Lumbago
Synonyms
Lumbago, low back pain, acute low back pain, sudden back pain, blockage
definition
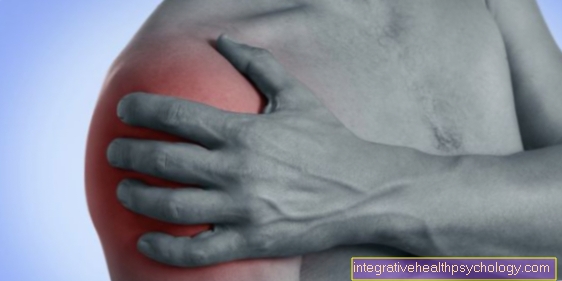
The term Lumbago is not a medical diagnosis in the strict sense. Rather, it describes a disease state. A lumbago is understood as a sudden, violent one that leads to the inability to move Back pain of the Lumbar spine.

Terminology
The term lumbago is a widely used term in the population for sudden back pain. The medical term for lumbago is that Lumbago, the acute low back pain or that acute Lumbar spine syndrome Lumbar spine pain. While the term acute low back pain emphasizes the sudden pain event, the term lumbago can also stand for simple, perhaps longer back pain. However, both terms do not represent a real diagnosis because they do not provide any information about the cause of the disease.
In the case of sudden, painful and movement-restricting events in the neck and cervical spine, one speaks in a similar way of a shot in the neck, an acute cervicalgia (Cervicobrachialgia) or an acute one Torticollis.
A distinction should be made between the acute aggravation chronic back pain, which usually has a less ambitious character.
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Symptoms of lumbago
Lumbago can be caused by various causes. Most patients report a minor movement that triggered the sudden back pain from being completely free of symptoms, e.g. straightening up the upper body from a stooped position, lifting objects in a stooped position or turning the upper body in an awkward position.
Read more on the topic: pain in the back
Either immediately or shortly after the triggering event, there is almost no mobility in the lumbar spine area. Every small movement leads to the greatest back pain and causes the back muscles to contract like a spasm. The pain is usually localized to the lower lumbar region of the spine. If the symptoms have existed for a little longer, there may also be radiating pain in the buttocks, groin or thighs. The pain almost never reaches the foot or is associated with disorders of skin sensitivity.
Read more on the topic Symptoms of lumbago at our partner
Not sure what is causing your back pain? Find out more in our article:
- How do I distinguish a herniated disc from a lumbago?
Diagnosis of lumbago

Patients with lumbago are mostly dependent on outside help to reach the doctor.
The diagnosis of lumbago is quick based on the Medical history (Anamnesis) as well as the clinical appearance. Patient with a Lumbago report on the above-mentioned minor movements, as they are actually carried out every day, and on the sudden painful event that followed. Every movement leads to the greatest back pain. Often forced postures are adopted because only then is a reasonably tolerable body positioning achieved. One example is the common appearance of a patient who appears at the doctor in a bent upper body and reports that it is no longer possible to straighten up.
For the doctor, it is primarily important whether there is a serious illness that requires quick action, otherwise permanent damage could remain.
This can be in the case of an acute one Herniated disc be the case. Through a thorough physical examination with testing of strength, feeling and muscle reflexes as well as the question of bladder and rectal control (Cauda Syndrome), an acutely threatening illness can be ruled out with great certainty. The strength of the back pain is not decisive here.
Since the term lumbago is not a correct diagnosis, the doctor should try to get to the bottom of the cause of this sudden back pain. The physical examination is crucial here. Using manual therapeutic examination techniques, blockages of the small vertebral joints can be detected by examining the mobility of each individual vertebral joint pair in layers (segmental). Temporary vertebral joint blockage is probably the most common cause of lumbago. Otherwise the changes are not very characteristic. There is almost always increased, pain-related muscle tension in the die Lumbar spine accompanying (paravertebral) muscles. In most cases, point pain in the spine is reported. This point can be a little to the side of the spine, in the area of the vertebral joints, or directly in the middle between two vertebral spinous processes, in the area of the intervertebral discs (whirl).
If an intensive examination is not possible in the case of lumbago due to the severe pain, it does not have to be forced if serious illnesses can be safely ruled out. A symptomatic Pain therapy is first priority here.
Especially in younger patients who have had lumbago for the first time, an X-ray is recommended despite the acute pain.roentgen) not necessarily required. Vertebral joint blockages, herniated disc or Pulled muscles cannot be seen on an X-ray. The case is different if there was previously chronic back pain, an accident (e.g. a fall) or older patients are ill. Especially in older patients with a previously unknown reduction in bone mass (Osteoporosis) can even make a minor move to one Vertebral fracture to lead.
To ensure optimal therapy in these cases (Vertebroplasty / Kyphoplasty) not to be missed, it is worth taking an X-ray. The same applies to falls and chronic back pain. In these cases, an X-ray should be taken.
Carrying out a Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine (MRI examination) Should be carried out in the case of radiating pain to the lower leg or foot, or if there is paralysis of the muscles, which is a reasonable suspicion of a herniated disc.
You can find more about this under our topic: MRI of the lumbar spine
root cause
The main cause of lumbago lies in one wrong load of the back or in his overload. A rather back-unfriendly everyday life paves the way for weak, shortened back muscles, which are then not adequately prepared for sudden loads and capitulate. The muscles tense reflexively and cramp quickly: The hardening of the muscles that results block the mobility of the back and can be extremely painful.
Some patients also report from Weather as an influencing factor to the development of a lumbago. Especially in autumn / winter when it gets cold and wet.
Also a Influence of the psyche on back pain is known and should not be underestimated as an important factor, especially in the case of chronic or long-lasting back pain!
Therapy for lumbago
First of all, when treating lumbago, one should always try to remedy the cause of the disease.
In the case of a vertebral joint blockage, the Manual therapy unblocking the Lumbago or, as it is conceptually widespread, a Adjust respectively. The aim here is to achieve the normal (physiological) Restore the joint play of the vertebral joint.
Can the Cause of complaint of lumbago cannot be determined with certainty or if the cause cannot be eliminated without further ado, then the Pain therapy of lumbago in the foreground of the treatment. Suitable treatment measures for lumbago are:
- Bed rest: A temporary bed rest relieves the back.
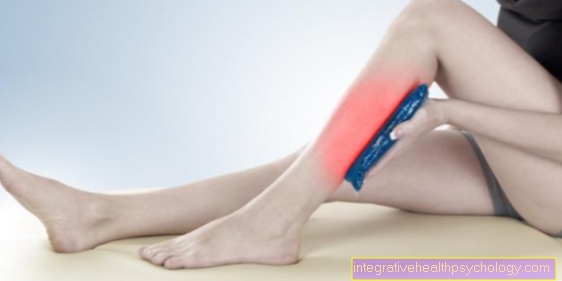
- Heat therapy (Hot water bottle, heat pack, heat pack, etc.): The effect of therapy with heat is mainly muscle-relaxing. The proportion of pain in lumbago that is caused by muscle tension can be treated well.
- Pain medication in tablet form (analgesics, NSAIDs): They have a purely symptomatic effect by dampening the pain and the inflammatory stimulus.
- Pain infusion: Stronger form of drug therapy for lumbago with faster onset of action.
- Muscle Relaxing Drugs: The portion of the pain that is caused by muscle tension can be treated well.
- Infiltrations into the pain area: Pain injections with a local anesthetic into the skin, muscles or vertebral joints are very effective. Pain injections into the muscles of the buttocks are widespread in general practitioners.
- Physical therapy: Physiotherapy exercise treatment techniques such as the strain and Traction (Traction treatment) have a pain-relieving effect. Mobilization techniques (part of manual therapy) are used to treat spinal segments with impaired movement.
- Massages: Massages are used to loosen up tissue and muscles.
Injection therapy
In the vernacular and among patients, the “syringe” describes what doctors describe as injection therapy: a drug, usually a drug long-acting local anesthetic or else cortisone, is injected directly into the painful area. This can be done relatively superficially to give tense muscles quick relaxation. In contrast, if the pain is severe, the injections can also be performed under imaging control (for example under X-rays) directly to the nerve rootsthat emerge from the spine. With the latter, of course, there is a higher risk of complications, which is why this type of procedure should only be performed by experienced doctors.
Nonetheless, many patients have had very good experiences with an injection for long-lasting back pain and use it as a bridge so that movement and stretching of the back are initially possible again.
forecast
The disease process in lumbago is usually not long-lasting under the above-mentioned therapeutic efforts. In this respect, the prognosis for a relatively quick recovery is good. In the rare event that a herniated disc is the cause of the lumbago, recovery may take longer and, under certain circumstances, surgical therapy may be necessary.
In order to prevent further occurrences of this kind (prevention), the rules of Back school to be learned and internalized. Well trained back muscles also protect them Spine. But you can never protect yourself 100% from lumbago.
Duration of a lumbago
In the simplest and most uncomplicated case of lumbago, it disappears after a few days all by itself again. About 50% of those affected show no more symptoms within a week. After about 4 to 6 weeks, almost all patients (90%) are symptom-free again.
More serious casessuch as a complete herniated disc or an entrapment of a nerve, must be treated by a doctor and the healing process is much more protracted. In these cases, under no circumstances can an improvement be expected after a period of a few days.
Attentive should be one with complaints that over a period of time more than 6 weeks consist. There is a risk of the back pain becoming chronic. Regardless of this, the question of how long it lasts is important for the majority of patients on sick leave need to be and how long they have to be on Sports should do without. Both points must be answered very individually but basically similar: The type and severity of the pain influence the duration of the sick note as well as the personality of the patient and the type of his job or the type of sport to be practiced. Under certain circumstances, an office worker can return to his or her place of work earlier than a movers and craftsmen and swimming is faster than starting a mountain bike race.
Every doctor will allow the patient's suffering and his individual professional and personal situation to flow into his assessment and will try to find the optimal solution for the patient. Nonetheless, it is important to mention again that Sport and exercise, even if the time for this cannot be defined across the board, is clearly recommended for all patients.
Prevent lumbago
The best prophylactic measures with which a lumbago can be effectively prevented or at least delayed are back-friendly working techniques in any situation. Professionally and privately you should Bad posture avoided and walking, standing and sitting are often alternated.
Conscious Work breaks and relaxation exercises are as important as one Strengthening the muscles. Targeted muscle building training to stabilize the stomach and back protects and supports the spine permanently.
In addition, it helps too Reduce stress factors and getting rid of inner tension. Whether the body is then less prone to pain in the sense of lumbago or whether you avoid hectic, overloading movements that can trigger lumbago, cannot be conclusively answered here.
Lumbago in the neck
Lumbago does not necessarily have to manifest itself as a classic low back pain, i.e. pain in the lower back. All too other sections of the spine can be affected. Almost every adult suffers from at some point in their life Pain in the neck. Lumbago in the neck is a relevant manifestation of the disease in at least ¼ of the cases.
Especially people who live in Sitting in front of your computer screen work, are at risk of lumbago in the neck due to the rather unfavorable head position. Here, too, it is ultimately above all the fast and persistent one Muscle tension in the neckthat causes pain. Especially with complaints in the neck, this also plays Psyche plays a major role When the disease develops: If the stress is insufficient in everyday life, the muscles in the neck area often "block" first and develop complaints.
Symptoms of lumbago in the neck
Similar to classic lumbago, i.e. lumbago, also causes lumbago in the neck or in the area of the cervical spine (Cervical spine) initially severe pain. Here, too, the pain can shoot in suddenly and surprisingly after a triggering movement. It is not uncommon for pain to radiate from lumbago of the cervical spine as a headache; these are often perceived in the back of the mind. But other types of headache are also not uncommon.
In addition, there may be pain in the shoulder girdle and / or arm, which, however, cannot always be observed.
Not sure what is causing your back pain? Find out more in our article:
- How do I distinguish a herniated disc from a lumbago?