Liver skin signs
introduction
With liver damage or liver cirrhosis, so-called liver skin signs can occur. These are different skin rashes that are directly related to damage to the liver.
These liver skin signs can be triggered, for example, by ingesting substances that are toxic to the liver, such as alcohol, drugs or some medications. Pathogens can also attack and damage the liver as part of a disease. Furthermore, a weak heart can lead to the blood congestion in the liver, thereby affecting the tissue. The liver skin signs are often visible in liver cirrhosis.

These liver skin signs exist
- Jaundice (Jaundice),
- Palm rash (Red coloring of the palm)
- White nails,
- Vascular spiders (Spider naevi),
- Caput medusae (Expansion of the superficial veins around the navel)
- Lacquer tongue
- Lacquer lip
- Bald head
- Dupuytren's contracture (Stiffening of the finger muscles with knot-like thickening of the tendons)
- Parchment skin (Thinning of the skin layers so that the skin appears like parchment paper)
These types of skin changes are, in most cases, an indication of chronic liver disease.
Read more on the subject below: These are the symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver.
causes
The liver is important for very different processes in the body and if its function is restricted, this can be shown by an equally large variability in symptoms. The liver produces vital coagulation factors for the blood, i.e. blood components that enable a balanced blood consistency and prevent bleeding to death. If the liver is damaged by an illness, a toxin such as alcohol or other causes, it is possible that these coagulation factors can no longer be provided. This can lead to small bleeding in the skin or later in other organs.
Liver diseases also affect the appearance of the skin. Liver damage or cirrhosis of the liver means that the blood from the gastrointestinal area can no longer flow properly through the liver, since the liver has been converted into connective tissue, its function is restricted and its size is reduced. As a result, the blood backs up in the portal vein circulation and one speaks of one portal hypertension. This backwater is called "Caput medusae“, These are thickened veins in the area of the abdominal wall around the belly button, visible.
The disturbed metabolism and the liver's lack of detoxification function cause hormones, toxins and the bile pigment to accumulate Bilirubin in the body. The bilirubin turns the skin yellow (Jaundice or jaundice). The nails become whitish (white nails) and the inside of the hands are reddened (palmar rash). The tongue is strikingly red and shiny (lacquer tongue).
Due to the changed blood pressure conditions, the so-called Spider naevi on the upper body and face. These are small, star-shaped extensions of small vessels.
Baldness is the name given to the loss of abdominal hair in men. Balding the abdomen is a typical sign of the liver, as the damage to the liver leads to hormonal disorders. Sex hormones can no longer be excreted in the bile and must be converted into female sex hormones, which increases estrogen levels. The estrogen in turn is responsible for the lack of abdominal hair.
Jaundice
Jaundice, known in medicine as jaundice, is a sign of the skin of the liver that appears as yellowing of the eyes first and then the skin. The liver plays an important role in breaking down hemoglobin, the pigment from the blood, so that these breakdown products accumulate in the body as soon as the liver can no longer perform all of its tasks. This can happen, for example, through direct damage to the liver cells or through congestion in the drainage of the bile acid, which is also produced in the liver and then concentrated in the gallbladder.
Read more on the topic: Jaundice
Palmar erythema
A palmar erythema, i.e. the red color of the palms of the hands, is also a typical sign of the liver skin that can occur as part of damage to the liver. If the pressure in the liver vessels is increased, it can lead to an expansion of the vessels in areas of the body that are further away from the heart. This widening of the blood vessels can then lead to the characteristic reddening of the skin. In some cases this can also affect the hollow side of the foot.
Caput Medusae
The blood in the veins flows from the majority of the abdominal organs via the liver to the heart. If the blood vessels in the liver become more impermeable and the pressure in these vessels increases, the body can form alternative bypass circuits in which the blood then flows out to get back to the heart. For example, superficial abdominal vessels are used, which increase in volume over time and are clearly visible on the abdomen. This symptom picture is called "Caput Medusae".
Liver damage from alcohol
The most common cause of liver damage and the resulting cirrhosis of the liver is chronic alcohol abuse.
There is a close relationship between the amount of alcohol that is consumed and the occurrence of the Cirrhosis of the liver. Alcohol is a cell toxin that is broken down in the liver. Excessive alcohol consumption leads to changes in the liver cells, the tissue becomes fatty and eventually becomes cirrhotic.
Liver skin signs on the face
Typical skin changes also occur on the face in the event of liver damage or liver cirrhosis.
The lacquer tongue
The liver damage leads to a vitamin deficiency and as a result the tongue papillae atrophy. This means that the small bumps on the back of the tongue gradually disappear and the tongue mucous membrane takes on a shiny, lacquer-like appearance and is very reddened. The changes can also lead to abnormal sensations (Paresthesia) come to the surface of the tongue. This symptom is known as varnish tongue and often occurs together with varnish lips, i.e. noticeably shiny and very red lips.
Spider naevi
The liver cells are not only responsible for the vital detoxification of harmful substances in the body. Important proteins are also produced in these liver cells, which, for example, ensure that the blood is not too thin and people do not bleed to death. If these important proteins, the “clotting factors”, are missing in the event of liver damage, bleeding can occur anywhere in the body. This becomes clear, for example, in the "Spider naevi", the spider-leg-like superficial hemorrhages in the smallest of veins that appear permanently on the skin.
These occur especially on the face and neck. The point-shaped vascular nodules are only a few centimeters in size and can be pushed away. Spider neavi are among the liver skin signs and should definitely be clarified. However, there are also a number of harmless explanations for the occurrence of Spider naevi, such as puberty or pregnancy.
Spider naevi in pregnancy
Spider naevi, the small, star-shaped heaped vessels, may also develop in pregnant women. The reason for this is the increased pressure in the abdomen during pregnancy, which in turn causes high pressure in the vascular system and is therefore also responsible for the formation of varicose veins. At the end of pregnancy, the vascular pressure drops again and the spider naevi disappear.
Spider naevi during pregnancy are therefore harmless and do not require further treatment. Usually, skin changes fade on their own after pregnancy. If this does not happen, laser therapy can be considered. The Spider naevi are removed in several sessions with a laser beam.
Concomitant symptoms
General symptoms such as tiredness and weakness can occur as further symptoms in addition to the liver skin signs in the context of damage to the liver tissue. In some cases, patients experience itching.
Especially when the liver is enlarged, a sensation of pressure and fullness can occur in the right upper abdomen. In the advanced stages of liver damage, there can be a dangerous build-up of toxic substances in the blood as the liver's detoxification function is reduced. Some of these toxins, such as ammonia, can do a lot of damage to the brain. This is known medically as "hepatic encephalopathy".
Ascites
Due to the high blood pressure in the portal vein system (portal hypertension) fluid collects in the abdominal cavity between the abdominal organs. This clinical picture is known as ascites (ascites).
In addition, patients feel tired and exhausted, complain of loss of appetite and weight loss. Generally it is said that fatigue (of course only combined with other symptoms) expresses the "suffering of the liver".
Hepatic encephalopathy
In the case of advanced liver damage, the concentration of toxins can have risen to such an extent that they reach the brain and cause hepatic encephalopathy there. Those affected show neurological abnormalities, such as concentration disorders, impaired consciousness, a decrease in performance and impaired cognitive abilities.
itching
If the liver is damaged, metabolic end products and toxins can no longer be excreted in the bile and accumulate in the blood. Bile acids also pass from the damaged liver into the blood and cause itching all over the body. For liver disease can also be a Prurigo simplex subacuta occur. This is a rash that makes the skin red and itchy. The exact cause of the occurrence of prurigo simplex subacuta is not yet fully understood.
Gynecomastia
In addition, in the context of liver damage, changes in the hormone metabolism can occur with a shift in the natural proportions of estrogen and testosterone towards a significant excess of estrogen. In men, this can cause the mammary glands to grow in what is medically known as gynecomastia. Too much estrogen in men can therefore lead to the development of breasts, which is often associated with a great feeling of discomfort in the patient. Women may have no menstrual period and both sexes may experience a decrease in pleasure.
For more information, see: Gynecomastia
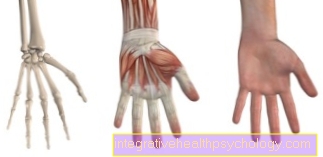
Dupuytren's contracture
The Dupuytren's contracture is a stiffening of the finger muscles with a knot-like thickening of the tendons and can occur, among other things, as part of protracted liver damage. The exact mechanism is not yet understood, but it is known that the trigger for this stiffening of the fingers is the accumulation of toxic substances in the human body.
In the beginning, occupational therapy is the therapy of choice, while surgery is recommended if the disease progresses. Following an operation on the hand, continuous training of the hand muscles must take place in order to achieve the best possible result.
Read more on the subject at: Dupuytren's disease
diagnosis
Liver skin signs can be more or less pronounced and a doctor should always be consulted if these skin changes are present. The doctor recognizes the typical skin changes and skin rashes by means of an inspection (eye diagnosis) of the patient.
He can then evaluate the liver using an ultrasound scan and determine the liver values in the blood. This can be used to determine whether there is liver damage or cirrhosis. Accordingly, the disease can be treated.
Liver values
If there are skin changes that indicate liver damage, the doctor always also checks the so-called liver values in the blood. This is the concentration of certain enzymes (i.e. proteins) in the blood that provide information about liver function. These enzymes do not normally belong in the blood. But if their concentration in the blood increases, it is a sign that liver cells have perished - this is the case with liver damage.
Liver parameters include
- GPT (glutamate pyruvate transaminase also called alanine aminotransaminase (ALT, ALAT)),
- GOT (glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase also called aspartate aminotransferase (AST, ASAT)),
- Gamma-GT (gamma-glutamyl transferase)
- and alkaline phosphatase (AP).
An increase in these values indicates liver damage and requires further clarification.
therapy
Skin changes in the event of liver damage are treated by treating the underlying disease that caused it.
Patients with liver damage must absolutely avoid substances that have a toxic effect on the liver. These include alcohol and certain drugs that are toxic to the liver.
In addition, you should pay attention to a balanced, low-salt diet with sufficient energy intake. In the case of deficiency symptoms, fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E and K) and vitamins B12 must be substituted.
The administration of coagulation factors may also be necessary if there is an increased risk of bleeding.
Portal hypertension can be controlled with medication (e.g.non-selective beta-blockers such as propranolol), which leads to an improvement in the head of the medus and the spider naevi.
The ascites is treated with dehydrating drugs (loop diuretics).
Untreated chronic liver diseases always result in liver cirrhosis, which is irreversible and can no longer be treated. The only option for the patient is then a liver transplant.