Heart murmurs
Introduction / definition
When listening to the heart, you can usually only hear so-called Heart sounds Listen. These reflect the beat of the heart and should rhythmical and clearly be heard. A heart murmur, on the other hand, is a sound that does not belong to the normal heartbeat.
Heart murmurs can without disease value insist, but also on one Heart defect or one Heart valve disease indicate.

The doctor describes a heart murmur according to when it occurs during normal heart action. When the heart muscle contracts and the blood is pressed from the heart into the body, that's what it is called Systole. If there is a noise here, it is called systolic heart murmur or Systolic designated.
When the heart muscle relaxes and the heart fills with blood again, this is called diastole. If a heart murmur is heard during this period, the doctor describes it as diastolic heart murmur or Diastolic.
In addition to specifying the time, the doctor can also specify the volume and the Art of the noise. The volume is given on a scale from 1 to 6. The type of noise can describe, for example, whether the noise is increasing or decreasing in nature. Also the Forwarding the murmur of the heart, for example in the carotid artery, can provide clues to the cause.
Causes of Heart Murmur
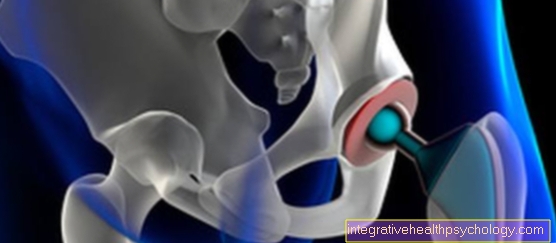
Many heart diseases are associated with various types of heart murmur. The majority of diseases form the Flap failurethat can be both congenital and acquired. The heart valves either no longer close properly so that blood can flow back (Valve insufficiency) or they have become rigid due to tissue changes and no longer open properly (Valve stenosis).
Please also read our pages Aortic regurgitation and Mitral valve stenosis
Also different Heart defect can cause heart murmurs. The further examination should be carried out by a heart specialist (Cardiologists) can be left. If you can hear a continuous, machine-like noise, this may indicate a Reflux from the left side of the heart to the right side (Shunt connection) indicate.
If the heart murmur has a rubbing character when it occurs continuously, there may be one Pericardial disease, for example a Pericarditis (Pericarditis) in front. The pericardium surrounds the heart and separates it from the rest of the organs of the chest.
Heart murmurs the no disease value are considered accidental (random) designated. They join particularly frequently healthy children or adolescents on, are very quiet and change with movement and change of position. Even with particularly high activity of the heart, eddies can arise in the blood, which lead to the development of a heart murmur. Here, too, the person concerned does not have to worry, as it is not a pathological condition.
Is a heart murmur dangerous?
A heart murmur doesn't have to be dangerous. Especially at young peoplewho are perfectly healthy and no symptoms have a heart disease, it is doubtful that an existing heart murmur has a pathological background. Such heart murmurs are called accidental - as a coincidence. They are very quiet and can be influenced by the position of the body or the increased work of the heart.
However, if a heart murmur is heard, the heart must be examined closely. If the heart valve is defective, the heart can otherwise damage to take. The extra work that the heart muscle has to do due to the valve defect can first be compensated for. But the longer the condition persists, the sooner the heart can no longer perform its full function. This is how it comes to Water retention in the Legs or the lung, possibly even to Loss of consciousness due to insufficient blood supply to the brain, too Difficulty breathing and Cardiac arrhythmias.
Various heart defects also trigger heart murmurs. Their consequences can different dimensions accept. Therefore, intensive care by a cardiologist is required so that the cause of the heart murmur can be found, corrected if possible and long-term consequences prevented.
Heart murmurs in toddlers

So-called accidental (random) Heart murmurs that have no disease value. Between 4 and 10 years it is most likely that one harmless cause for the heart murmur.
If a heart murmur can be detected in a child in infancy, it is more likely to have a pathological background than in older children. A Systolic may hint for a toddler Heart defect, Anemia or severe fever be.
A common heart defect in newborns is that open ductus arteriosus botalli. This vessel ensures the fetal circulation during pregnancy, but has to close itself for the regular work of the independent circulation at birth. If this closure does not occur, heart murmurs can arise during the Systole, as well as in the diastole can be heard.
Will the noise in the upper part of the chest or the Carotid artery forwarded, there may be a Clasp or one Narrowing the exit valve of the heart (Aortic stenosis).
The aforementioned accidental noises are usually systolic or mixed systolic-diastolic Sounds. If you hear a purely diastolic heart murmur in a child, it is very likely connected with an illness and should be discovered as soon as possible.
Heart murmurs in adults
In adults, most common heart murmurs are due to Valve failures. Medicine distinguishes between one Stenosis and one insufficiency. Valve stenosis is one Narrowing or an almost complete one Clasp one valve, the insufficiency incomplete ending the flap with the following Blood reflux when the heart muscle contracts. Depending on the heart valve and valve defect, the noise occurs in systole or diastole.
The most common valve defects are one Aortic stenosis and the Mitral valve regurgitation. In the case of aortic stenosis, the valve between the heart (left chamber) and aorta ( artery) no longer completely what a systolic Causes heart murmur. This means that the heart has to exert more force to move the blood out of the heart into the large circulation system. Initially this force can be applied, but over time the heart loses its function and it can close Failure symptoms come. An important Late symptom is in dizziness or unconsciousness due to insufficient blood supply to the brain.
In the Mitral valve regurgitation closes the valve between the pulmonary circulation and the heart (left atrium) no longer complete, which is also a systolic Generates heart murmur. Due to the backflow of blood during contraction (Tension) of the heart muscle, it can back up into the lungs and associated with it Water retention in the lungs come (Pulmonary edema).
The consequences are Breathing problems and increasing shortness of breath.
One can distinguish the two heart murmurs from one another, although they take place at the same time, namely in the systole. Aortic stenosis is most likely to be resolved with a stethoscope to the right of the sternum, listen below the 2nd rib. Mitral regurgitation is heard the loudest to the left of the sternum, between the 4th and 5th rib.
Heart murmur in the ear
Noises in the ear are mostly considered in medicine Tinnitus designated. When tinnitus is usually a persistent noise in the ear, usually whistling or whistling. When a patient of a Heart murmur in the ear reported - a so-called pulsatile tinnitus - the attending physician should be attentive.
A noise in the ear related to the person's heartbeat is very likely to have one diagnosable cause in the field of Vascular supply in the head. It can be a pathological change or one Standard variant act of vessels. The changes affect the vessels that supply the head with blood. Typical arterial changes are connections between arteries and veins, Vascular wall sacs (Aneurysm), Bleeding between the wall layers (Dissection) and Vascular calcifications with subsequent vascular closure. The venous system can through Thrombosis or also through Wall bulges (Ectasia) to be affected.
A diagnosis should also be made tumor be excluded. Particularly vascularized neoplasms near the ear canal or tumors that narrow certain vessels can trigger pulsatile tinnitus. Other possible causes are a high blood pressure in the head, Anemia and a basic Increase in heart work from an overactive thyroid or pregnancy.
The cause of the noise in the ear must be treated depending on the patient's level of suffering and the risk of consequential damage. Due to the constant noises in the ear, many affected people can no longer sleep well, which can have a massive impact on the quality of life. Vascular damage in the head can lead to life threatening bleeding which must be prevented in any case.