - Upper (proximal) wrist -
Articulatio radiocarpalis
II - Lower (distal) wrist -
Articulatio mediocarpalis
III - Carpal-metacarpal joints -
Articulationes carpometacarpales
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Symptoms
Typically, a broken wrist is directly associated with pain, which increases with pressure and movement.
A swelling of the joint usually develops very quickly after the accident. A misalignment of the wrist is also often found.
This is due to the fact that the fracture moves towards the back of the hand and the spoke, resulting in the classic picture of the bayonet position.
Since mobility is restricted as a result of the pain and swelling, the patient usually carries the hand in a typical relieving position to relieve the joint.
If the hand is moved, bone parts that rub against each other can lead to so-called "Crepitations“Come, a crackling sound.
If this occurs together with a misalignment, a broken wrist can be considered safe. In some cases, there is also a tingling sensation or a similar sensory disorder in the area of the fingers, which suggests that nerves were also irritated or damaged by the break.
Read more on the topic: Pain in the metacarpal boil and Bump on the wrist
diagnosis

The diagnosis of a broken wrist can usually only be made by the anamnese (i.e. the questioning of the patient) and the clinical picture including a physical exam be asked.
If a patient comes after a fall with a swollen, painful wrist, which also has crepitations and the typical misalignment, the diagnosis of a broken wrist is practically confirmed.
The physical examination can also check mobility, blood flow and the feeling in the wrist.
In order to confirm the suspected diagnosis or to obtain more precise information (for example where exactly the fracture is in the bone or whether parts of the bone have loosened and / or displaced), the doctor can also ask X-ray image request. This is usually made in 2 levels, i.e. once from the front and once from the side to cover everything bone to have a good view of the wrist.
This is especially helpful in order to be able to decide on an appropriate therapy afterwards. One comes more rarely Computed Tomography (CT) to diagnose a broken wrist, for example when the information from the X-ray is not accurate enough.
Wrist fracture therapy

For therapy one Wrist fracture There are several options available, which are preferred depending on the case.
In principle, one decides between conservative (i.e. non-operative) and surgical therapies.
Both forms of therapy aim to completely restore the original shape of the joint, which means that the axes and lengths of the bones should be normal again, so that the wrist is fully functional again.
With a simple one Broken wrist, which is not postponed, the treatment consists simply in the Applying a plaster castthat usually has to be worn for 6 weeks.
By immobilizing the arm, the bone pieces can grow back together correctly. However, it is important to have regular X-ray checks carried out in order to see whether the bones have not subsequently shifted so that they can be recognized at an early stage and then adequately treated.
On the other hand, if the wrist fracture is displaced (dislocated), then a Set up (Repositioning). To do this, the fracture site is first numbed by a Local anesthetic is injected into the fracture gap. Then the bone brought back into the correct position by simultaneously pulling on the upper arm and fingers. This process should always be carried out under X-ray control.
If the dislocation is more serious, but the break is still stable, a closed reduction respectively. This means the insertion of wires that are supposed to stabilize the break during the healing process. This procedure can be carried out on an outpatient basis, but it must be followed by one plaster be worn for 6 weeks.
In the case of an unstable wrist fracture (a fracture is considered to be unstable if it has at least three of the following criteria: debris fracture, involvement of the articular surface, dislocations, involvement of the wrist, patient older than 60), a open surgery preferred. Here, the stabilization takes place with the help of plates, which are normally used on the flexor side, as they lead to fewer complications here. These plates can remain in the body for the rest of life.Although this type of operation is more invasive and cannot be carried out on an outpatient basis, it has the advantage that patients do not have to wear a cast and can practically fully relieve their wrist.
Surgery for a broken wrist
To an operational Treatment of the broken wrist the attending physician always decides
- if it is a unstable (radius)fracture acts
- the ends of the fracture cannot be brought into the correct position by repositioning
- are shifted too much against each other
- joint involvement has occurred or
- there is even an open fracture or a comminuted fracture.
In the same way, surgical therapy can also be preferred to conservative therapy if prolonged immobilization is limited (z. B. in older, multimorbid patients) or high loads should be possible again as quickly as possible (z. B. in competitive athletes).
The aim of the surgical fracture treatment is to bring the individual fragments into an optimal position so that they can grow together again without consequences. It is important that the original length proportions and angles of the wrist bones are restored.
Depending on the type of spoke fracture, there are different approaches at the surgical treatment of the hernia.
What they all have in common is that the intervention is under general anesthetic or local anesthesia (Regional anesthesia / plexus anesthesia; only the affected arm is anesthetized) is performed and the surgeon first repositions the broken bone pieces into the correct position (manual reduction) before he then fixes it in this position. How the broken spoke is ultimately fixed depends on the type of wrist book.
- One possibility is that Wire fixation the spoke fracture, which is used for rather slightly displaced wrist fractures without joint involvement. Small wires (so-called spike wires or Kirschner wires) is drilled and anchored into the spoke via previously made, small skin incisions in such a way that the fracture gap is fixed. The forearm is then immobilized for 3-4 weeks and the wires are removed again after approx. 6 weeks under local anesthesia. This technique is preferred in young patients and less so in adults.
A disadvantage here is that the collapse of the bones in the area of the fracture zone cannot be completely prevented and in isolated cases it does secondary shifts can come. - If, in the course of the wrist fracture, in addition to the spoke fracture, the stylus process of the spoke also breaks off mostly screws for fixation used to screw the bone fragments back together and to stabilize the fracture (so-called screw osteosynthesis). An additional wire may be inserted to give the break even more strength.
Here, too, a plaster of paris is applied afterwards, which can be removed after approx. 1 week so that mobilizing physiotherapy can be started immediately. The screws and wires in this fracture restoration were removed under local anesthesia after about 4 weeks. - If the wrist fracture is particularly unstable, if a joint surface is involved, or if the fracture has moved again after surgical therapy has already taken place, often only the Implantation of a metal plate ensure sufficient fixation (so-called plate osteosynthesis). This plate is usually attached to the flexor side and close to the wrist on the spoke in order to straighten the joint surface, which is usually compressed.
The metal plate lies directly on the crack and is attached to the left and right of it with screws in the spoke. Thanks to the plating, the broken wrist is usually immediately stable during exercise, so that no plaster of paris has to be put on and mobilizing physiotherapy can be started straight away. The plate and screw material can also remain in the body so that no further intervention is necessary. The disadvantage here is that the introduction of the plate requires a significantly larger skin incision than with wire fixation or screw osteosynthesis. Thus, there is also a greater risk of nerve, vascular and soft tissue damage. - If there are more than two fragments of a wrist fracture or if it is even a debris fracture, a external fixator Be the means of choice. During the operation, the doctor inserts two metal pins into the spoke above the wrist and two into the second metacarpal bone, which are braced from the outside using rods.
In this way, all fragments are kept in the correct position externally. The disadvantage here is the greater risk of infection compared to the other methods, since bacteria can easily get into the body from the outside via the metal pins and therefore careful wound care is necessary. The external fixator is usually removed after about 6 weeks and then immediately followed by physiotherapy.
Aftercare
Regardless of whether the wrist fracture had to be treated surgically or was treated conservatively from the beginning - with or without repositioning the fragments - it usually occurs (except for an operative plate fixation) to a Plaster plant to the forearm for 4-6 weeks (The duration of the immobilization can also be shorter after an operative treatment).
Proper aftercare includes:
- for one, regular Plaster change and X-ray controls
- such as early exercise for the thumb and the remaining long fingers that are not included in the cast. #
- The elbow and shoulder joints should also be actively mobilized through targeted movement exercises during the period of rest.
- In addition, attention should always be paid to proper blood circulation and sensitivity, as well as an undisturbed movement function in all five fingers.
Likewise, with all plaster changes, the intactness of the skin or a smooth one must be ensured Wound healing (e.g. at Surgical wounds) to be controlled. Any sutures should be removed after 10-14 days. After the immobilization, outpatient physiotherapeutic treatment is usually indicated in order to restore the affected wrist to full functionality and load capacity as quickly as possible.
forecast
With the right therapy, the wrist fracture shows one very good prognosis. The dreaded permanent misalignment of the wrist as a result of a fracture can actually almost always be prevented if, in high-risk cases, a surgery and if any treatment is accompanied by regular x-ray check-ups.
Otherwise, a radius fracture is associated with few complications. As after any fracture, the risk in the affected joint is one arthrosis to train increased. Also, in rare cases, it can lead to a Pain syndrome such as Sudeck's disease come.
Wrist fracture healing
A complete fracture of a bone - also known as a bone fracture - usually results in a complete severing of the bone structure into two or more fragments. If the bone is only partially broken, it is called a bone fissure. A broken wrist, like any broken bone, can heal in two different ways. A distinction is made between a direct (primary) from an indirect (secondary) Fracture healing.
- Direct fracture healing always takes place when the periosteum is still intact (v. a. in children's flexural or greenwood fractures) or the two ends of the broken bone are in contact, cannot slide against each other and are well supplied with blood (z. B. after surgical care using screws and plates). Starting from the closely spaced bone ends, newly formed bone cells are deposited in the fracture gap and gradually interlock the fragments. After only 3 weeks, the functionality of the broken bone is largely restored and the wrist is gradually resilient.
- Indirect fracture healing always occurs when the two ends of the fracture are no longer in direct contact with one another and are slightly displaced from one another.
During immobilization by means of a splint or a plaster of paris, the bone healing takes place in several phases, which begins with an inflammatory reaction after the fracture phase, in which blood escapes from the beech ends into the fracture gap.
This leads to the activation of inflammatory cells that migrate into the clotted blood in the fracture gap and activate the cells located there for the formation of new bone. In the subsequent granulation phase, the clotted blood is then converted into connective tissue (Granulation tissue, soft callus), into which new blood vessels gradually grow. Bone-degrading cells remove broken and poorly perfused bone parts at the broken ends, bone-building cells replace them with new bone substance.
Until then, however, at least 4-6 weeks have passed, but the broken bone or wrist fracture is now considered resilient again. In the subsequent phase of callus hardening, minerals are incorporated into the newly formed bone over time, so that it regains its original strength.
However, the fracture point is only completely mineralized after 3-4 months. Over time, however, the newly formed bone substance of the hardened callus is further remodeled (Remodeling) until, after 6-24 months, it is completely aligned again in the direction of the main stress in the bone and corresponds to the original bone.
How long does it take to heal?
The time it takes to fully heal from a broken wrist depends on the one hand Severity of the break and the healing process from, but also from Age of patient and type of fracture restoration.
As a rule, surgically treated wrist fractures can be loaded again earlier than conservatively treated. This is due to the fact that the surgical insertion of screws and plates brings the fracture ends back into direct contact with one another and thus direct bone healing occurs and the wrist can be exposed to stress again after 3-4 weeks.
On the other hand, wrist fractures treated conservatively - with a plaster of paris - usually require a healing time of 4-6 weeks before the first mobilization exercises and light loads should take place. Ultimately, one speaks of complete healing of the fracture with unrestricted resilience after a period of 8-12 weeks.
prophylaxis
A broken wrist can only be prevented to a limited extent.
High-risk sports should be avoided if possible.
In some areas you can learn to fall "properly" without injuring yourself additionally when you fall. Since intercepting the case with the hand however, if it is often a reflex action, this happens completely unconsciously and cannot be prevented.
Summary
All in all you can say that the Broken wrist Although it is a very frequent consequence of accidents, which acutely leads to massive functional impairment and pain, it is usually very treatable thanks to modern therapy techniques and does not cause any lasting discomfort.
Wrist fracture in children
Both Wrist fractures in children are usually - unlike adults - so-called Greenwood fractures.
This type of fracture is characterized by the fact that there is only an incomplete bone fracture, as only the internal bone structure breaks, the outer periosteum surrounding the bone (Periosteum) but remains intact. This - also called Flexion fracture - type of fracture occurs mainly in the long tubular bones of children who are still growing, as the bone substance in them has not yet hardened and is therefore still elastic and malleable.
The forces acting in the event of a broken wrist then cause the bony cortex to break on one side of the bone, while on the other hand it only yields through deformation and is deformed.
The periosteum, which always remains intact, prevents the broken bone parts from shifting, thus enabling conservative therapy in most cases. It is usually sufficient if the child's forearm is immobilized with a plaster splint and the break can heal without consequences. However, exist within the framework of the greenwood fracture Bone bending over 20 °However, it may also be possible that the radial bone has to be set up again under anesthesia or even surgically straightened.